By Nathan Lambert, Aaron Snoswell, Sarah Dean, Thomas Krendl Gilbert, and Tom Zick
Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) is transitioning from a research field focused on game playing to a technology with real-world applications. Notable examples include DeepMind’s work on controlling a nuclear reactor or on improving Youtube video compression, or Tesla attempting to use a method inspired by MuZero for autonomous vehicle behavior planning. But the exciting potential for real world applications of RL should also come with a healthy dose of caution – for example RL policies are well known to be vulnerable to exploitation, and methods for safe and robust policy development are an active area of research.
At the same time as the emergence of powerful RL systems in the real world, the public and researchers are expressing an increased appetite for fair, aligned, and safe machine learning systems. The focus of these research efforts to date has been to account for shortcomings of datasets or supervised learning practices that can harm individuals. However the unique ability of RL systems to leverage temporal feedback in learning complicates the types of risks and safety concerns that can arise.
This post expands on our recent whitepaper and research paper, where we aim to illustrate the different modalities harms can take when augmented with the temporal axis of RL. To combat these novel societal risks, we also propose a new kind of documentation for dynamic Machine Learning systems which aims to assess and monitor these risks both before and after deployment.
What’s Special About RL? A Taxonomy of Feedback
Reinforcement learning systems are often spotlighted for their ability to act in an environment, rather than passively make predictions. Other supervised machine learning systems, such as computer vision, consume data and return a prediction that can be used by some decision making rule. In contrast, the appeal of RL is in its ability to not only (a) directly model the impact of actions, but also to (b) improve policy performance automatically. These key properties of acting upon an environment, and learning within that environment can be understood as by considering the different types of feedback that come into play when an RL agent acts within an environment. We classify these feedback forms in a taxonomy of (1) Control, (2) Behavioral, and (3) Exogenous feedback. The first two notions of feedback, Control and Behavioral, are directly within the formal mathematical definition of an RL agent while Exogenous feedback is induced as the agent interacts with the broader world.
1. Control Feedback
First is control feedback – in the control systems engineering sense – where the action taken depends on the current measurements of the state of the system. RL agents choose actions based on an observed state according to a policy, which generates environmental feedback. For example, a thermostat turns on a furnace according to the current temperature measurement. Control feedback gives an agent the ability to react to unforeseen events (e.g. a sudden snap of cold weather) autonomously.
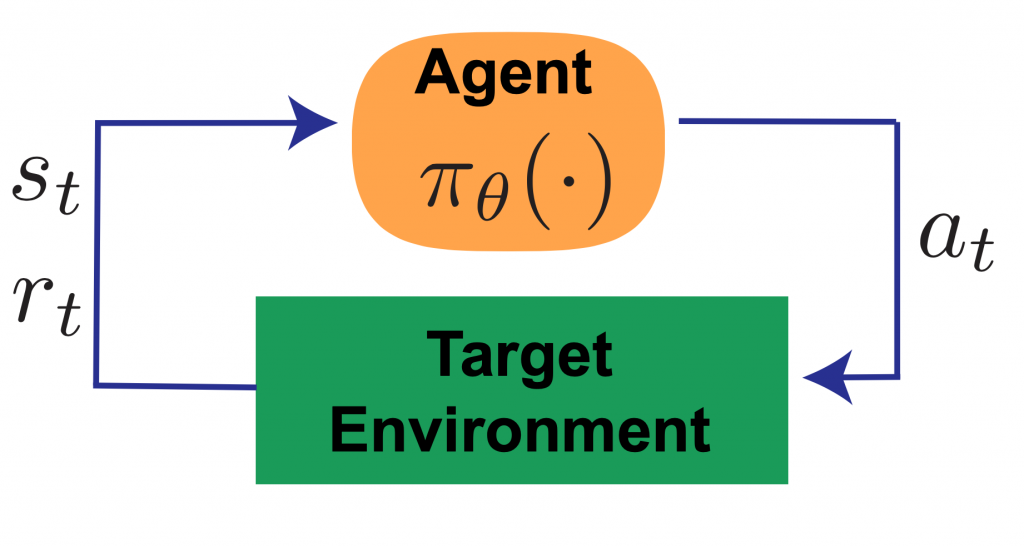
Figure 1: Control Feedback.
