What role does automation play in the manufacturing supply chain?
AI helps robots manipulate objects with their whole bodies
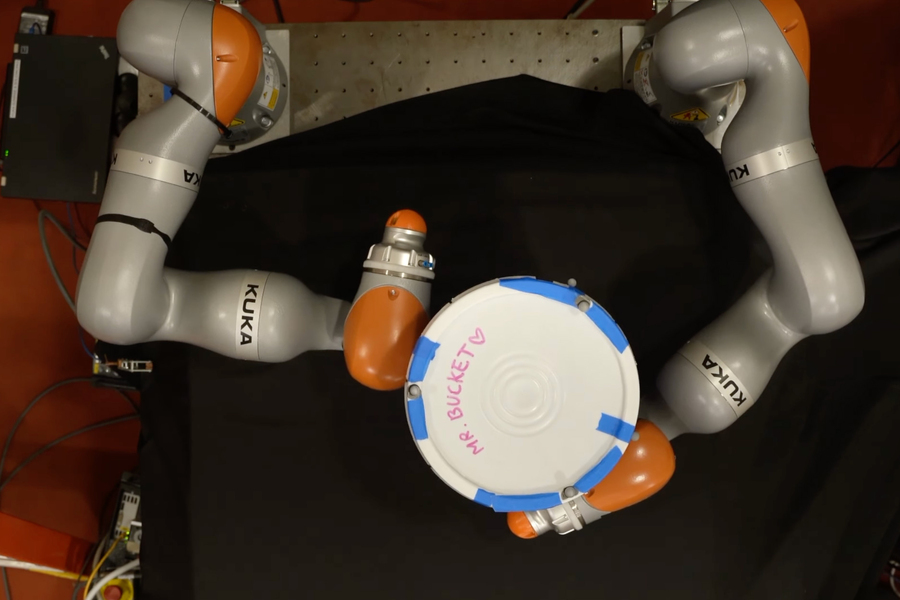

MIT researchers developed an AI technique that enables a robot to develop complex plans for manipulating an object using its entire hand, not just the fingertips. This model can generate effective plans in about a minute using a standard laptop. Here, a robot attempts to rotate a bucket 180 degrees. Image: Courtesy of the researchers
By Adam Zewe | MIT News
Imagine you want to carry a large, heavy box up a flight of stairs. You might spread your fingers out and lift that box with both hands, then hold it on top of your forearms and balance it against your chest, using your whole body to manipulate the box.
Humans are generally good at whole-body manipulation, but robots struggle with such tasks. To the robot, each spot where the box could touch any point on the carrier’s fingers, arms, and torso represents a contact event that it must reason about. With billions of potential contact events, planning for this task quickly becomes intractable.
Now MIT researchers found a way to simplify this process, known as contact-rich manipulation planning. They use an AI technique called smoothing, which summarizes many contact events into a smaller number of decisions, to enable even a simple algorithm to quickly identify an effective manipulation plan for the robot.
While still in its early days, this method could potentially enable factories to use smaller, mobile robots that can manipulate objects with their entire arms or bodies, rather than large robotic arms that can only grasp using fingertips. This may help reduce energy consumption and drive down costs. In addition, this technique could be useful in robots sent on exploration missions to Mars or other solar system bodies, since they could adapt to the environment quickly using only an onboard computer.
“Rather than thinking about this as a black-box system, if we can leverage the structure of these kinds of robotic systems using models, there is an opportunity to accelerate the whole procedure of trying to make these decisions and come up with contact-rich plans,” says H.J. Terry Suh, an electrical engineering and computer science (EECS) graduate student and co-lead author of a paper on this technique.
Joining Suh on the paper are co-lead author Tao Pang PhD ’23, a roboticist at Boston Dynamics AI Institute; Lujie Yang, an EECS graduate student; and senior author Russ Tedrake, the Toyota Professor of EECS, Aeronautics and Astronautics, and Mechanical Engineering, and a member of the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL). The research appears this week in IEEE Transactions on Robotics.
Learning about learning
Reinforcement learning is a machine-learning technique where an agent, like a robot, learns to complete a task through trial and error with a reward for getting closer to a goal. Researchers say this type of learning takes a black-box approach because the system must learn everything about the world through trial and error.
It has been used effectively for contact-rich manipulation planning, where the robot seeks to learn the best way to move an object in a specified manner.
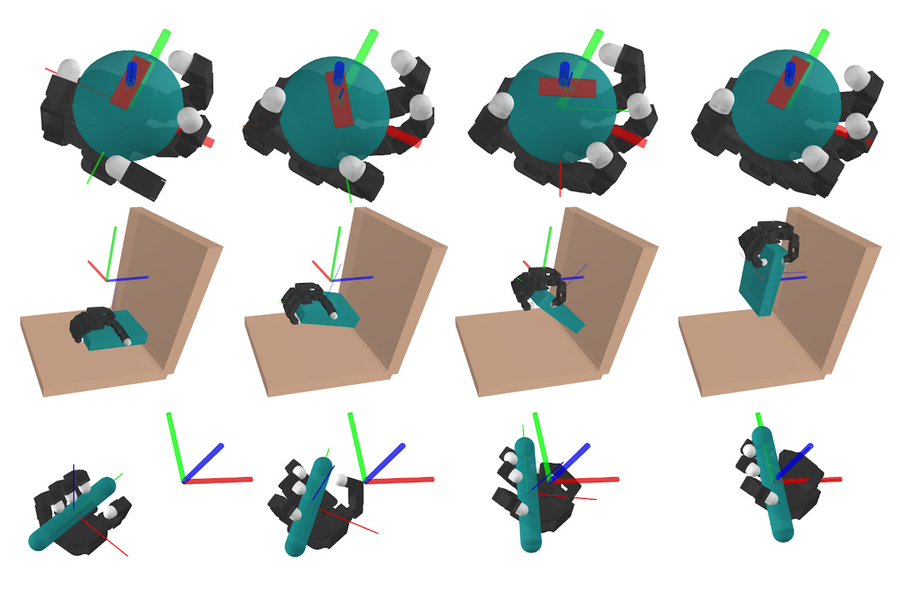
In these figures, a simulated robot performs three contact-rich manipulation tasks: in-hand manipulation of a ball, picking up a plate, and manipulating a pen into a specific orientation. Image: Courtesy of the researchers
But because there may be billions of potential contact points that a robot must reason about when determining how to use its fingers, hands, arms, and body to interact with an object, this trial-and-error approach requires a great deal of computation.
“Reinforcement learning may need to go through millions of years in simulation time to actually be able to learn a policy,” Suh adds.
On the other hand, if researchers specifically design a physics-based model using their knowledge of the system and the task they want the robot to accomplish, that model incorporates structure about this world that makes it more efficient.
Yet physics-based approaches aren’t as effective as reinforcement learning when it comes to contact-rich manipulation planning — Suh and Pang wondered why.
They conducted a detailed analysis and found that a technique known as smoothing enables reinforcement learning to perform so well.
Many of the decisions a robot could make when determining how to manipulate an object aren’t important in the grand scheme of things. For instance, each infinitesimal adjustment of one finger, whether or not it results in contact with the object, doesn’t matter very much. Smoothing averages away many of those unimportant, intermediate decisions, leaving a few important ones.
Reinforcement learning performs smoothing implicitly by trying many contact points and then computing a weighted average of the results. Drawing on this insight, the MIT researchers designed a simple model that performs a similar type of smoothing, enabling it to focus on core robot-object interactions and predict long-term behavior. They showed that this approach could be just as effective as reinforcement learning at generating complex plans.
“If you know a bit more about your problem, you can design more efficient algorithms,” Pang says.
A winning combination
Even though smoothing greatly simplifies the decisions, searching through the remaining decisions can still be a difficult problem. So, the researchers combined their model with an algorithm that can rapidly and efficiently search through all possible decisions the robot could make.
With this combination, the computation time was cut down to about a minute on a standard laptop.
They first tested their approach in simulations where robotic hands were given tasks like moving a pen to a desired configuration, opening a door, or picking up a plate. In each instance, their model-based approach achieved the same performance as reinforcement learning, but in a fraction of the time. They saw similar results when they tested their model in hardware on real robotic arms.
“The same ideas that enable whole-body manipulation also work for planning with dexterous, human-like hands. Previously, most researchers said that reinforcement learning was the only approach that scaled to dexterous hands, but Terry and Tao showed that by taking this key idea of (randomized) smoothing from reinforcement learning, they can make more traditional planning methods work extremely well, too,” Tedrake says.
However, the model they developed relies on a simpler approximation of the real world, so it cannot handle very dynamic motions, such as objects falling. While effective for slower manipulation tasks, their approach cannot create a plan that would enable a robot to toss a can into a trash bin, for instance. In the future, the researchers plan to enhance their technique so it could tackle these highly dynamic motions.
“If you study your models carefully and really understand the problem you are trying to solve, there are definitely some gains you can achieve. There are benefits to doing things that are beyond the black box,” Suh says.
This work is funded, in part, by Amazon, MIT Lincoln Laboratory, the National Science Foundation, and the Ocado Group.