New programmable materials can sense their own movements
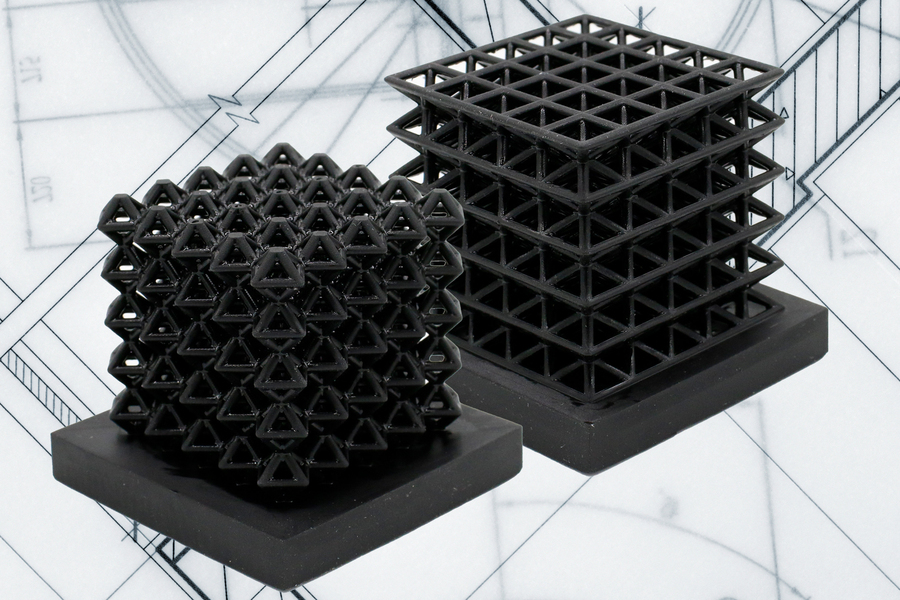
This image shows 3D-printed crystalline lattice structures with air-filled channels, known as “fluidic sensors,” embedded into the structures (the indents on the middle of lattices are the outlet holes of the sensors.) These air channels let the researchers measure how much force the lattices experience when they are compressed or flattened. Image: Courtesy of the researchers, edited by MIT News
By Adam Zewe | MIT News Office
MIT researchers have developed a method for 3D printing materials with tunable mechanical properties, that sense how they are moving and interacting with the environment. The researchers create these sensing structures using just one material and a single run on a 3D printer.
To accomplish this, the researchers began with 3D-printed lattice materials and incorporated networks of air-filled channels into the structure during the printing process. By measuring how the pressure changes within these channels when the structure is squeezed, bent, or stretched, engineers can receive feedback on how the material is moving.
The method opens opportunities for embedding sensors within architected materials, a class of materials whose mechanical properties are programmed through form and composition. Controlling the geometry of features in architected materials alters their mechanical properties, such as stiffness or toughness. For instance, in cellular structures like the lattices the researchers print, a denser network of cells makes a stiffer structure.
This technique could someday be used to create flexible soft robots with embedded sensors that enable the robots to understand their posture and movements. It might also be used to produce wearable smart devices that provide feedback on how a person is moving or interacting with their environment.
“The idea with this work is that we can take any material that can be 3D-printed and have a simple way to route channels throughout it so we can get sensorization with structure. And if you use really complex materials, then you can have motion, perception, and structure all in one,” says co-lead author Lillian Chin, a graduate student in the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL).
Joining Chin on the paper are co-lead author Ryan Truby, a former CSAIL postdoc who is now as assistant professor at Northwestern University; Annan Zhang, a CSAIL graduate student; and senior author Daniela Rus, the Andrew and Erna Viterbi Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and director of CSAIL. The paper is published today in Science Advances.
Architected materials
The researchers focused their efforts on lattices, a type of “architected material,” which exhibits customizable mechanical properties based solely on its geometry. For instance, changing the size or shape of cells in the lattice makes the material more or less flexible.
While architected materials can exhibit unique properties, integrating sensors within them is challenging given the materials’ often sparse, complex shapes. Placing sensors on the outside of the material is typically a simpler strategy than embedding sensors within the material. However, when sensors are placed on the outside, the feedback they provide may not provide a complete description of how the material is deforming or moving.
Instead, the researchers used 3D printing to incorporate air-filled channels directly into the struts that form the lattice. When the structure is moved or squeezed, those channels deform and the volume of air inside changes. The researchers can measure the corresponding change in pressure with an off-the-shelf pressure sensor, which gives feedback on how the material is deforming.
Because they are incorporated into the material, these “fluidic sensors” offer advantages over conventional sensor materials.
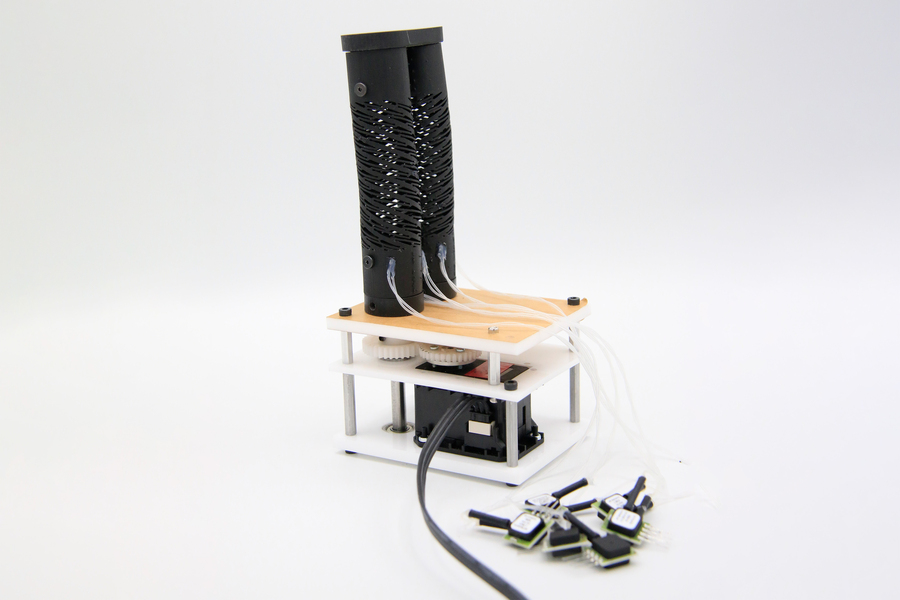

