Coding for underwater robotics
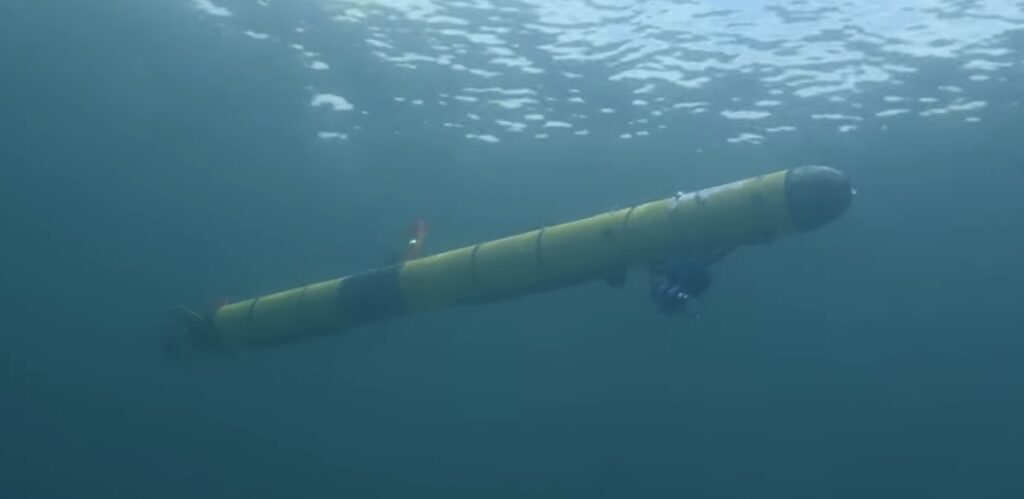 Screenshot from video showing underwater robotic vehicle. Credit: Tim Briggs/MIT Lincoln Laboratory.
Screenshot from video showing underwater robotic vehicle. Credit: Tim Briggs/MIT Lincoln Laboratory.
During a summer internship at MIT Lincoln Laboratory, Ivy Mahncke, an undergraduate student of robotics engineering at Olin College of Engineering, took a hands-on approach to testing algorithms for underwater navigation. She first discovered her love for working with underwater robotics as an intern at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution in 2024. Drawn by the chance to tackle new problems and cutting-edge algorithm development, Mahncke began an internship with Lincoln Laboratory’s Advanced Undersea Systems and Technology Group in 2025.
Mahncke spent the summer developing and troubleshooting an algorithm that would help a human diver and robotic vehicle collaboratively navigate underwater. The lack of traditional localization aids — such as the Global Positioning System, or GPS — in an underwater environment posed challenges for navigation that Mahncke and her mentors sought to overcome. Her work in the laboratory culminated in field tests of the algorithm on an operational underwater vehicle. Accompanying group staff to field test sites in the Atlantic Ocean, Charles River, and Lake Superior, Mahncke had the opportunity see her software in action in the real world.
“One of the lead engineers on the project had split off to go do other work. And she said, ‘Here’s my laptop. Here are the things that you need to do. I trust you to go do them.’ And so I got to be out on the water as not just an extra pair of hands, but as one of the lead field testers,” Mahncke says. “I really felt that my supervisors saw me as the future generation of engineers, either at Lincoln Lab or just in the broader industry.”
Says Madeline Miller, Mahncke’s internship supervisor: “Ivy’s internship coincided with a rigorous series of field tests at the end of an ambitious program. We figuratively threw her right in the water, and she not only floated, but played an integral part in our program’s ability to hit several reach goals.”
Lincoln Laboratory’s summer research program runs from mid-May to August. Applications are now open.
Video by Tim Briggs/MIT Lincoln Laboratory | 2 minutes, 59 seconds
Making Automation Real for Existing Warehouses
Hybrid AI planner turns images into robot action plans
Spatial Intelligence for Next-Generation Indoor Navigation
Poultry processing robotics advances with ChicGrasp
Robot hands so sensitive they can grab a potato chip
Restoring surgeons’ sense of touch with robotic fingertips
By Anthony King
Modern surgery has gone from long incisions to tiny cuts guided by robots and AI. In the process, however, surgeons have lost something vital: the chance to feel inside the body directly. Without palpation, it becomes harder to detect tissue abnormalities during an operation.
A group of surgeons and engineers across Europe is now trying to bring back this vital aspect of surgery.
Working within an EU-funded research collaboration called PALPABLE, they are developing a soft robotic “fingertip” that can sense how firm or soft tissue is during minimally invasive and robotic surgery. The research runs until the end of 2026, with a first prototype expected to be tested by surgeons around March 2026.
By combining optical sensing, soft robotics and AI, the team is designing a probe that mimics the way a fingertip presses and feels during surgery. It would gently probe organs and create a visual map of tissue stiffness, displayed on a screen to guide surgeons as they operate.