2. Behavioral Feedback
Next in our taxonomy of RL feedback is ‘behavioral feedback’: the trial and error learning that enables an agent to improve its policy through interaction with the environment. This could be considered the defining feature of RL, as compared to e.g. ‘classical’ control theory. Policies in RL can be defined by a set of parameters that determine the actions the agent takes in the future. Because these parameters are updated through behavioral feedback, these are actually a reflection of the data collected from executions of past policy versions. RL agents are not fully ‘memoryless’ in this respect–the current policy depends on stored experience, and impacts newly collected data, which in turn impacts future versions of the agent. To continue the thermostat example – a ‘smart home’ thermostat might analyze historical temperature measurements and adapt its control parameters in accordance with seasonal shifts in temperature, for instance to have a more aggressive control scheme during winter months.
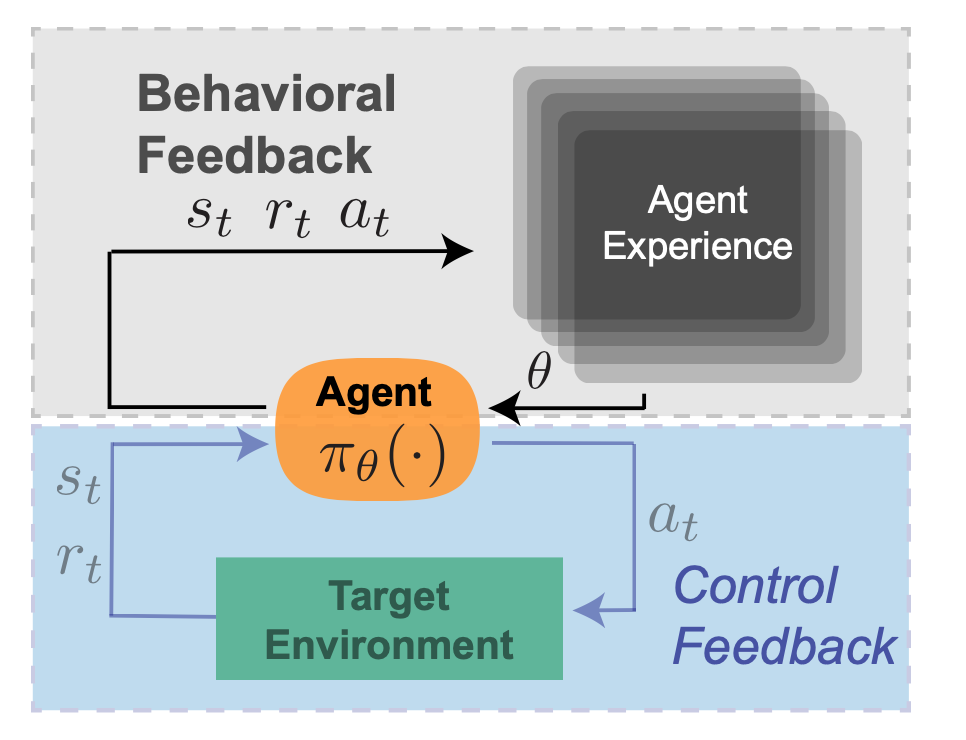
Figure 2: Behavioral Feedback.
3. Exogenous Feedback
Finally, we can consider a third form of feedback external to the specified RL environment, which we call Exogenous (or ‘exo’) feedback. While RL benchmarking tasks may be static environments, every action in the real world impacts the dynamics of both the target deployment environment, as well as adjacent environments. For example, a news recommendation system that is optimized for clickthrough may change the way editors write headlines towards attention-grabbing clickbait. In this RL formulation, the set of articles to be recommended would be considered part of the environment and expected to remain static, but exposure incentives cause a shift over time.
