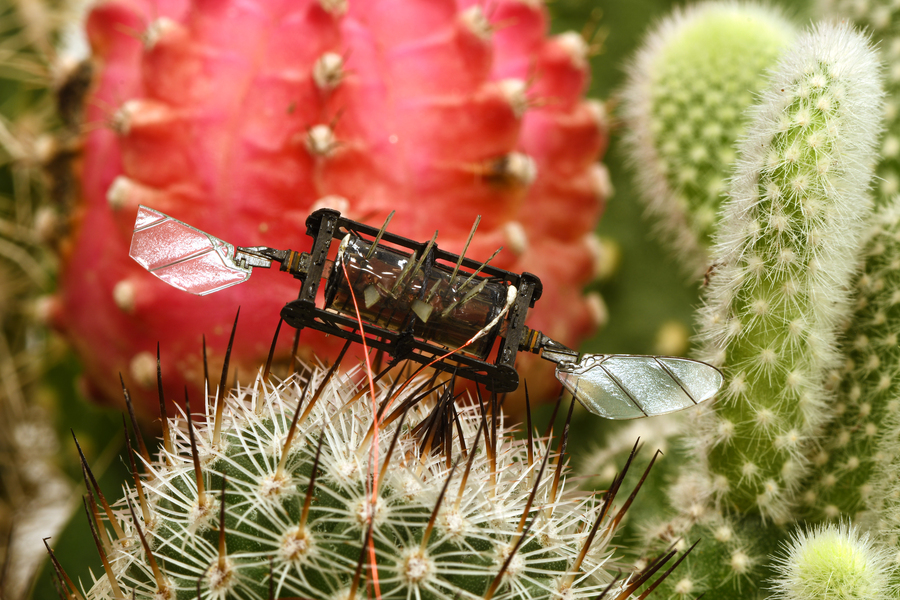
MIT researchers have developed resilient artificial muscles that can enable insect-scale aerial robots to effectively recover flight performance after suffering severe damage. Photo: Courtesy of the researchers
By Adam Zewe | MIT News Office
Bumblebees are clumsy fliers. It is estimated that a foraging bee bumps into a flower about once per second, which damages its wings over time. Yet despite having many tiny rips or holes in their wings, bumblebees can still fly.
Aerial robots, on the other hand, are not so resilient. Poke holes in the robot’s wing motors or chop off part of its propellor, and odds are pretty good it will be grounded.
Inspired by the hardiness of bumblebees, MIT researchers have developed repair techniques that enable a bug-sized aerial robot to sustain severe damage to the actuators, or artificial muscles, that power its wings — but to still fly effectively.
They optimized these artificial muscles so the robot can better isolate defects and overcome minor damage, like tiny holes in the actuator. In addition, they demonstrated a novel laser repair method that can help the robot recover from severe damage, such as a fire that scorches the device.
Using their techniques, a damaged robot could maintain flight-level performance after one of its artificial muscles was jabbed by 10 needles, and the actuator was still able to operate after a large hole was burnt into it. Their repair methods enabled a robot to keep flying even after the researchers cut off 20 percent of its wing tip.
This could make swarms of tiny robots better able to perform tasks in tough environments, like conducting a search mission through a collapsing building or dense forest.
“We spent a lot of time understanding the dynamics of soft, artificial muscles and, through both a new fabrication method and a new understanding, we can show a level of resilience to damage that is comparable to insects,” says Kevin Chen, the D. Reid Weedon, Jr. Assistant Professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS), the head of the Soft and Micro Robotics Laboratory in the Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE), and the senior author of the paper on these latest advances. “We’re very excited about this. But the insects are still superior to us, in the sense that they can lose up to 40 percent of their wing and still fly. We still have some catch-up work to do.”
Chen wrote the paper with co-lead authors Suhan Kim and Yi-Hsuan Hsiao, who are EECS graduate students; Younghoon Lee, a postdoc; Weikun “Spencer” Zhu, a graduate student in the Department of Chemical Engineering; Zhijian Ren, an EECS graduate student; and Farnaz Niroui, the EE Landsman Career Development Assistant Professor of EECS at MIT and a member of the RLE. The article appeared in Science Robotics.
Robot repair techniques

Using the repair techniques developed by MIT researchers, this microrobot can still maintain flight-level performance even after the artificial muscles that power its wings were jabbed by 10 needles and 20 percent of one wing tip was cut off. Credit: Courtesy of the researchers.
The tiny, rectangular robots being developed in Chen’s lab are about the same size and shape as a microcassette tape, though one robot weighs barely more than a paper clip. Wings on each corner are powered by dielectric elastomer actuators (DEAs), which are soft artificial muscles that use mechanical forces to rapidly flap the wings. These artificial muscles are made from layers of elastomer that are sandwiched between two razor-thin electrodes and then rolled into a squishy tube. When voltage is applied to the DEA, the electrodes squeeze the elastomer, which flaps the wing.
But microscopic imperfections can cause sparks that burn the elastomer and cause the device to fail. About 15 years ago, researchers found they could prevent DEA failures from one tiny defect using a physical phenomenon known as self-clearing. In this process, applying high voltage to the DEA disconnects the local electrode around a small defect, isolating that failure from the rest of the electrode so the artificial muscle still works.
