AUCTION – FACILITY CLOSURE – MAJOR ROBOTICS AUTOMATION COMPANY
BTM Industrial -The industry leader in assisting companies with surplus assets.
Artificial tendons give muscle-powered robots a boost
Automatic Visual Inspection: The Secret to Flawless Manufacturing Quality
Why companies don’t share AV crash data – and how they could
 Anton Grabolle / Autonomous Driving / Licenced by CC-BY 4.0
Anton Grabolle / Autonomous Driving / Licenced by CC-BY 4.0
By Susan Kelley
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) have been tested as taxis for decades in San Francisco, Pittsburgh and around the world, and trucking companies have enormous incentives to adopt them.
But AV companies rarely share the crash- and safety-related data that is crucial to improving the safety of their vehicles – mostly because they have little incentive to do so.
Is AV safety data an auto company’s intellectual asset or a public good? It can be both – with a little tweaking, according to a team of Cornell researchers.
The team has created a roadmap outlining the barriers and opportunities to encourage AV companies to share the data to make AVs safer, from untangling public versus private data knowledge, to regulations to creating incentive programs.
“The core of AV market competition involves who has that crash data, because once you have that data, it’s much easier for you to train your AI to not make that error. The hope is to first make this data transparent and then use it for public good, and not just profit,” said Hauke Sandhaus, M.S. ’24, a doctoral candidate at Cornell Tech and co-author of “My Precious Crash Data,” published Oct. 16 in ACM on Human-Computer Interaction and presented at the ACM SIGCHI Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work & Social Computing.
His co-authors are Qian Yang, assistant professor at the Cornell Ann S. Bowers College of Computing and Information Science; Wendy Ju, associate professor of information science and design tech at Cornell Tech, the Cornell Ann S. Bowers College of Computing and Information Science and the Jacobs Technion-Cornell Institute; and Angel Hsing-Chi Hwang, a former postdoctoral associate at Cornell and now assistant professor of communication at the University of Southern California, Annenberg.
The team interviewed 12 AV company employees who work on safety in AV design and deployment, to understand how they currently manage and share safety data, the data sharing challenges and concerns they face, and their ideal data-sharing practices.
The interviews revealed the AV companies have a surprising diversity of approaches, Sandhaus said. “Everyone really has some niche, homegrown data set, and there’s really not a lot of shared knowledge between these companies,” he said. “I expected there would be much more commonality.”
The research team discovered two key barriers to sharing data – both underscoring a lack of incentives. First, crash and safety data includes information about the machine-learning models and infrastructure that the company uses to improve safety. “Data sharing, even within a company, is political and fraught,” the team wrote in the paper. Second, the interviewees believed AV safety knowledge is private and brings their company a competitive edge. “This perspective leads them to view safety knowledge embedded in data as a contested space rather than public knowledge for social good,” the team wrote.
And U.S. and European regulations are not helping. They require only information such as the month when the crash occurred, the manufacturer and whether there were injuries. That doesn’t capture the underlying unexpected factors that often cause accidents, such as a person suddenly running onto the street, drivers violating traffic rules, extreme weather conditions or lost cargo blocking the road.
To encourage more data-sharing, it’s crucial to untangle safety knowledge from proprietary data, the researchers said. For example, AV companies could share information about the accident, but not raw video footage that would reveal the company’s technical infrastructure.
Companies could also come up with “exam questions” that AVs would have to pass in order to take the road. “If you have pedestrians coming from one side and vehicles from the other side, then you can use that as a test case that other AVs also have to pass,” Sandhaus said.
Academic institutions could act as data intermediaries with which AV companies could leverage strategic collaborations. Independent research institutions and other civic organizations have set precedents working with industry partners’ public knowledge. “There are arrangements, collaboration, patterns for higher ed to contribute to this without necessarily making the entire data set public,” Qian said.
The team also proposes standardizing AV safety assessment via more effective government regulations. For example, a federal policymaking agency could create a virtual city as a testing ground, with busy traffic intersections and pedestrian-heavy roads that every AV algorithm would have to be able to navigate, she said.
Federal regulators could encourage car companies to contribute scenarios to the testing environment. “The AV companies might say, ‘I want to put my test cases there, because my car probably has passed those tests.’ That can be a mechanism for encouraging safer vehicle development,” Yang said. “Proposing policy changes always feels a little bit distant, but I do think there are near-future policy solutions in this space.”