To continue the thermostat example, as a ‘smart thermostat’ continues to adapt its behavior over time, the behavior of other adjacent systems in a household might change in response – for instance other appliances might consume more electricity due to increased heat levels, which could impact electricity costs. Household occupants might also change their clothing and behavior patterns due to different temperature profiles during the day. In turn, these secondary effects could also influence the temperature which the thermostat monitors, leading to a longer timescale feedback loop.
Negative costs of these external effects will not be specified in the agent-centric reward function, leaving these external environments to be manipulated or exploited. Exo-feedback is by definition difficult for a designer to predict. Instead, we propose that it should be addressed by documenting the evolution of the agent, the targeted environment, and adjacent environments.
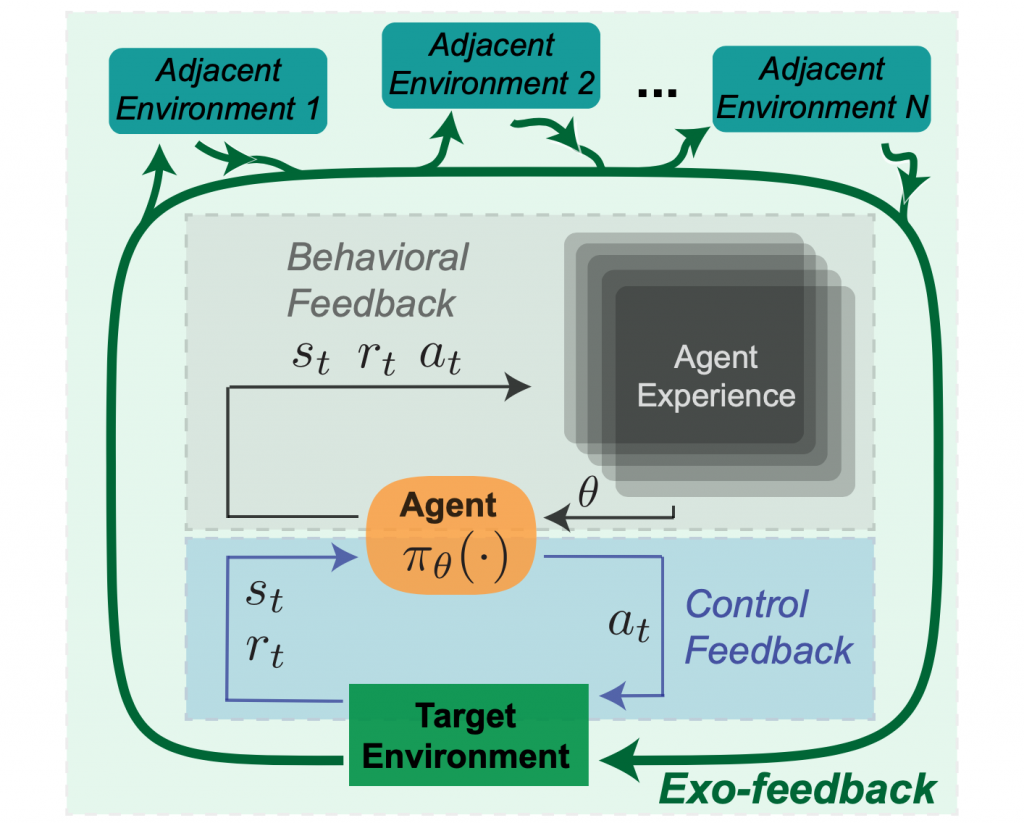
Figure 3: Exogenous (exo) Feedback.
How can RL systems fail?
Let’s consider how two key properties can lead to failure modes specific to RL systems: direct action selection (via control feedback) and autonomous data collection (via behavioral feedback).
