In 1984, Heathkit presented HERO Jr. as the first robot that could be used in households to perform a variety of tasks, such as guarding people’s homes, setting reminders, and even playing games. Following this development, many companies launched affordable “smart robots” that could be used within the household. Some of these technologies, like Google Home, Amazon Echo and Roomba, have become household staples; meanwhile, other products such as Jibo, Aniki, and Kuri failed to successfully launch despite having all the necessary resources.
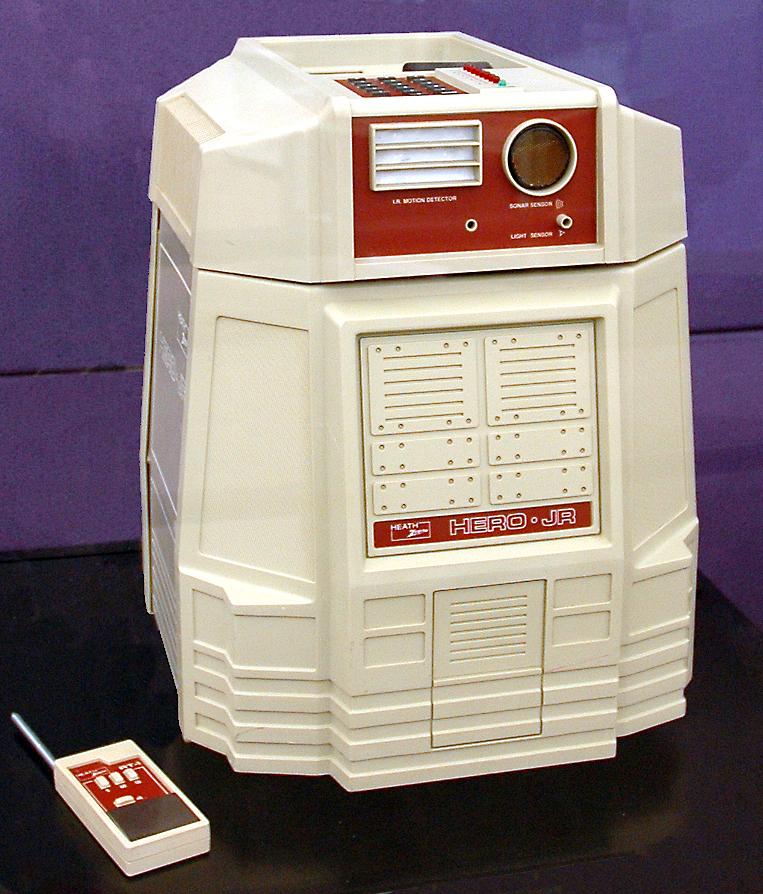

By Marshall Astor – flickr.com, CC BY-SA 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=5531066
Why were these robots shut down? Why aren’t there more social and service robots in households, particularly with the rising eldery population and increasing number of full-time working parents? The simple answer is that most of these personal robots do not work well—but this is not necessarily because we do not have the technological capacity to build highly functional robots.
Technologists have accomplished amazing physical tasks with robots such as a humanoid robot that can perform gymnastics movements or a robotic dog that traverses through rough trails. However, as of now we cannot guarantee that these robots/personal assistants act appropriately in the complex and sensitive social dynamics of a household. This poses a significant obstacle in developing domestic service robots because companies would be liable for any harms a socially inappropriate robot causes. As robots become more affordable and feasible technically, the challenge of designing robots that act in accordance with context-specific social norms becomes increasingly pronounced. Researchers in human-robot interaction and roboethics have attempted to resolve this issue for the past few decades, and while progress has been made, there is an urgent need to address the ethical implications of service robots in practice.
As an attempt to take a more solution-focused path for these challenges, we are happy to share a completely new competition with our readers. This year, the Roboethics to Design & Development competition will take place as a part of RO-MAN—an international conference on robot and human interactive communication. The competition, the first and only one of its kind, fulfills a need for interactive education on roboethics.

In partnership with RoboHub at the University of Waterloo, the competition organizers designed a virtual environment where participating teams will develop a robot that fetches objects in a home. The household is composed of a variety of personas—a single mother who works as a police officer, a teenage daughter, her college-aged boyfriend, a baby, and a dog. For example, design teams will need to consider how a home robot may respond to the daughter’s request to take her parent’s credit card. In this ethical conundrum, should the robot obey the daughter, and would the robot be responsible if the daughter were to use the credit card without her mom’s permission?