The research was funded by the National Science Foundation and Schmidt Sciences.
“Cleanest Prose I’ve Ever Seen”
One Writer’s Take on Gemini 3.0
Extensive creative writing tests by ‘The Nerdy Novelist’ – known for its take-no-prisoners evaluation of AI writing – have revealed that Gemini 3.0 is head-and-shoulders above all others when it comes to being the go-to for writers.
Essentially, the author behind the channel – Jason Hamilton – found that no other AI even came close to delivering Gemini 3.0’s exquisite prose when he put each through its paces.
For an in-depth look at how Hamilton came up with his Gemini 3.0 recommendation, check-out this 36-minute video.
In other news and analysis on AI writing:
*ChatGPT Voice: Now Even Easier to Use: ChatGPT’s maker is out with an upgrade to its voice mode, which enables you to talk with ChatGPT without leaving the ChatGPT interface.
Previously, voice users needed to interact with a separate screen if they wanted to use voice.
*Killer Image App Nano Banana Gets an Upgrade: Fresh-off its take-the-world-by-storm campaign as the globe’s most preferred image editor, ‘Nano Banana’ is out with a new ‘Pro’ version.
Officially known as ‘Gemini 3 Pro Image,’ the tool has grabbed the AI image-making crown with its ability to create extremely detailed images, engage in extremely precise editing – and do it all with incredible speed.
Observes writer Abner Li: “The new model is also coming to AI Mode for subscribers in the U.S., while it’s available to paid NotebookLM users globally. Nano Banana Pro will be available in Flow with Google AI Ultra.”
*AI Research Tool Perplexity Adds AI Assistance With Memory: Perplexity is out with a major new feature to its AI research tool, which embeds AI assistants – with memory – into its research mix.
Like many AI tools, Perplexity now remembers key details of your chats on its service in an effort to ensure responses are sharper and more personalized.
The new feature is optional and can be turned-off at any time.
*ChatGPT Competitor Releases Major Upgrade: Anthropic is out with a major update of one of its key AI engines: Claude Opus, now in version 4.5.
Framed as an inexpensive alternative that offers infinite chats, the AI engine has also scored high marks with amped-up reasoning skills.
Anthropic’s AI primarily targets the enterprise market and is known for killer coding capabilities.
*ChatGPT Voice: Now Even Easier to Use: ChatGPT’s maker is out with an upgrade to its voice mode, which enables you to talk with ChatGPT without leaving the ChatGPT interface.
Previously, voice users needed to interact with a separate screen if they wanted to use ChatGPT voice.
Interestingly, voice mode still relies on an older – and some say more creative – mode of ChatGPT to talk: ChatGPT-4.0.
*New AI Singer Number One on Christian Music Chart: Add virtual AI singer Solomon Ray to the increasing number of AI artists who are minting number one song hits.
Marketed as a ‘soul singer,’ the AI has a full album, dubbed “A Soulful Christmas,” with tunes like “Soul To the World” and “Jingle Bell Soul.”
Other AI singers have also been crowding-out mere fleshbags lately with number one hits on the Country charts and R&B charts.
*AI Can Already Eliminate 12% of U.S. Workforce: A new study from MIT finds that AI can already eliminate 12% of everyday jobs.
Dubbed the “Iceberg Index,” the study simulated AI’s ability to handle – or partially handle – nearly 1,000 occupations that are currently worked by more than 150 million in the U.S.
Observes writer Megan Cerullo: “AI is also already doing some of the entry-level jobs that have historically been reserved for recent college graduates or relatively inexperienced workers.”
*He’s No Tool: Show Your New AI ‘Colleague’ Some Respect: A new study finds that 76% of business leaders now see AI as your office ‘colleague’ – and not a tool.
Specifically, those leaders are referring to agentic AI – an advanced form of the tech that can ideally perform a number of tasks to complete a mission without the need of human supervision.
Even so, real-world tests show agents regularly hallucinate, mis-route data or misinterpret a mission’s goals on their way from here- to-there.
*U.S. Congress Seeks Answers on Alleged Chinese AI CyberAttack: The CEO of a major competitor of ChatGPT – Anthropic – will be testifying before the U.S Congress this month about a recent cyberattack that relied on Anthropic AI to infiltrate finance and government servers.