First is decision-time safety. One current practice in RL research to create safe decisions is to augment the agent’s reward function with a penalty term for certain harmful or undesirable states and actions. For example, in a robotics domain we might penalize certain actions (such as extremely large torques) or state-action tuples (such as carrying a glass of water over sensitive equipment). However it is difficult to anticipate where on a pathway an agent may encounter a crucial action, such that failure would result in an unsafe event. This aspect of how reward functions interact with optimizers is especially problematic for deep learning systems, where numerical guarantees are challenging.
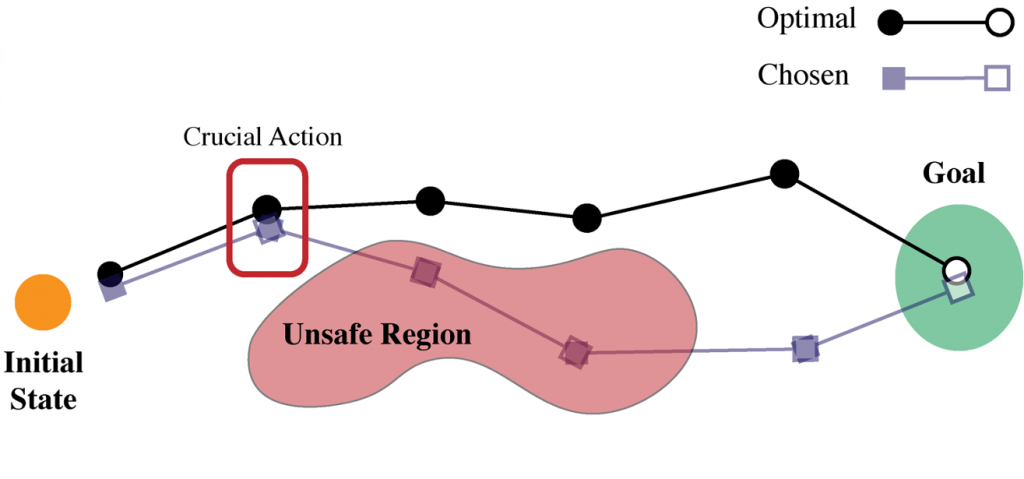
Figure 4: Decision time failure illustration.
As an RL agent collects new data and the policy adapts, there is a complex interplay between current parameters, stored data, and the environment that governs evolution of the system. Changing any one of these three sources of information will change the future behavior of the agent, and moreover these three components are deeply intertwined. This uncertainty makes it difficult to back out the cause of failures or successes.
In domains where many behaviors can possibly be expressed, the RL specification leaves a lot of factors constraining behavior unsaid. For a robot learning locomotion over an uneven environment, it would be useful to know what signals in the system indicate it will learn to find an easier route rather than a more complex gait. In complex situations with less well-defined reward functions, these intended or unintended behaviors will encompass a much broader range of capabilities, which may or may not have been accounted for by the designer.