Losing the surgeon’s touch
For many surgeons, the loss of direct touch has been one of the quiet trade-offs of modern surgery.
Sooner or later, I believe the vast majority of surgeries will be robotic.
“We started 30 years ago with open surgery and using our fingers,” said Professor Alberto Arezzo from the University of Turin, Italy. He specialises in minimally invasive and robotic surgery and mostly treats patients with colorectal cancer.
“Then we moved into the era of keyhole surgery, which reduced tactile feedback because we began to use long instruments,” he said.
From the 1990s, keyhole surgery became increasingly common, allowing surgeons to operate through small incisions with the help of a camera. Patients benefited from less trauma, shorter hospital stays and faster recovery.
But this came at the expense of physical touch. That matters because tumours often feel different from healthy tissue – stiffer, less pliable or irregular – important differences that experienced hands can detect.
Finding tumour margins
When operating on cancer, surgeons walk a fine line: remove too much tissue and function may suffer; remove too little and cancer may remain, and then spread again, requiring more surgery.
“We don’t want to do that. We want it done in one shot,” said Dr Gadi Marom at Hadassah Medical Centre in Jerusalem, one of the clinicians involved in the research, who specialises in minimally invasive and robotic surgery on patients with stomach and oesophagus diseases.
This is where sensing technology could help. By translating physical contact into visual information, such as a colour-coded map showing softer and firmer areas, surgeons could regain a functional equivalent of touch.
“With a new instrument, we want to be able to determine the margins around a tumour,” said Marom.
Using light to feel
To do that, engineers on the team are turning to light.
The probe they are developing contains fibre-optic cables embedded in a soft, flexible tip. When pressed against tissue, the tip deforms and the light travelling through the fibres changes.
“A silicone dome presses against soft tissue, allowing us to map both the direction and the magnitude of the applied force,” explained Dr Georgios Violakis at Hellenic Mediterranean University in Heraklion, Crete.
Those tiny shifts in light intensity and wavelength are then translated into information about tissue stiffness.
In the lab, the team has already built and calibrated early versions of the soft membrane and light-based sensors, with partners contributing across the system.
Queen Mary University of London (UK) is helping design and refine the membranes, the Fraunhofer Institute (Germany) is developing the functional films, while Bendabl (Greece), Tech Hive Labs (Greece) and the University of Essex (UK) are advancing the software needed to visualise stiffness and tactile maps.
The prototype will be validated in lab tests before it is used on patients.
The bottom line is that we will be able to give better care to our patients.
The fibre‑optic cables are each about the width of a human hair. Similar sensing technology has long been used to detect small movements in large structures such as aircraft, skyscrapers and nuclear reactors. Here it is being applied on a much smaller scale to detect subtle differences in human tissue.
“For touching organs inside an anaesthetised patient, the device needs to be both highly accurate and high resolution,” said Professor Panagiotis Polygerinos, a soft robotics researcher at Hellenic Mediterranean University.
“Something like this might have been possible sooner, but the technology would have been far more expensive and less precise, making it impractical for clinical use.”
Bringing touch to robots
As surgery grows increasingly robotic, the loss of tactile feedback is becoming more pressing – and restoring a sense of touch even more vital.
“When I operate with a robot I have the advantage of 3D vision,” said Marom. “And I don’t have to stand for the entire surgery.” That matters in long procedures, such as removing a patient’s oesophagus, which can take up to eight hours.
Robotic surgery also raises new possibilities. Marom hopes it may eventually allow surgeons, in carefully selected cases, to remove small tumours from the oesophagus without removing the entire organ.
But there is a downside.
“In robotic surgery, tactile feedback is largely absent,” said Arezzo. “That’s why this work is so important.”
Both surgeons believe robotics will continue to expand in operating theatres, but only if surgeons are given better sensory information.
“Sooner or later, I believe the vast majority of surgeries will be robotic,” said Arezzo.
For Marom, working closely with engineers has been essential. “I am exposed to soft robotics and many new technologies,” he said. “I see how new instruments can be developed.”
“The bottom line is that we will be able to give better care to our patients,” he added.
Research in this article was funded by the EU’s Horizon Programme. The views of the interviewees don’t necessarily reflect those of the European Commission. If you liked this article, please consider sharing it on social media.
This article was originally published in Horizon, the EU Research and Innovation magazine.
When Factory Logistics Falls Out of Sync with Production: Three Operational Turning Points in Automotive and Chemical Industries
Sneaker-sized ‘Electronic Dolphin’ robot could transform oil spill cleanup
From games to biology and beyond: 10 years of AlphaGo’s impact
Peak Season is the Lie Detector for Warehouse Robotics
ChatGPT Now Clocking 900 Million Weekly Users
It’s official: 900 million people are now flocking to ChatGPT each week for AI-powered writing, answers, thinking and more.
