Multiple swimming robots able to create a vortex for transportation of microplastics
General Purpose Programming Languages Are the Future for the Industrial Automation Industry and Are Overtaking Traditional PLC IEC 61131-3
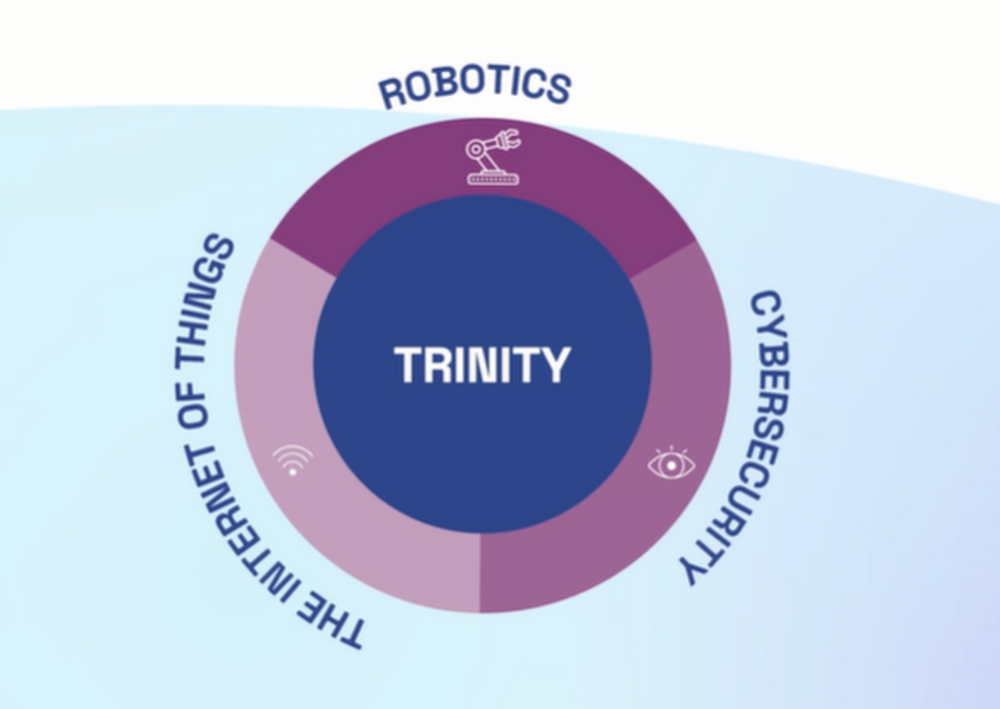
TRINITY, the European network for Agile Manufacturing

The fast-changing customer demands in modern society seek flexibility, innovation and a rapid response from manufacturers and organisations that, in order to respond to market needs, are creating tools and processes in order to adopt an approach that welcomes change.
That approach is found to be Agile Manufacturing – and the Trinity project is the magnet that connects every segment of agile with everyone involved, creating a network that supports people, organisations, production and processes.
The main objective of TRINITY is to create a network of multidisciplinary and synergistic local digital innovation hubs (DIHs) composed of research centres, companies, and university groups that cover a wide range of topics that can contribute to agile production: advanced robotics as the driving force and digital tools, data privacy and cyber security technologies to support the introduction of advanced robotic systems in the production processes.
Trinity network
The Trinity project is funded by Horizon 2020 the European Union research and innovation programme.
Currently, Trinity brings together a network of 16 Digital Innovation Hubs (DIHs) and so far has 37 funded projects with 8.1 million euros in funding.
The network starts its operation by developing demonstrators in the areas of robotics it identified as the most promising to advance agile production, e.g. collaborative robotics including sensory systems to ensure safety, effective user interfaces based on augmented reality and speech, reconfigurable robot workcells and peripheral equipment (fixtures, jigs, grippers, …), programming by demonstration, IoT, secure wireless networks, etc.
These demonstrators will serve as a reference implementation for two rounds of open calls for application experiments, where companies with agile production needs and sound business plans will be supported by TRINITY DIHs to advance their manufacturing processes.