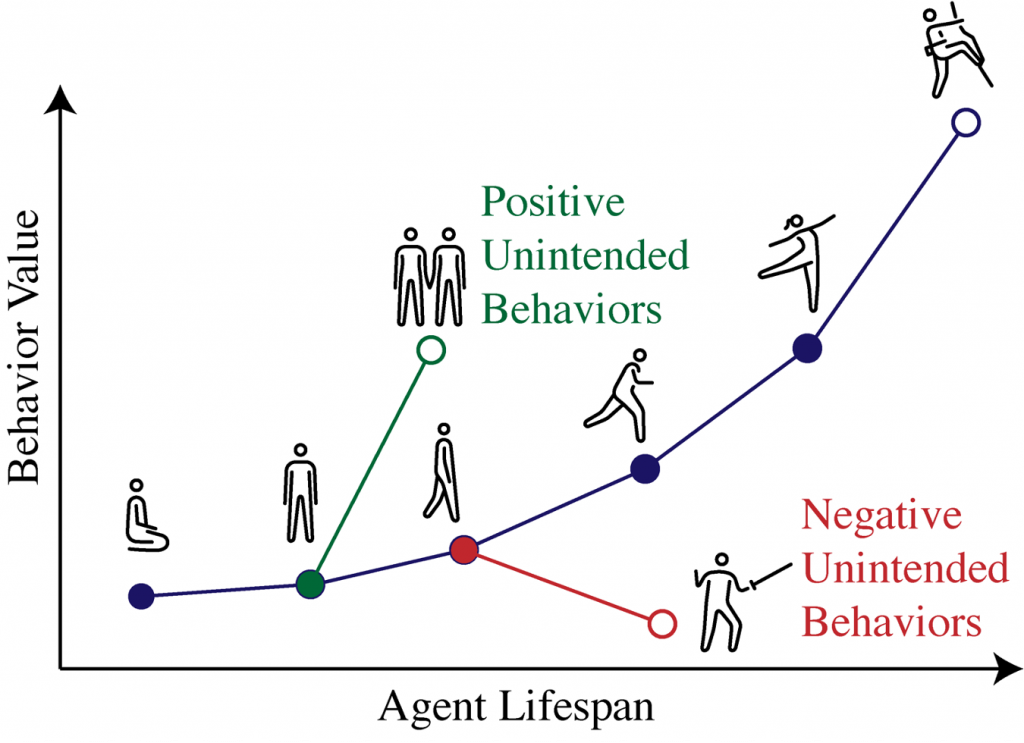
Figure 5: Behavior estimation failure illustration.
While these failure modes are closely related to control and behavioral feedback, Exo-feedback does not map as clearly to one type of error and introduces risks that do not fit into simple categories. Understanding exo-feedback requires that stakeholders in the broader communities (machine learning, application domains, sociology, etc.) work together on real world RL deployments.
Risks with real-world RL
Here, we discuss four types of design choices an RL designer must make, and how these choices can have an impact upon the socio-technical failures that an agent might exhibit once deployed.
Scoping the Horizon
Determining the timescale on which aRL agent can plan impacts the possible and actual behavior of that agent. In the lab, it may be common to tune the horizon length until the desired behavior is achieved. But in real world systems, optimizations will externalize costs depending on the defined horizon. For example, an RL agent controlling an autonomous vehicle will have very different goals and behaviors if the task is to stay in a lane, navigate a contested intersection, or route across a city to a destination. This is true even if the objective (e.g. “minimize travel time”) remains the same.
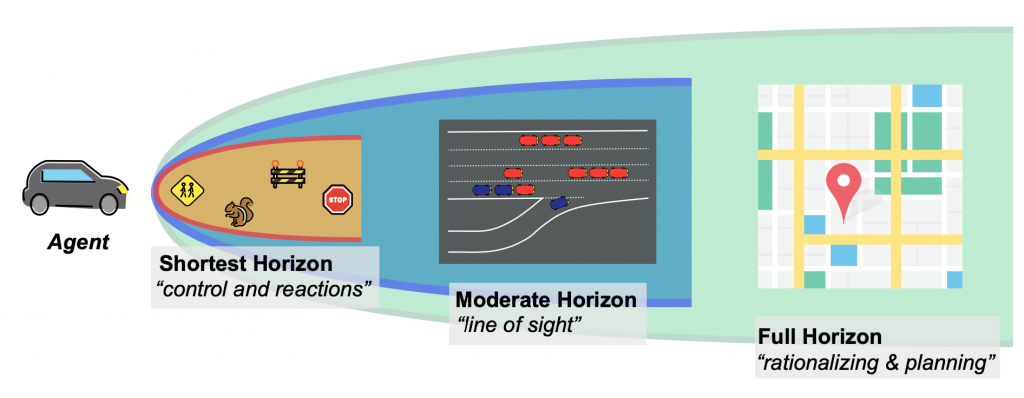
Figure 6: Scoping the horizon example with an autonomous vehicle.