This image shows a soft robotic finger made from two cylinders comprised of a new class of materials known as handed shearing auxetics (HSAs), which bend and rotate. Air-filled channels embedded within the HSA structure connect to pressure sensors (pile of chips in the foreground), which actively measure the pressure change of these “fluidic sensors.” Image: Courtesy of the researchers
“Sensorizing” structures
The researchers incorporate channels into the structure using digital light processing 3D printing. In this method, the structure is drawn out of a pool of resin and hardened into a precise shape using projected light. An image is projected onto the wet resin and areas struck by the light are cured.
But as the process continues, the resin remains stuck inside the sensor channels. The researchers had to remove excess resin before it was cured, using a mix of pressurized air, vacuum, and intricate cleaning.
They used this process to create several lattice structures and demonstrated how the air-filled channels generated clear feedback when the structures were squeezed and bent.
“Importantly, we only use one material to 3D print our sensorized structures. We bypass the limitations of other multimaterial 3D printing and fabrication methods that are typically considered for patterning similar materials,” says Truby.
Building off these results, they also incorporated sensors into a new class of materials developed for motorized soft robots known as handed shearing auxetics, or HSAs. HSAs can be twisted and stretched simultaneously, which enables them to be used as effective soft robotic actuators. But they are difficult to “sensorize” because of their complex forms.
They 3D printed an HSA soft robot capable of several movements, including bending, twisting, and elongating. They ran the robot through a series of movements for more than 18 hours and used the sensor data to train a neural network that could accurately predict the robot’s motion.
Chin was impressed by the results — the fluidic sensors were so accurate she had difficulty distinguishing between the signals the researchers sent to the motors and the data that came back from the sensors.
“Materials scientists have been working hard to optimize architected materials for functionality. This seems like a simple, yet really powerful idea to connect what those researchers have been doing with this realm of perception. As soon as we add sensing, then roboticists like me can come in and use this as an active material, not just a passive one,” she says.
“Sensorizing soft robots with continuous skin-like sensors has been an open challenge in the field. This new method provides accurate proprioceptive capabilities for soft robots and opens the door for exploring the world through touch,” says Rus.
In the future, the researchers look forward to finding new applications for this technique, such as creating novel human-machine interfaces or soft devices that have sensing capabilities within the internal structure. Chin is also interested in utilizing machine learning to push the boundaries of tactile sensing for robotics.
“The use of additive manufacturing for directly building robots is attractive. It allows for the complexity I believe is required for generally adaptive systems,” says Robert Shepherd, associate professor at the Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at Cornell University, who was not involved with this work. “By using the same 3D printing process to build the form, mechanism, and sensing arrays, their process will significantly contribute to researcher’s aiming to build complex robots simply.”
This research was supported, in part, by the National Science Foundation, the Schmidt Science Fellows Program in partnership with the Rhodes Trust, an NSF Graduate Fellowship, and the Fannie and John Hertz Foundation.
The Wheelbot: A symmetric unicycle with jumping reaction wheels
Cobots — electric or pneumatic?
Robots will open more doors than they close