Chen and his collaborators employed this self-clearing process in their robot repair techniques.
First, they optimized the concentration of carbon nanotubes that comprise the electrodes in the DEA. Carbon nanotubes are super-strong but extremely tiny rolls of carbon. Having fewer carbon nanotubes in the electrode improves self-clearing, since it reaches higher temperatures and burns away more easily. But this also reduces the actuator’s power density.
“At a certain point, you will not be able to get enough energy out of the system, but we need a lot of energy and power to fly the robot. We had to find the optimal point between these two constraints — optimize the self-clearing property under the constraint that we still want the robot to fly,” Chen says.
However, even an optimized DEA will fail if it suffers from severe damage, like a large hole that lets too much air into the device.
Chen and his team used a laser to overcome major defects. They carefully cut along the outer contours of a large defect with a laser, which causes minor damage around the perimeter. Then, they can use self-clearing to burn off the slightly damaged electrode, isolating the larger defect.
“In a way, we are trying to do surgery on muscles. But if we don’t use enough power, then we can’t do enough damage to isolate the defect. On the other hand, if we use too much power, the laser will cause severe damage to the actuator that won’t be clearable,” Chen says.
The team soon realized that, when “operating” on such tiny devices, it is very difficult to observe the electrode to see if they had successfully isolated a defect. Drawing on previous work, they incorporated electroluminescent particles into the actuator. Now, if they see light shining, they know that part of the actuator is operational, but dark patches mean they successfully isolated those areas.
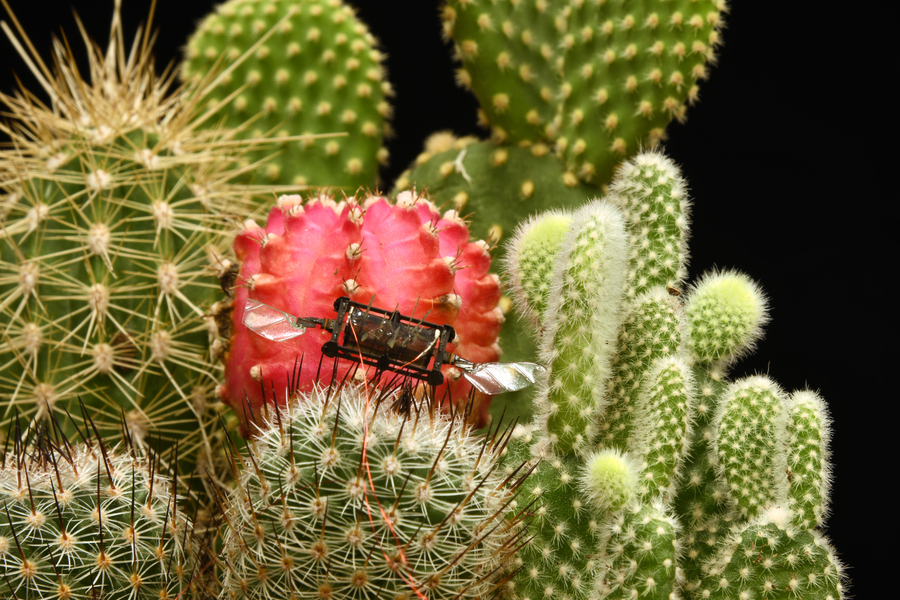

The new research could make swarms of tiny robots better able to perform tasks in tough environments, like conducting a search mission through a collapsing building or dense forest. Photo: Courtesy of the researchers
Flight test success
Once they had perfected their techniques, the researchers conducted tests with damaged actuators — some had been jabbed by many needles while other had holes burned into them. They measured how well the robot performed in flapping wing, take-off, and hovering experiments.
Even with damaged DEAs, the repair techniques enabled the robot to maintain its flight performance, with altitude, position, and attitude errors that deviated only very slightly from those of an undamaged robot. With laser surgery, a DEA that would have been broken beyond repair was able to recover 87 percent of its performance.
“I have to hand it to my two students, who did a lot of hard work when they were flying the robot. Flying the robot by itself is very hard, not to mention now that we are intentionally damaging it,” Chen says.
These repair techniques make the tiny robots much more robust, so Chen and his team are now working on teaching them new functions, like landing on flowers or flying in a swarm. They are also developing new control algorithms so the robots can fly better, teaching the robots to control their yaw angle so they can keep a constant heading, and enabling the robots to carry a tiny circuit, with the longer-term goal of carrying its own power source.
“This work is important because small flying robots — and flying insects! — are constantly colliding with their environment. Small gusts of wind can be huge problems for small insects and robots. Thus, we need methods to increase their resilience if we ever hope to be able to use robots like this in natural environments,” says Nick Gravish, an associate professor in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at the University of California at San Diego, who was not involved with this research. “This paper demonstrates how soft actuation and body mechanics can adapt to damage and I think is an impressive step forward.”
This work is funded, in part, by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and a MathWorks Fellowship.