Defining Rewards
A second design choice is that of actually specifying the reward function to be maximized. This immediately raises the well-known risk of RL systems, reward hacking, where the designer and agent negotiate behaviors based on specified reward functions. In a deployed RL system, this often results in unexpected exploitative behavior – from bizarre video game agents to causing errors in robotics simulators. For example, if an agent is presented with the problem of navigating a maze to reach the far side, a mis-specified reward might result in the agent avoiding the task entirely to minimize the time taken.
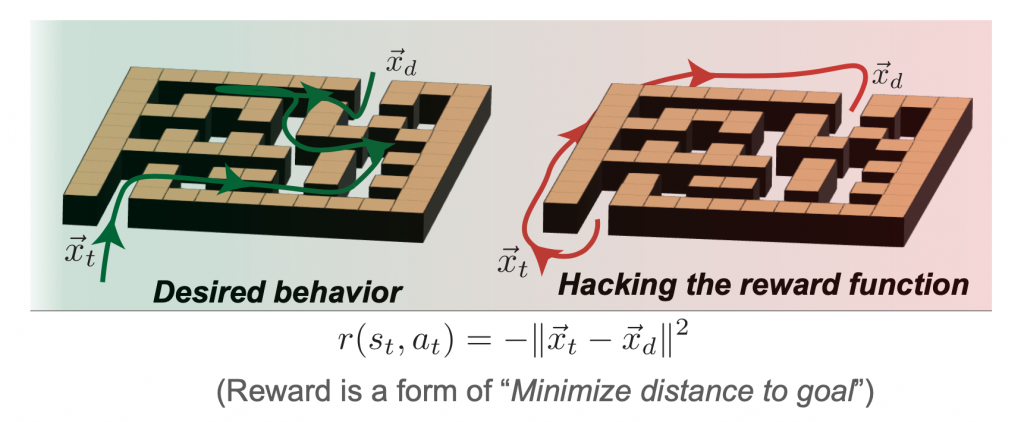
Figure 7: Defining rewards example with maze navigation.
A common practice in RL research is to redefine the environment to fit one’s needs – RL designers make numerous explicit and implicit assumptions to model tasks in a way that makes them amenable to virtual RL agents. In highly structured domains, such as video games, this can be rather benign.However, in the real world redefining the environment amounts to changing the ways information can flow between the world and the RL agent. This can dramatically change the meaning of the reward function and offload risk to external systems. For example, an autonomous vehicle with sensors focused only on the road surface shifts the burden from AV designers to pedestrians. In this case, the designer is pruning out information about the surrounding environment that is actually crucial to robustly safe integration within society.
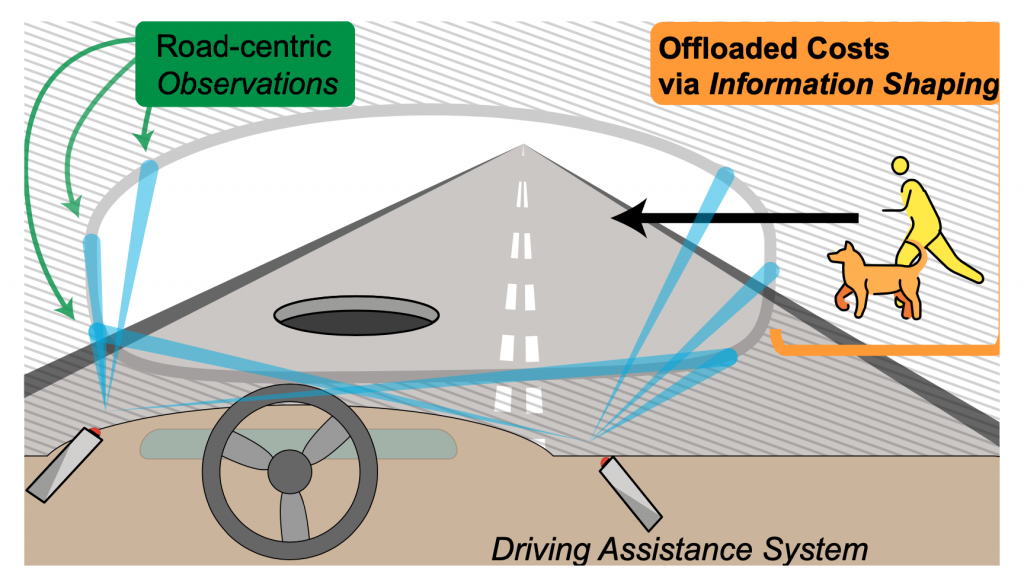
Figure 8: Information shaping example with an autonomous vehicle.