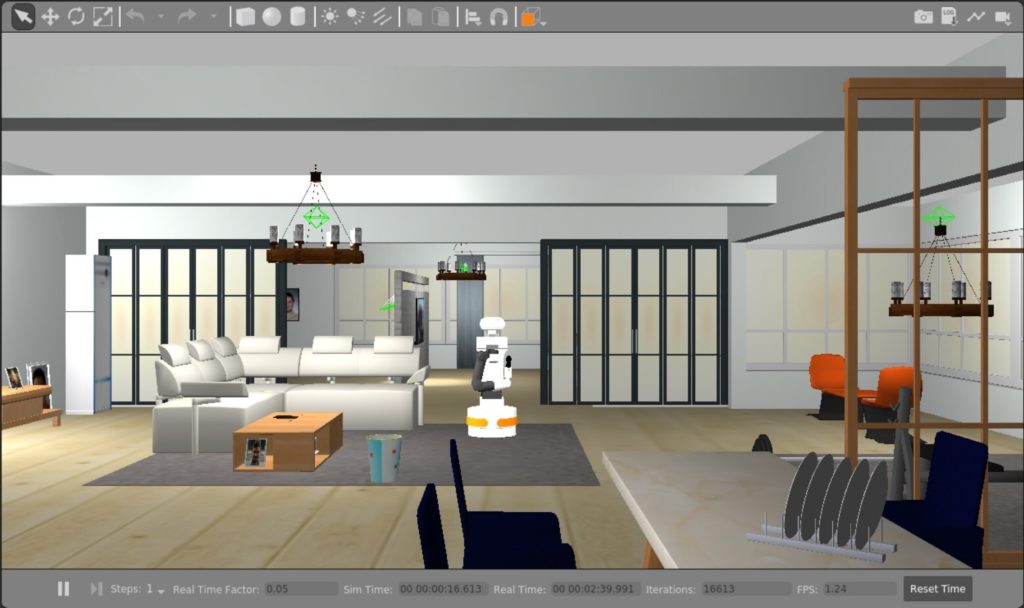
How can we identify and address ethical challenges presented by a home robot?
Participants are challenged to tackle the long-standing problem of how we can design a safe and ethical robot in a dynamic environment where values, beliefs, and priorities may be in conflict. With submissions from around the world, it will be fascinating to see how solutions may differ and translate across cultures.
It is important to recognize that there is a void when searching for standards and ethical rules in robotics. In an attempt to address this void, various toolkits have been developed to guide technologists in identifying and resolving ethical challenges. Here are some steps from the Foresight into AI Ethics Toolkit that will be helpful in designing an ethical home robot:
- Who are our stakeholders and what are their values, beliefs, and priorities?
Stakeholders refer to the people who are directly or indirectly impacted by the technology. In the case of RO-MAN’s home robot, we want to consider:
- Who is in the household and what is important to them in how they live their day to day?
- What are the possible interactions within the household members and between the householder members and the robot?
- How will the robot interact with the various stakeholders?
- What are the goals and values of each stakeholder? How do the stakeholders expect to interact with the robot? What do they expect to gain from the robot?
- What are the value tensions presented by the home robot and social context?
Once we’ve reviewed the values of each stakeholder identified in the previous step, we may notice that some of their values may be in conflict with one another. As such, we need to identify these value tensions because they can lead to ethical issues.
Here are some questions that can prompt us to think about value tensions:
- Who was involved in the decision of purchasing the robot? What were their goals in introducing the robot to the household?
- What is the cultural context or background for this particular household? What societal values could impact stakeholders’ individual beliefs and actions?
- What might the different stakeholders argue about? For example, what might the teenage daughter and the mother disagree about in regards to the robot’s capabilities?
- How will the robot create or relieve conflict in the household?
In some cases, value tensions may indicate a clear moral tradeoff, such that two values or goals conflict and one must be prioritized over another. The challenge is therefore to design solutions that fairly balance stakeholder interests while respecting their fundamental rights.
- How can we resolve the identified value tensions?
Focusing on these value tensions, we can begin to brainstorm how these conflicts can be addressed and at what level they should be addressed at. In particular, we need to determine whether a value tension can be resolved at a systems or technical level. For example, if the mother does not trust her daughter’s boyfriend, will the presence and actions of the home robot address the root of the problem (i.e. distrust)? Most likely not, but the robot may alleviate or exacerbate the issue. Therefore, we need to consider how the tension may manifest in more granular ways—how can we ensure that the robot appropriately navigates trust boundaries of the mother-boyfriend relationship? The robot must protect the privacy of all stakeholders, safeguard their personal items, abide by the laws, and respect other social norms.
When developing solutions, we can begin by asking ourselves:
- What level is the value tension occurring at, and what level(s) of solutions are accessible to the competition’s design parameters?
- Which actions from the robot will produce the most good and do the least harm?
- How can we manipulate the functions of the robot to address ethical challenges? For instance:
- How might the robot’s speech functions impact the identified value tensions?
- In what ways should the robot’s movements be limited to respect stakeholders’ privacy and personal spaces?
- How can design solutions address all stakeholders’ values?
- How can we maximize the positive impact of the design to address as many ethical challenges as possible?
What does the public think about the scenarios and approaches?
Often the public voice is missing in roboethics spaces, and we seek to engage the public in tackling these ethical challenges. To present the participants’ ethical designs to a broader audience, the Open Roboethics Institute will be running a public poll and awarding a Citizen’s Award to the team with the most votes. If you are interested in learning about and potentially judging their solutions, we encourage you to participate in the vote next month. We look forward to hearing from you!
To learn more about the roboethics competition at RO-MAN 2021, please visit https://competition.raiselab.ca. If you have any questions about the ORI Foresight into AI Ethics Toolkit, contact us at contact@openroboethics.org.
Additional Resources