Michael M. Lee
In early 19th-century England, the Luddites rebelled against the introduction of machinery in the textile industry. The Luddites’ name originates from the mythical tale of a weaver’s apprentice called Ned Ludd who, in an act of anger against increasingly dangerous and poor working conditions, supposedly destroyed two knitting machines. Contrary to popular belief, the Luddites were not against technology because they were ignorant or inept at using it (1). In fact, the Luddites were perceptive artisans who cared about their craft, and some even operated machinery. Moreover, they understood the consequences of introducing machinery to their craft and working conditions. Specifically, they were deeply concerned about how technology was being used to shift the balance of power between workers and owners of capital.
The problem is not the advent of technology; the problem is how technology is applied. This is the essence of the intensely polarizing debate on robotic labor. Too often the debate is oversimplified to two opposing factions: the anti-tech pessimist versus the pro-tech optimist. On the one hand, the deeply pessimistic make the case that there will be greatly diminished workers’ rights, mass joblessness, and a widening gulf between socioeconomic classes. On the other hand, the overly optimistic believe that technology will bring better jobs and unbridled economic wealth. The reality is that, although extreme, both sides have valid points. The debate in its present form lacks a middle ground, leaving little room for nuanced and thoughtful discussion. It is simplistic to assume those who are pessimistic towards technological change do not understand the potential of technology as it is incorrect to conclude those who are optimistic about technological change are not thinking about the consequences. Pessimists may fully understand the potential for technological change and still feel that the drawbacks outweigh benefits. Optimists may not want change at any cost, but they feel that the costs are worthwhile.
There are various examples of how the introduction of machines have made industries more efficient and innovative, raising both the quality of work and the quality of output (for example, automated teller machines in banking, automated telephone exchanges in telecommunications, and industrial robots in manufacturing). An important detail in these success stories that is rarely mentioned, however, are timelines. The first industrial revolution did lead to higher levels of urbanization and rises in output; however, crucially, it took several decades before workers saw higher wages. This period of constant wages in the backdrop of rising output per worker is known as Engels’ pause, named after Friedrich Engels, the philosopher who first observed it (2).
Timing matters because, although there will be gains in the long term, there will certainly be losses in the short term. Support for retraining those most at risk of job displacement is needed to bridge this gap. Unfortunately, progress is disappointingly slow on this front. On one level, there are those who are apathetic to the challenges facing the workforce and feel that the loss of jobs is part of the cut and thrust of technological change. On another level, it is possible that there is a lack of awareness of the challenges of transitioning people to a new era of work. We need to bring change and light to both cases, respectively. Those at risk of being displaced by machines need to feel empowered by being a part of the change and not a by-product of change. Moreover, in developing the infrastructure to retrain and support those at risk, we must also recognize that retraining is itself a solution encased in many unsolved problems that include technical, economic, social, and even cultural challenges.
There is more that roboticists should be doing to advance the debate on robotic labor beyond the current obsessive focus on job-stealing robots. First, roboticists should provide a critical and fair assessment of the current technological state of robots. If the public were aware of just how far the field of robotics needs to advance to realize highly capable and truly autonomous robots, then they might be more assured. Second, roboticists should openly communicate the intent of their research goals and aspirations. Understanding that, in the foreseeable future, robotics will be focused on task replacement, not comprehensive job replacement, changes the conversation from how robots will take jobs from workers to how robots can help workers do their job better. The ideas of collaborative robots and multiplicity are not new (3), but they seldom get the exposure that they deserve. Opening an honest and transparent dialogue between roboticists and the general public will go a long way to building a middle ground that will elevate discussion on the future of work.
References
- J. Sadowski, “I’m a Luddite. You should be one too,” The Conversation, 25 November 2021 [accessed 3 April 2022].
- R. C. Allen, Engels’ pause: Technical change, capital accumulation, and inequality in the British industrial revolution. Explor. Econ. Hist. 46, 418–435 (2019).
- K. Goldberg, Editorial multiplicity has more potential than singularity. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 12, 395 (2015).
From “Lee, M. M., Robots will open more doors than they close. Science Robotics, 7, 65 (2022).” Reprinted with permission from AAAS. Further distribution or republication of this article is not permitted without prior written permission from AAAS.
How a slender, snake-like robot could give doctors new ways to save lives
The Developing Role of Drones In Manufacturing
The best sci-fi books that describe how robots really work

I have loved science fiction ever since I was a kid and read all my Dad’s ancient issues of Analog Science Fiction and Fact from the 1940s. The first book I can remember reading was The Green Hills of Earth anthology by Robert Heinlein. Fast forward to the 1990s, when, as a new professor of computer science, I began adding sci-fi short stories and movies as extra credit for my AI and robotics courses. Later as a Faculty Fellow for Innovation in High-Impact Learning Experiences at Texas A&M, I created the Robotics Through Science Fiction book series as a companion to my textbook, Introduction to AI Robotics.
The books I picked & why

|
Little Eyes A Firby-like robot pet becomes an international fad, where a “keeper” buys a little wheeled robot and is randomly paired with a “dweller” who teleoperates the robot. The robot has only a camera and microphone, but no audio output, and the identity of the keeper and dweller are hidden. The game is that the keeper is entertained trying to figure out why the robot does what it does, while the dweller is entertained by exploring a new place. What could go wrong? Lots. Lots! Little Eyes absolutely terrified me, much more than any Stephen King novel because there is nothing supernatural, it could really happen. |

|
The Warehouse This is my favorite introduction to the state of automation and autonomy in manufacturing. In a near future, a Sam Walton type has made a fortune through drone delivery and warehouse automation. The warehouse automation is based on a well-intentioned, but shallow, interpretation of the outdated Fitts Law in human factors that divide different jobs between robots and humans. Except humans can’t match robot speed and endurance. The tension is whether a corporate spy who has infiltrated a warehouse to steal secrets is there to expose the inherent cruelty or, worse, to replicate the work practices at a competitor’s facility. |

|
Rendezvous with Rama This 1973 hard sci-fi classic is perhaps the best fictional introduction to behavioral robotics there is, appearing a decade before researchers, most notably Rod Brooks, created the behavioral paradigm. An alien spaceship is passing through our solar system on a slingshot orbit. It is autonomous but controlled strictly by simple biological affordances that enable it to respond to the human intruders without applying any of the HAL 9000 reasoning Clarke popularized in his more famous 2001: A Space Odyssey. I mentally throw this book at engineers when they try to make unnecessarily complex robots. |

|
Kill Decision When Kill Decision came out, I sent an email to all my Department of Defense colleagues saying: finally, a book that gets swarms, drones, computer vision, and lethal autonomous weapons right! The book shows behavioral robotics can duplicate insect intelligence to create simple, but relentlessly effective, drones. The inexpensive individual drones are limited in intelligence but a greater, more adaptive intelligence emerges from the swarm. It’s on par with a Michael Crichton technothriller with lots of action (plus romance), making it an easy read. |

|
Head On: A Novel of the Near Future The second in his entertaining detective series in a near future where 2% of the population is paralyzed and has to teleoperate robots in order to interact with the world (interestingly, it was written before the pandemic). The protagonist, Chris (we never are told their gender, making for a delightful guessing game), is an FBI agent investigating a murder and along the way faces the kind of casual discrimination that the disabled undoubtedly face every day. Chris maintains a wry sense of humor through it all, adding an Elmore Leonard or Donald E. Westlake vibe that makes me laugh out loud. |
Original article published in Shepherd. Shepherd also has bookshelves about robots and robotics.
10 emerging technologies that will have a significant impact in the coming years
Today, society is involved in a hyperconnected world and the questioning about what will be the technologies that will shape the world in the future. Likewise, a lot of data is analyzed to try to understand which technological innovations will have a radical impact on the world economy, the environment, or the social order. In...
The post 10 emerging technologies that will have a significant impact in the coming years appeared first on 1redDrop.