Training Multiple Agents
There is growing interest in the problem of multi-agent RL, but as an emerging research area, little is known about how learning systems interact within dynamic environments. When the relative concentration of autonomous agents increases within an environment, the terms these agents optimize for can actually re-wire norms and values encoded in that specific application domain. An example would be the changes in behavior that will come if the majority of vehicles are autonomous and communicating (or not) with each other. In this case, if the agents have autonomy to optimize toward a goal of minimizing transit time (for example), they could crowd out the remaining human drivers and heavily disrupt accepted societal norms of transit.
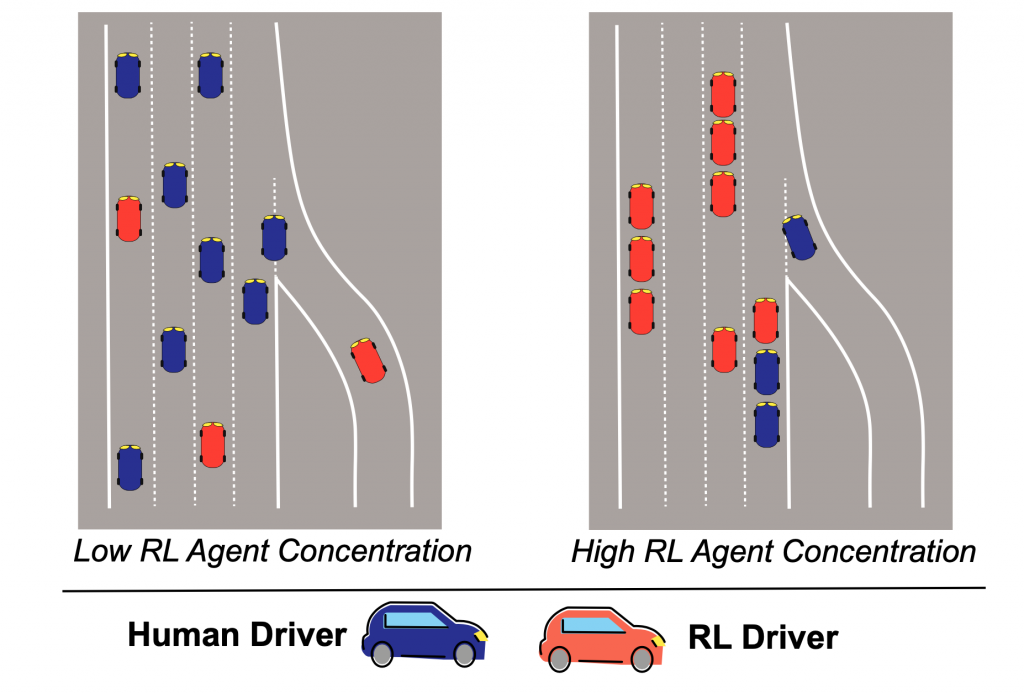
Figure 9: The risks of multi-agency example on autonomous vehicles.
Making sense of applied RL: Reward Reporting
In our recent whitepaper and research paper, we proposed Reward Reports, a new form of ML documentation that foregrounds the societal risks posed by sequential data-driven optimization systems, whether explicitly constructed as an RL agent or implicitly construed via data-driven optimization and feedback. Building on proposals to document datasets and models, we focus on reward functions: the objective that guides optimization decisions in feedback-laden systems. Reward Reports comprise questions that highlight the promises and risks entailed in defining what is being optimized in an AI system, and are intended as living documents that dissolve the distinction between ex-ante (design) specification and ex-post (after the fact) harm. As a result, Reward Reports provide a framework for ongoing deliberation and accountability before and after a system is deployed.