Most of those people use the free version of ChatGPT, while about 50 million users access the AI via a paid subscription, according to writer Aisha Malik.
Adds Malik: “The new weekly active user figure marks a jump of 100 million users from the 800 million that OpenAI reported in October 2025.”
In other news and analysis in AI writing:
*Meet Your Even Tougher Workplace Competitor: ChatGPT-5.4: OpenAI says its newest AI engine – GPT-5.4 — matches or outperforms many human professionals 83% of the time, according to the maker.
The new model is also more accurate and is 18% less likely to generate errors and 33% less likely to come back with false claims, according to OpenAI.
GPT-5.4 is currently rolling out as ChatGPT-5.4 and is also available via direct computer API access.
*U.S. Military, Government Pivots Away from Anthropic Products: Angry that AI titan Anthropic refused to share full access to its tools for any legal purpose, President Donald Trump has banned use of Anthropic products by the U.S. government.
Observes lead writer Kali Hays: “The company had grown concerned in recent months about the government potentially using its AI tools — like Claude — in what it described as mass surveillance and fully autonomous weapons.”
Claude and similar Anthropic tools are currently the number one choice among many computer coders.
*Hyperlocal Newsletter Firm — Powered by AI — Has a Million Subscribers: Newsletter maker Patch has come up with a new way to hyper-personalize newsletters with AI – even if only one person subscribes.
Observes writer Liz Skalka: “Give the site your zip code and it would produce a daily or twice-weekly newsletter customized for your town, for a minimum readership of one subscriber.
“The newsletters rely heavily on aggregation, automated event calendars and posts from Nextdoor (a hyperlocal social media network).”
*Grammarly Offering ‘Expert Reviews’ of Your Writing – Without Permission From Those Experts: AI proofreading tool Grammarly is now offering free reviews of your writing by prominent virtual academics, authors and similar experts – both living and dead – using AI.
Problem is, none of those experts granted Grammarly permission to use their thinking for such a purpose – which has more than a few people ticked.
Observes writer Miles Klee: “Instead of producing what looks like a generic critique from a nameless LLM, it lists a number of real academics and authors available to weigh in on your text. To be clear: Those people have nothing to do with this process.”
*The More You Chat, The More Errors You Get: New research finds that the more questions you ask in a specific chat, the more likely you’ll encounter errors and hallucinations.
Bottom line: Expect chatbots like ChatGPT-5.0 and newer to lose up to 33% accuracy if you engage in multi-message chats.
Even worse: Expect older AI engines to lose up to 39% accuracy.
*Another AI Tool Promises to Auto-Generate Press Releases: Add ‘Free AI Press Release Generator’ to the growing cadre of tools promising to create press releases for you with AI.
Unlike many AI writing tools, this one focuses entirely on press release writing and follows standard press release form and function developed by journalists.
*AI Agents May Soon Face Special Microsoft Fee: Microsoft is currently mulling adding a special fee for AI agents that use Microsoft products.
Observes writer Richard Speed: “The megacorp is considering a new Microsoft 365 subscription tier, informally dubbed E7, that would bundle Copilot and agent management tools.”
The reasoning: “As AI agents function as digital workers, they need identities, email accounts, Teams access, and policy controls – capabilities currently tied to user subscriptions,” Speed adds.
*Microsoft ‘Copilot Tasks:’ Redmond Takes Another Shot at AI Agents: Microsoft has rolled out a slightly different AI agent for consumer users of Copilot, designed to take a more active role in getting tasks done.
Observes writer Laurent Giret: “Microsoft described the feature as a To-Do list that does itself, done by an AI agent using its own computer and web browser in the background.”
Potential uses include creation of draft email replies each morning, general AI writing, online shopping, event planning, and more.
*Facebook Parent Meta Out With New AI Shopping Assistant: CEO Mark Zuckerberg’s empire has expanded a bit with a new, experimental AI shopping assistant.
Observes writer Mariella Moon: “At the moment, it’s reportedly only showing up on desktop browsers when select users visit Meta AI on the Web.”
Users prompting the assistant for shopping tips get back a virtual carousel of product images and pricing — as well as a link to where they can buy the product.
The AI is also able to customize suggestions based on gender and location if you share that personal data with Meta.

Share a Link: Please consider sharing a link to https://RobotWritersAI.com from your blog, social media post, publication or emails. More links leading to RobotWritersAI.com helps everyone interested in AI-generated writing.
–Joe Dysart is editor of RobotWritersAI.com and a tech journalist with 20+ years experience. His work has appeared in 150+ publications, including The New York Times and the Financial Times of London.
The post ChatGPT Now Clocking 900 Million Weekly Users appeared first on Robot Writers AI.