The attack – allegedly orchestrated by Chinese state actors – hacked Anthropic AI’s agentic abilities to penetrate the servers.
Observes writer Sam Sabin: “As AI rapidly intensifies the cyber threat landscape, lawmakers are just starting to wrap their heads around the problem.”
*AI Big Picture: This Generation’s Manhattan Project: The Genesis Mission: The Trump Administration has embraced AI as a key defense initiative in what it is calling “The Genesis Mission.”
Observes writer Chuck Brooks: “This mission is not merely another government program: it represents a bold strategic move that aligns with my belief that science, data, and computing should be regarded as essential components of our national strength rather than optional extras.
“For too long, we have considered science and technology to be secondary to our national strategy. The Genesis Mission reverses that idea.”

Share a Link: Please consider sharing a link to https://RobotWritersAI.com from your blog, social media post, publication or emails. More links leading to RobotWritersAI.com helps everyone interested in AI-generated writing.
–Joe Dysart is editor of RobotWritersAI.com and a tech journalist with 20+ years experience. His work has appeared in 150+ publications, including The New York Times and the Financial Times of London.
The post “Cleanest Prose I’ve Ever Seen” appeared first on Robot Writers AI.
How Rapid Repair Services Are Fueling a Competitive Edge in Automation
Robots combine AI learning and control theory to perform advanced movements
Scientists uncover the brain’s hidden learning blocks
Robot Talk Episode 135 – Robot anatomy and design, with Chapa Sirithunge

Claire chatted to Chapa Sirithunge from University of Cambridge about what robots can teach us about human anatomy, and vice versa.
Chapa Sirithunge is a Marie Sklodowska-Curie fellow in robotics at the University of Cambridge. She has an undergraduate degree and PhD in Electrical Engineering from the University of Moratuwa. Before joining the University of Cambridge in 2022, she was a lecturer at Sri Lanka Technological Campus and a visiting lecturer at the University of Moratuwa Sri Lanka. Her research interests span assistive robotics, soft robots and physical human-robot interaction. In addition to her research, she founded Women in Robotics Cambridge to help young minds navigate their path into robotics.
BrainBody-LLM algorithm helps robots mimic human-like planning and movement
China says humanoid robot buzz carries bubble risk
Humanoid robots reliably manipulate different objects with 87% success using new framework
Learning robust controllers that work across many partially observable environments
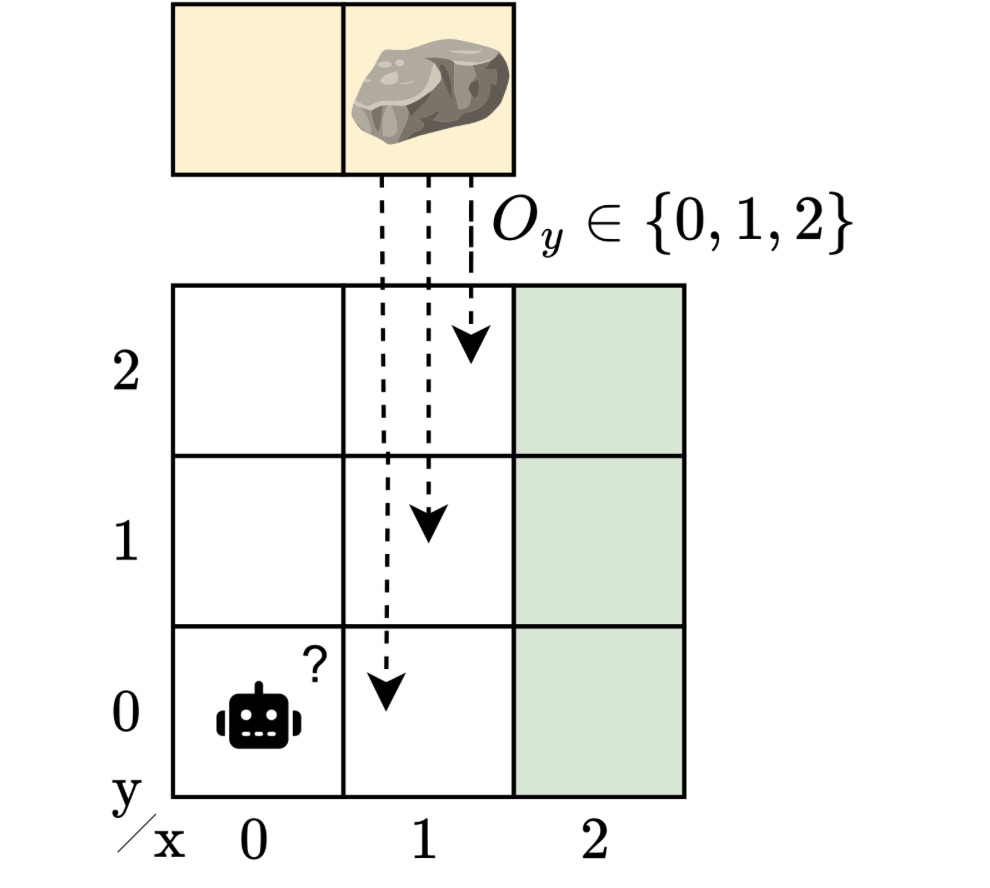
In intelligent systems, applications range from autonomous robotics to predictive maintenance problems. To control these systems, the essential aspects are captured with a model. When we design controllers for these models, we almost always face the same challenge: uncertainty. We’re rarely able to see the whole picture. Sensors are noisy, models of the system are imperfect; the world never behaves exactly as expected.
Imagine a robot navigating around an obstacle to reach a “goal” location. We abstract this scenario into a grid-like environment. A rock may block the path, but the robot doesn’t know exactly where the rock is. If it did, the problem would be reasonably easy: plan a route around it. But with uncertainty about the obstacle’s position, the robot must learn to operate safely and efficiently no matter where the rock turns out to be.
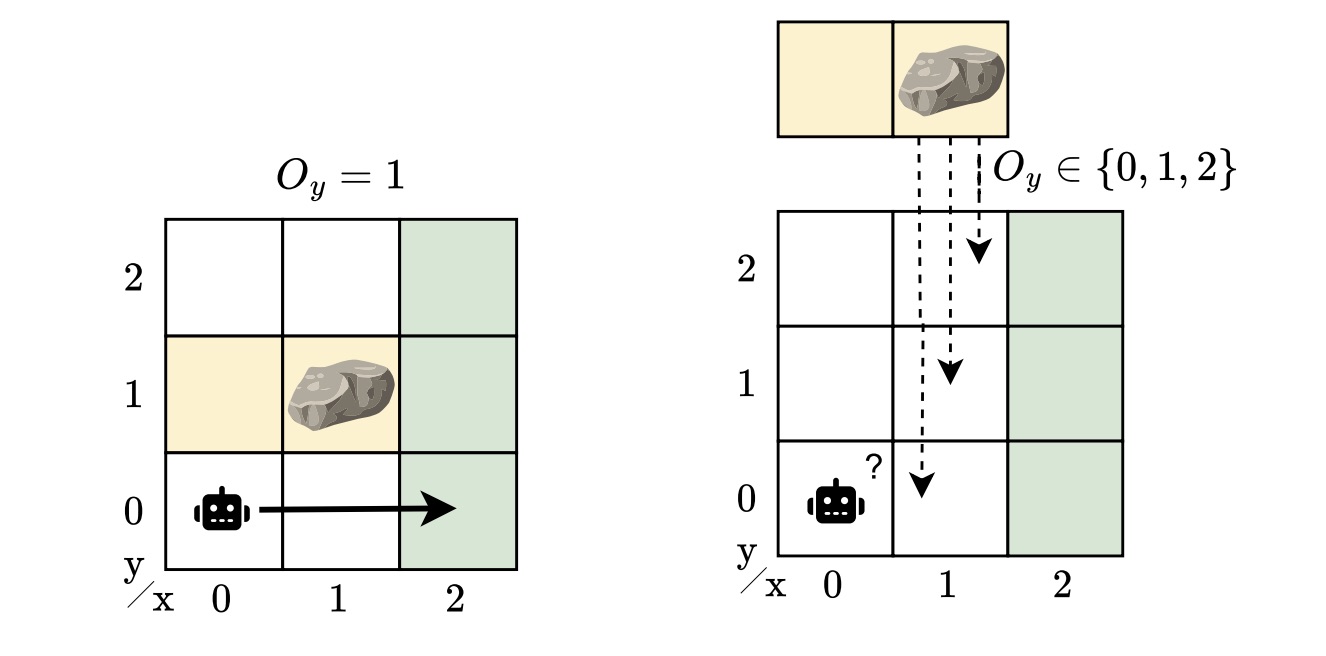
This simple story captures a much broader challenge: designing controllers that can cope with both partial observability and model uncertainty. In this blog post, I will guide you through our IJCAI 2025 paper, “Robust Finite-Memory Policy Gradients for Hidden-Model POMDPs”, where we explore designing controllers that perform reliably even when the environment may not be precisely known.
When you can’t see everything
When an agent doesn’t fully observe the state, we describe its sequential decision-making problem using a partially observable Markov decision process (POMDP). POMDPs model situations in which an agent must act, based on its policy, without full knowledge of the underlying state of the system. Instead, it receives observations that provide limited information about the underlying state. To handle that ambiguity and make better decisions, the agent needs some form of memory in its policy to remember what it has seen before. We typically represent such memory using finite-state controllers (FSCs). In contrast to neural networks, these are practical and efficient policy representations that encode internal memory states that the agent updates as it acts and observes.
From partial observability to hidden models
Many situations rarely fit a single model of the system. POMDPs capture uncertainty in observations and in the outcomes of actions, but not in the model itself. Despite their generality, POMDPs can’t capture sets of partially observable environments. In reality, there may be many plausible variations, as there are always unknowns — different obstacle positions, slightly different dynamics, or varying sensor noise. A controller for a POMDP does not generalize to perturbations of the model. In our example, the rock’s location is unknown, but we still want a controller that works across all possible locations. This is a more realistic, but also a more challenging scenario.
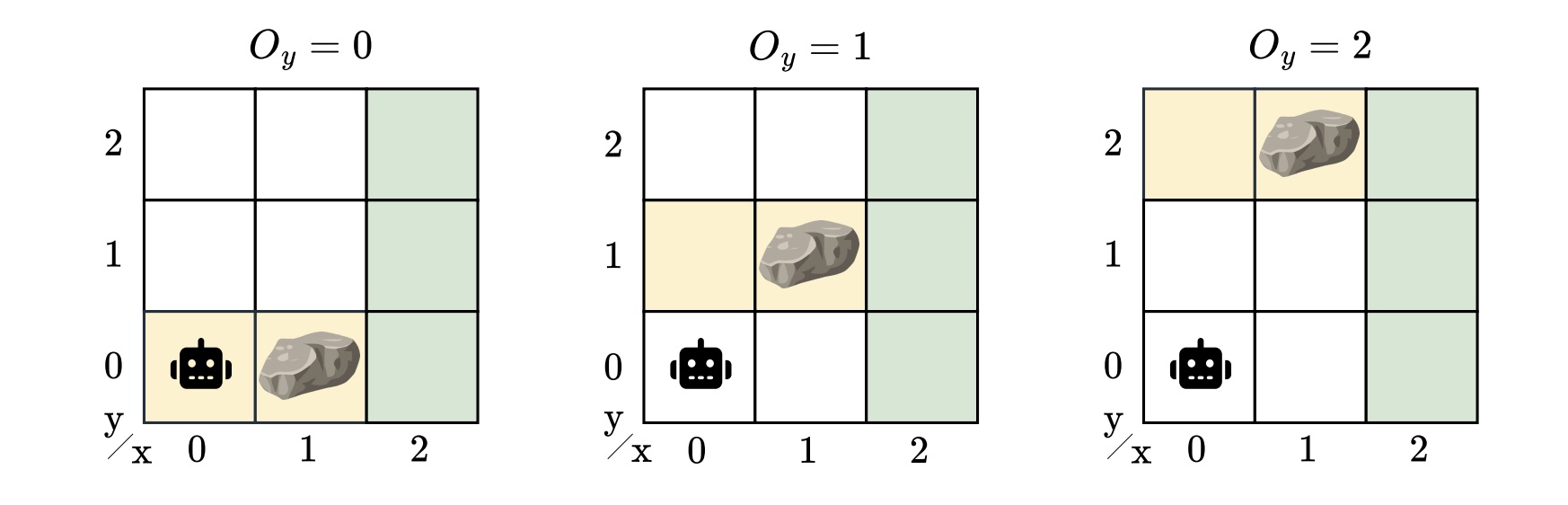
To capture this model uncertainty, we introduced the hidden-model POMDP (HM-POMDP). Rather than describing a single environment, an HM-POMDP represents a set of possible POMDPs that share the same structure but differ in their dynamics or rewards. An important fact is that a controller for one model is also applicable to the other models in the set.
The true environment in which the agent will ultimately operate is “hidden” in this set. This means the agent must learn a controller that performs well across all possible environments. The challenge is that the agent doesn’t just have to reason about what it can’t see but also about which environment it’s operating in.
A controller for an HM-POMDP must be robust: it should perform well across all possible environments. We measure the robustness of a controller by its robust performance: the worst-case performance over all models, providing a guaranteed lower bound on the agent’s performance in the true model. If a controller performs well even in the worst case, we can be confident it will perform acceptably on any model of the set when deployed.
Towards learning robust controllers
So, how do we design such controllers?
We developed the robust finite-memory policy gradient rfPG algorithm, an iterative approach that alternates between the following two key steps:
- Robust policy evaluation: Find the worst case. Determine the environment in the set where the current controller performs the worst.
- Policy optimization: Improve the controller for the worst case. Adjust the controller’s parameters with gradients from the current worst-case environment to improve robust performance.

Over time, the controller learns robust behavior: what to remember and how to act across the encountered environments. The iterative nature of this approach is rooted in the mathematical framework of “subgradients”. We apply these gradient-based updates, also used in reinforcement learning, to improve the controller’s robust performance. While the details are technical, the intuition is simple: iteratively optimizing the controller for the worst-case models improves its robust performance across all the environments.
Under the hood, rfPG uses formal verification techniques implemented in the tool PAYNT, exploiting structural similarities to represent large sets of models and evaluate controllers across them. Thanks to these developments, our approach scales to HM-POMDPs with many environments. In practice, this means we can reason over more than a hundred thousand models.
What is the impact?
We tested rfPG on HM-POMDPs that simulated environments with uncertainty. For example, navigation problems where obstacles or sensor errors varied between models. In these tests, rfPG produced policies that were not only more robust to these variations but also generalized better to completely unseen environments than several POMDP baselines. In practice, that implies we can render controllers robust to minor variations of the model. Recall our running example, with a robot that navigates a grid-world where the rock’s location is unknown. Excitingly, rfPG solves it near-optimally with only two memory nodes! You can see the controller below.

By integrating model-based reasoning with learning-based methods, we develop algorithms for systems that account for uncertainty rather than ignore it. While the results are promising, they come from simulated domains with discrete spaces; real-world deployment will require handling the continuous nature of various problems. Still, it’s practically relevant for high-level decision-making and trustworthy by design. In the future, we will scale up — for example, by using neural networks — and aim to handle broader classes of variations in the model, such as distributions over the unknowns.
Want to know more?
Thank you for reading! I hope you found it interesting and got a sense of our work. You can find out more about my work on marisgg.github.io and about our research group at ai-fm.org.
This blog post is based on the following IJCAI 2025 paper:
- Maris F. L. Galesloot, Roman Andriushchenko, Milan Češka, Sebastian Junges, and Nils Jansen: “Robust Finite-Memory Policy Gradients for Hidden-Model POMDPs”. In IJCAI 2025, pages 8518–8526.
For more on the techniques we used from the tool PAYNT and, more generally, about using these techniques to compute FSCs, see the paper below:
- Roman Andriushchenko, Milan Češka, Filip Macák, Sebastian Junges, Joost-Pieter Katoen: “An Oracle-Guided Approach to Constrained Policy Synthesis Under Uncertainty”. In JAIR, 2025.
If you’d like to learn more about another way of handling model uncertainty, have a look at our other papers as well. For instance, in our ECAI 2025 paper, we design robust controllers using recurrent neural networks (RNNs):
- Maris F. L. Galesloot, Marnix Suilen, Thiago D. Simão, Steven Carr, Matthijs T. J. Spaan, Ufuk Topcu, and Nils Jansen: “Pessimistic Iterative Planning with RNNs for Robust POMDPs”. In ECAI, 2025.
And in our NeurIPS 2025 paper, we study the evaluation of policies:
- Merlijn Krale, Eline M. Bovy, Maris F. L. Galesloot, Thiago D. Simão, and Nils Jansen: “On Evaluating Policies for Robust POMDPs”. In NeurIPS, 2025.