Trinity services
Besides technology-centred services, primary laboratories with advanced robot technologies and know-how to develop innovative application experiments, the TRINITY network of DIHS also offers training and consulting services, including support for business planning and access to financing.
All the data (including the current network list with partners, type of organisation and contact information) is available to everybody searching for the right type of help and guidance. The list also contains information regarding the Trinity funded projects and can be found on the website.
Robotics solution catalogue
Discover a wide range of Trinity solutions – from use cases like Predictable bin picking of shafts and axles, Robotic solution for accurate grinding of complex metal parts, End-to-end automatic handling of small packages and many more, to modules such are Additive TiG welding, Depth-sensor Safety Model for HRC, Environment Detection, Mobile Robot Motion Control and other, all that can be found in robotics solution catalogue on Trinity website.
Each of the solutions is followed up by a video that shows what made them successful, so whether it‘s about catalogue, modules, training materials, SME results, webinars or Trinity-related topics, the Trinity YouTube channel is where you will find it all.
Join us
Trinity wants to expand its current community made of more than 90 SMEs and around 20 organisations. If you are a Digital Innovation Hub, an innovative SME, a technical university, or a research centre focused on agile manufacturing, do not hesitate to contact us and exploit all the opportunities that Trinity offers.
You will be on board an ecosystem full of sectoral industry experts, facilities to put in practice your innovative ideas, and several partners with whom to develop new projects. Everything is on a user-centric platform and you will receive continuous support from the community!
Discuss with us
Be a part of the Trinity world by joining in on the discussions on agile production on social media or stay in touch with the latest news by signing in for the newsletter or simply by visiting the Trinity website.
Whatever your preferred type of communication is, all the contact information can be found here – so let‘s stay in touch!
Fighting tumours with magnetic bacteria
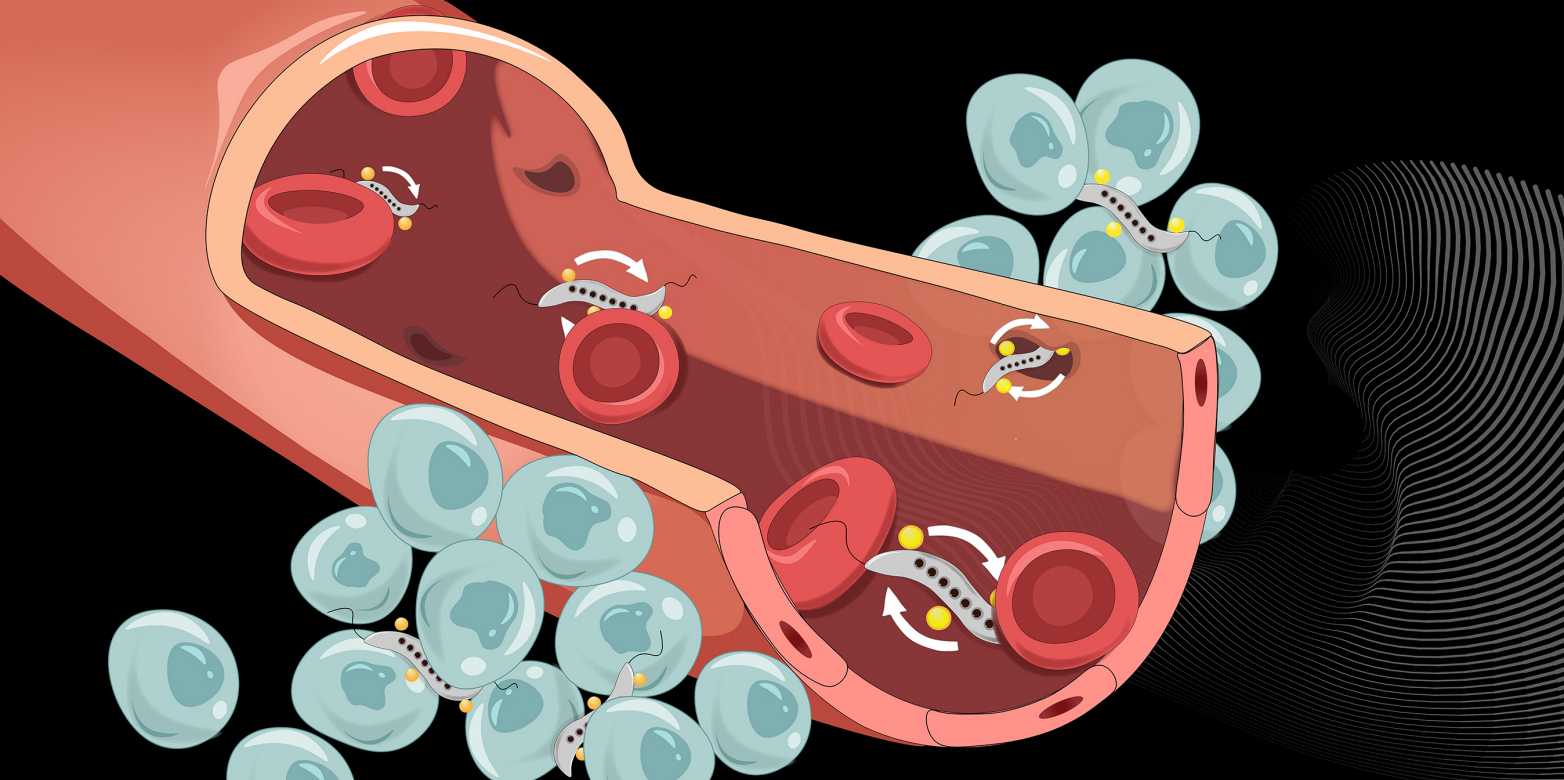
Magnetic bacteria (grey) can squeeze through narrow intercellular spaces to cross the blood vessel wall and infiltrate tumours. (Visualisations: Yimo Yan / ETH Zurich)
By Fabio Bergamin
Scientists around the world are researching how anti-cancer drugs can most efficiently reach the tumours they target. One possibility is to use modified bacteria as “ferries” to carry the drugs through the bloodstream to the tumours. Researchers at ETH Zurich have now succeeded in controlling certain bacteria so that they can effectively cross the blood vessel wall and infiltrate tumour tissue.
Led by Simone Schürle, Professor of Responsive Biomedical Systems, the ETH Zurich researchers chose to work with bacteria that are naturally magnetic due to iron oxide particles they contain. These bacteria of the genus Magnetospirillum respond to magnetic fields and can be controlled by magnets from outside the body; for more on this, see an earlier article in ETH News.
Exploiting temporary gaps
In cell cultures and in mice, Schürle and her team have now shown that a rotating magnetic field applied at the tumour improves the bacteria’s ability to cross the vascular wall near the cancerous growth. At the vascular wall, the rotating magnetic field propels the bacteria forward in a circular motion.
To better understand the mechanism to cross the vessel wall works, a detailed look is necessary: The blood vessel wall consists of a layer of cells and serves as a barrier between the bloodstream and the tumour tissue, which is permeated by many small blood vessels. Narrow spaces between these cells allow certain molecules from the to pass through the vessel wall. How large these intercellular spaces are is regulated by the cells of the vessel wall, and they can be temporarily wide enough to allow even bacteria to pass through the vessel wall.
Strong propulsion and high probability
With the help of experiments and computer simulations, the ETH Zurich researchers were able to show that propelling the bacteria using a rotating magnetic field is effective for three reasons. First, propulsion via a rotating magnetic field is ten times more powerful than propulsion via a static magnetic field. The latter merely sets the direction and the bacteria have to move under their own power.
The second and most critical reason is that bacteria driven by the rotating magnetic field are constantly in motion, travelling along the vascular wall. This makes them more likely to encounter the gaps that briefly open between vessel wall cells compared to other propulsion types, in which the bacteria’s motion is less explorative. And third, unlike other methods, the bacteria do not need to be tracked via imaging. Once the magnetic field is positioned over the tumour, it does not need to be readjusted.
“Cargo” accumulates in tumour tissue
“We make use of the bacteria’s natural and autonomous locomotion as well,” Schürle explains. “Once the bacteria have passed through the blood vessel wall and are in the tumour, they can independently migrate deep into its interior.” For this reason, the scientists use the propulsion via the external magnetic field for just one hour – long enough for the bacteria to efficiently pass through the vascular wall and reach the tumour.
Such bacteria could carry anti-cancer drugs in the future. In their cell culture studies, the ETH Zurich researchers simulated this application by attaching liposomes (nanospheres of fat-like substances) to the bacteria. They tagged these liposomes with a fluorescent dye, which allowed them to demonstrate in the Petri dish that the bacteria had indeed delivered their “cargo” inside the cancerous tissue, where it accumulated. In a future medical application, the liposomes would be filled with a drug.
Bacterial cancer therapy
Using bacteria as ferries for drugs is one of two ways that bacteria can help in the fight against cancer. The other approach is over a hundred years old and currently experiencing a revival: using the natural propensity of certain species of bacteria to damage tumour cells. This may involve several mechanisms. In any case, it is known that the bacteria stimulate certain cells of the immune system, which then eliminate the tumour.
“We think that we can increase the efficacy of bacterial cancer therapy by using a engineering approach.”
– Simone Schürle
Multiple research projects are currently investigating the efficacy of E. coli bacteria against tumours. Today, it is possible to modify bacteria using synthetic biology to optimise their therapeutic effect, reduce side effects and make them safer.
Making non-magnetic bacteria magnetic
Yet to use the inherent properties of bacteria in cancer therapy, the question of how these bacteria can reach the tumour efficiently still remains. While it is possible to inject the bacteria directly into tumours near the surface of the body, this is not possible for tumours deep inside the body. That is where Professor Schürle’s microrobotic control comes in. “We believe we can use our engineering approach to increase the efficacy of bacterial cancer therapy,” she says.
E. coli used in the cancer studies is not magnetic and thus cannot be propelled and controlled by a magnetic field. In general, magnetic responsiveness is a very rare phenomenon among bacteria. Magnetospirillum is one of the few genera of bacteria that have this property.
Schürle therefore wants to make E. coli bacteria magnetic as well. This could one day make it possible to use a magnetic field to control clinically used therapeutic bacteria that have no natural magnetism.
‘Butterfly bot’ is fastest swimming soft robot yet
Mouser Gives a Closer Look at Autonomous Mobile Robots in New Installment of Empowering Innovation Together
Soft skills: Researchers invent robotic droplet manipulators for hazardous liquid cleanup
3D-printing microrobots with multiple component modules inside a microfluidic chip
Subsea Technologies: Optical Components in Deep Waters
Combating climate change with a soft robotics fish

Growing up in Rhode Island (the Ocean State), I lived very close to the water. Over the years, I have seen the effects of sea level rise and rapid erosion. Entire houses and beaches have slowly been consumed by the tide. I have witnessed first hand how climate change is rapidly changing the ocean ecosystem. Sometimes I feel overwhelmed by the inexorability of climate change. What can we do in the face of such a global, almost incomprehensible dilemma? The only way I can overcome this perception is by committing to doing something with my life to help, even if it’s in a small way. I think with such a big issue, the only way forward is by starting small, identifying one niche I can work in, and seeing how I can shape my research around solving that challenge.
One major challenge is rapid global ocean temperature rise. When scientists look to make climate associations using temperature data, they generally use fixed temperature loggers attached to buoys or on the ocean floor. Unfortunately, this approach discounts the area between the ocean’s surface and floor. Variable ocean conditions create microclimates, pockets of the ocean that are unaffected by general climate trends. Scientists have shown that most organisms experience climate change via these microclimates. Fish are greatly affected by this rapid increase in temperature as they can only lay eggs in a minimal range of temperatures. Microclimates are changing temperature with celerity. Hence, many species cannot adapt quickly enough to survive. At this rate, 60% of fish species could go extinct by 2100.
Of course, fish are not the only organisms affected by the rapid increase in temperature. Coral in the Great Barrier Reef can only survive in a minimal temperature threshold, and as temperature increases, reefs are experiencing mass coral bleaching. AIMS, the Australian Institute for Marine Science, the government agency that monitors the Great Barrier Reef, utilizes divers pulled behind boats to record reef observations and collect data. Unfortunately, this has led to some casualties due to shark attacks. They have begun deploying large, almost seven feet in length, ocean gliders that can mitigate this risk. These robots come with a hefty price tag of $125,000 to $500,000. They are also too large to navigate portions of the reef.
Our solution in the Soft Robotics Lab at Worcester Polytechnic Institute is building a free-swimming (tetherless), biologically inspired robotic fish, funded in part by the National Science Foundation Future of Robots in the Workplace Research and Development Program. Our goal is for the robot to navigate the complex environment of the Great Barrier Reef and record dense three-dimensional temperature data throughout the water column. Moreover, we will use non-hazardous and affordable material for the fish’s body. Since our motivation is to create a tool to use in climate research, a robot that is cheap and easy to manufacture will increase its effectiveness. Our approach is in stark contrast to traditional autonomous underwater vehicles that utilize propellers that are noisy and incongruous to underwater life. We chose to mimic the motion of real fish to reduce the environmental impact of our robot and enable close observation of other real fish.
We are, of course, not the first people to build a robot fish. In 1994, MIT produced the RoboTuna, a fully rigid fish robot, and since then, there have been many different iterations of fish robots. Some have been made of fully rigid materials like the RoboTuna and used motors that run the caudal tail (rear fin) actuation that powers the fish. However, this does not replicate the fluid motion achieved by real fish as they swim. A possible solution would be to use soft materials. Designs using soft materials, up to this point, utilize a silicone, pneumatically or hydraulically actuated tail. Unfortunately, these robots cannot operate in rough environments since any cuts or abrasions to the silicone could cause a leak in the system and lead to a total failure in the actuation of the tail. Other robots have combined the more durable rigid materials, actuated with cables, and then attached a soft silicone end that bends with the force of the water. All these previous robots are difficult to manufacture and require institutional knowledge to recreate.

MIT Robotuna and MIT SOFI robots
We have fabricated a 3D printed, cable-actuated wave spring tail made from soft materials that can drive a small robot fish. The wave spring gives the robot its biologically inspired shape, but it can bend fluidly like the silicone-based robots and real fish. The wave springis entirely 3D printed from a flexible material that is affordable and easy to use. This material and method creates a very soft yet durable robot, withstands harsh treatment, and runs for hundreds of thousands of cycles without any degradation to any of the robot’s systems. The robot sets itself apart by being very easy to assemble, with only a handful of parts, most of which can be 3D printed.
The wave spring itself has a biologically inspired design. Reef fish are morphologically diverse but share a similar body shape which we emulate with a tapered oval design. The wave spring itself is composed of a mesh of diamond-shaped cells that can compress and bend. To restrict our robot to only lateral bending, we added supports down the dorsal and ventral edges of the wave spring.
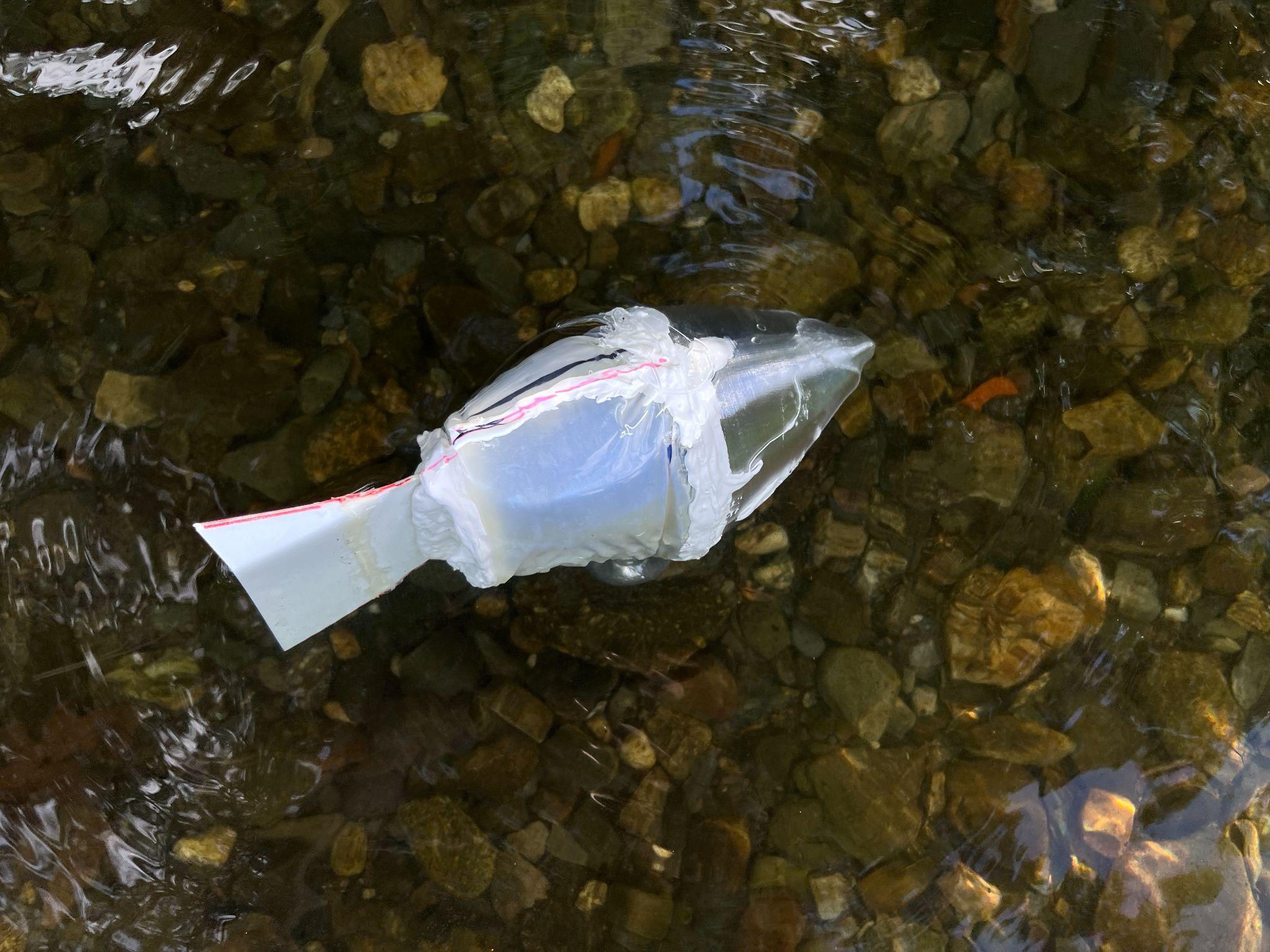

Using this design, we have successfully created a robot fish. The robot is able to swim freely in a fish tank, swimming pool, and in a lake. While testing the fish in these environments, we found that the speed and performance of our robot was comparable to other fish robots operating under similar parameters. In order to waterproof the robot (to protect the electronics required for tetherless swimming), we had to add a latex skin. This does increase the manufacturing complexity of the design, so we will look to improve not only the robot’s performance, but also its design to ensure a simplistic yet high functioning robot.
Most importantly, we will add the sensors required to collect data like temperature, which is imperative to a better understanding of the oceans’ rapidly changing microclimates. It’s crucial that we remain focused on this goal, as it drives not only the robot’s design, but our motivation for why we do this work. Climate change is the foremost crisis facing our world. I encourage everyone to connect their interests and work, no matter the field, in some way to this issue as we are the only ones who can do something about it.
The Ultimate Maintenance Guide For Diesel Engines
Diesel is preferred over gasoline for three primary reasons: better torque output, long-term durability, and fuel economy. Research shows that diesel engines are typically 20%-35% more fuel efficient than similarly sized gasoline engines, allowing diesel cars to travel greater distances on a single fuel tank. However, diesel engines require additional care and maintenance to function...
The post <strong>The Ultimate Maintenance Guide For Diesel Engines</strong> appeared first on 1redDrop.