Our proposed template for a Reward Reports consists of several sections, arranged to help the reporter themselves understand and document the system. A Reward Report begins with (1) system details that contain the information context for deploying the model. From there, the report documents (2) the optimization intent, which questions the goals of the system and why RL or ML may be a useful tool. The designer then documents (3) how the system may affect different stakeholders in the institutional interface. The next two sections contain technical details on (4) the system implementation and (5) evaluation. Reward reports conclude with (6) plans for system maintenance as additional system dynamics are uncovered.
The most important feature of a Reward Report is that it allows documentation to evolve over time, in step with the temporal evolution of an online, deployed RL system! This is most evident in the change-log, which is we locate at the end of our Reward Report template:
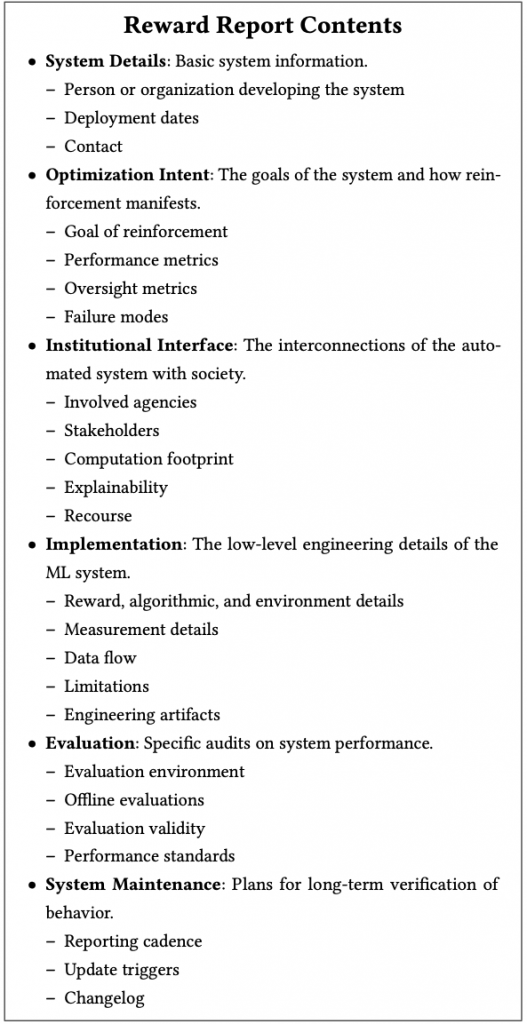
Figure 10: Reward Reports contents.
What would this look like in practice?
As part of our research, we have developed a reward report LaTeX template, as well as several example reward reports that aim to illustrate the kinds of issues that could be managed by this form of documentation. These examples include the temporal evolution of the MovieLens recommender system, the DeepMind MuZero game playing system, and a hypothetical deployment of an RL autonomous vehicle policy for managing merging traffic, based on the Project Flow simulator.
However, these are just examples that we hope will serve to inspire the RL community–as more RL systems are deployed in real-world applications, we hope the research community will build on our ideas for Reward Reports and refine the specific content that should be included. To this end, we hope that you will join us at our (un)-workshop.
Work with us on Reward Reports: An (Un)Workshop!
We are hosting an “un-workshop” at the upcoming conference on Reinforcement Learning and Decision Making (RLDM) on June 11th from 1:00-5:00pm EST at Brown University, Providence, RI. We call this an un-workshop because we are looking for the attendees to help create the content! We will provide templates, ideas, and discussion as our attendees build out example reports. We are excited to develop the ideas behind Reward Reports with real-world practitioners and cutting-edge researchers.
For more information on the workshop, visit the website or contact the organizers at geese-org@lists.berkeley.edu.
This post is based on the following papers:













