Generative AI analyzes medical data faster than human research teams
How to make a cash flow forecasting app work for other systems
Your cash flow forecasting app is working beautifully. Your teams add their own data to keep forecasts running smoothly. Its predictions, tracking variances, and insights seem great.
…Until you take a closer look at the details, and determine that none of these systems actually talk to one another. And that’s a problem.
Consolidating all of that data is time-consuming, burning up hours and creating blind spots, not to mention introducing the likelihood of human error. The best forecasting algorithms are only as good as the data they can access, and siloed systems mean predictions are being made with incomplete information.
The solution is making your existing systems work together intelligently.
By connecting your cash flow forecasting app to your broader tech stack, you can turn data-limited predictions into enterprise-wide intelligence that drives business outcomes.
Key takeaways
- Cash flow forecasts fail when systems stay siloed. ERP, CRM, banking, and payment data must work together or forecasts will always lag behind reality.
- Integration is a data and governance problem, not just a technical one. Inconsistent definitions, latency, and unclear ownership create blind spots that undermine forecast trust.
- AI agents enable real-time, adaptive forecasting across systems. By ingesting data continuously and orchestrating responses, agents turn delayed insights into proactive cash management.
- Unified data models are the foundation of accurate forecasting. Standardizing how transactions, timing, and confidence are defined prevents double-counting and hallucinated cash.
- Explainability is what makes AI forecasts usable in finance. Forecasts must show drivers, confidence ranges, and audit trails to earn CFO and auditor trust.
Why cross-system cash flow forecasting matters
Cash flow data lives everywhere. ERP systems track invoices, CRMs monitor payment patterns, banks process transactions. When these systems don’t talk to each other, neither can your forecasts.
The hidden cost is staggering: teams can spend 50–70% of their time preparing and validating data across systems. That’s at least two days every week spent on manual reconciliation instead of strategic analysis.
Think about what you’re missing. Your ERP shows a $5 million receivable due tomorrow, but your payment processor knows it won’t settle for three days. Your CRM flagged a major customer’s credit deterioration last week, but your forecast still assumes normal payment terms. Your team has to scramble to cover all of these disruptions that integrated systems would have predicted days ago.
The disconnect between these systems means you’re making million-dollar decisions with incomplete information. Invoice timing, settlement patterns, customer behavior, bank account balances, vendor terms. Without connecting this data, you’re forecasting in the dark.
Integrated forecasting transforms cash management from reactive firefighting to proactive optimization. Real-time, cross-system forecasting improves working capital decisions, strengthens liquidity control, and reduces financial risk.
Key challenges of integrating forecasting across multiple platforms
Integration takes technical sophistication and organizational alignment; the challenges that come with this are real enough to derail unprepared teams.
For example:
| Integration challenge | What goes wrong | Real cost to your business | How to fix it |
| Data inconsistencies | Your ERP calls it “payment received,” while your bank says “pending settlement,” with different date formats and three different IDs for the same customer. | 40% of your team’s time is spent on re-mapping data for integration. | Build a single source of truth with canonical data models that translate every system’s quirks into one language. |
| System latency | APIs time out during month-end. Batch jobs run at midnight. By 9 a.m., your “real-time” data is already nine hours old. | Strategic decision-making on stale data. Missed same-day funding opportunities. | Deploy event-driven architecture with smart caching to get updates as they happen, not when they’re scheduled. |
| Legacy limitations | The 2015 ERP has no API. Your finance system exports CSV only. IT says, “Six months to build connectors.” | Teams waste 10+ hours weekly on slicing and dicing manual exports. Automation ROI evaporates. | Start where you can win. Prioritize API-ready systems first, then build bridges for must-have legacy data. |
| Governance gaps | Finance owns GL data. Finance controls bank feeds. Sales guards CRM access. No one agrees on a formal forecast methodology. | Projects stall because different teams produce conflicting forecasts. Executives lose trust in the numbers. | Appoint a forecast owner with cross-functional authority. Document one source-of-truth methodology. |
By combining early ML-driven insights with an iterative approach to data quality and governance, organizations can realize value quickly while continuously enhancing forecasting precision.
The key is to start with the data you have. Even imperfect datasets can be used to build initial models and generate early forecasts, providing value over current manual methods. As integration processes mature through flexible data adapters, event-driven updates, and clear role-based access, forecast accuracy and reliability improve.
Organizations that acknowledge integration complexity and actively build safeguards can avoid the costly missteps that turn promising AI initiatives into expensive operational failures.
How AI agents work under the hood for cash flow forecasting
Forget what you know about “traditional” forecasting models. AI agents are autonomous systems that can learn, adapt, and get smarter every day.
They don’t just crunch numbers. Think of them as three layers working together:
- Data ingestion pulls data from every system (ERP, banks, payment processors) in real time. When your bank API crashes at month-end (and it will at some point), the agent itself keeps running. When payment processors change formats overnight, it adapts automatically.
- The machine learning engine runs multiple forecasting models simultaneously to uncover steady patterns, seasonal swings, and outlier relationships, and picks the winner for each scenario.
- Orchestration makes everything work together. Large payment hits unexpectedly? The system instantly recalculates, updates forecasts, and alerts finance accordingly.
So when a major customer delays a $2 million payment, the finance team knows within minutes, not days. Their AI agent spots the missing transaction, recalculates liquidity needs, and gives them a three-day head start on bridge financing.
These agents also improve upon themselves. Every market surprise or forecast error becomes a lesson that informs the next decision, with each new data source making predictions sharper.
Steps to automate and scale cash forecasting
If you’re ready to build cross-system forecasting capabilities, here’s a step-by-step forecasting process you can follow. It’s designed for organizations that want to move beyond proof-of-concept automated cash flow management.
1. Assess data sources and connectivity
Start by mapping what you actually have. You’ll map the obvious sources, like your ERP and banking platforms. You’ll also want to identify hidden cash flow drivers, like the Excel file that finance updates daily and the subsidiary system installed in 2017.
For each system, answer the following questions:
- Who owns the keys (data access)?
- Can it talk to other systems (API-ready)?
- How fresh is the data (real-time vs. overnight batch)?
- How accurate and complete is the output (rate 1–5)?
- Would bad data derail your forecast (business impact)?
Once you have a complete view of what you’re already working with, start with systems that are API-ready and business-critical. That industry-standard cloud ERP? Perfect. The DOS-based finance system from 1995? Push that to phase two.
2. Define unified data models
Create a unified data model and standard formats that all sources map to. This is important for your integration backbone to maintain consistency, regardless of differences across source systems.
Every transaction, regardless of source, is translated into the same language:
- What: Cash movement type (AR collection, AP payment, transfer)
- When: Standardized ISO-formatted timestamps that match across systems
- How much: Consistent currency and decimal handling (no more penny discrepancies)
- Where: Which account, entity, and business unit, using one naming convention
- Confidence: AI-generated score to keep tabs on how reliable the data is
Skipping this step will likely create downstream issues: your AI agent may hallucinate, predicting phantom cash because it counted the same payment two or three times under different names or IDs.
3. Configure and train AI agents
Start with your two or three best data sources to optimize forecasting with reliable, trusted data.
Give your AI agent enough historical data from those sources to learn your business rhythms. With at least 13 months of data, it should be able to identify patterns like “customers always pay late in December” or “we see a cash crunch every year.”
AI-powered time series modeling adds value through AutoML tests with multiple approaches simultaneously before making its decision:
- ARIMA for steady patterns
- Prophet for seasonal swings
- Neural networks for complex relationships
The best model wins automatically, every time.
During this phase, validate everything. Ruthlessly. Backtest against last year’s actuals. If your model predicts within 5%, that’s a great threshold. If it’s off by 30%, keep training.
4. Monitor and refine forecast accuracy
Far from a one-time project, your AI agent needs to learn from its mistakes. Daily variance analysis shows where predictions fell short of actual results. When accuracy drops below your defined thresholds, say, from 85% to 70%, the system automatically retrains itself on fresh data.
Manual data entry isn’t always a bad thing. Your team’s expertise and overrides are especially valuable, as well. When finance knows that a major customer always pays late in December (despite what the data says), capture that intelligence. Feed it back into the agent to make it smarter.
Measuring adoption rate is also a major driver, especially for scalability: the biggest roadblock is often organizational resistance. Teams wait for perfect data that never comes. Meanwhile, competitors are already optimizing working capital with “good enough” forecasts.
Get stakeholder and organizational buy-in by starting with two departments that are already decently engaged, along with their trusted data. Show accurate improvements in 30–60 days, letting success sell itself — and then scale.
Tips for building trust and explainability in AI forecasts
Your CFO won’t sign off on black box AI that spits out numbers. They need to know why the forecast jumped $2 million overnight.
- Make AI explain itself. When your forecast changes, the system should tell you exactly why. Be specific. For example, “Customer payment patterns shifted 20%, driving a $500K variance.” Every prediction needs a story your team can verify.
- Show confidence, not false precision. Present forecasts with context. For instance, “2.5 million” can be shown as “$2.5 million ± $200K (high confidence)” or “$2.5 million ± $800K (volatile conditions).” The ranges tell finance how much they can relax or if they need to start preparing contingencies.
- Track everything. Every data point, model decision, and human override should be logged and auditable. When auditors ask questions, you’ll have answers. When the model gets something wrong, you’ll know why.
- Let experts override. Your finance team knows your customers and their payment patterns. Allow them to adjust the forecast, but with specific context. That human intelligence makes your AI smarter.
Finance data will never be perfect. But trust in your system is built when it shows its work, calls out uncertainty, and learns from the experts who use it daily.
You can use different explainability approaches for your different audiences:
| Audience | Explainability need | Recommended approach |
| C-suite | High-level confidence and key drivers | Dashboard showing confidence level (“85% sure”) and top three drivers (“Customer delays driving -$500K variance”) |
| Finance | Detailed factor analysis and scenario impacts | Interactive scenario planning with drill-downs: click any number to see specific invoices, customers, and patterns in fluctuations and market conditions |
| Auditors | Audit trails and model governance | Complete audit trail: every data source, timestamp, model version, and human override with documented reasoning |
| IT/data science | Technical model performance and diagnostics | Technical diagnostics: prediction accuracy trends, feature importance scores, model drift alerts, performance metrics |
Common tools and models for end-to-end cash flow management
The build-vs-buy decision for accurate cash flow forecasting software comes down to spending 18 months building with TensorFlow or going live in six weeks with a platform that already works and plugs into the tools you currently use.
What to look for in a forecasting tool stack:
- AI platforms do the heavy lifting, running multiple models, picking winners, and explaining predictions. DataRobot’s enterprise-scale capabilities get you from Excel to AI without hiring a team of data scientists.
- Integration layer (MuleSoft, Informatica) moves data between systems. Pick this layer based on what you already have to avoid adding complexity.
- Visualization (Tableau, Power BI) turns forecasts into decisions. Leadership can quickly evaluate visual data and make a decision.
Your evaluation criteria checklist:
- Scale: Will it handle 5x or 10x your current volume?
- Compliance: Does it satisfy auditors and regulators?
- Real TCO: Factor in the hidden costs (integration, training, maintenance)
- Speed to value: Weeks, months, or quarters to first forecast?
Smart money leverages existing investments rather than ripping and replacing everything from scratch. Compare platforms that plug into your current stack to deliver value faster.
Transform your cash flow forecasting with production-ready AI
In 2022, AI-driven forecasting in supply chain management reportedly reduced errors by 20–50%. Fast-forward to today’s even more accurate and intelligent agent capabilities, and your cash flow forecasting potential is poised for even greater success:
- Connected data that eliminates blind spots
- Explainable AI that finance teams trust
- Continuous learning that gets smarter every day
- Built-in governance that keeps auditors happy
Better forecasts mean less idle cash and lower financing costs. Basically, improved financial health. Your team stops fighting with spreadsheets and starts preventing problems, while you negotiate from a position of strength because you know precisely when cash hits.
AI agent early adopters are already learning patterns, catching anomalies, and freeing up finance teams to think more strategically. These systems will autonomously predict cash flow, actively manage liquidity, negotiate payment terms, and optimize working capital across global operations.
Learn how DataRobot’s financial services solutionsintegrate with your existing systems and deliver enterprise-grade forecasting that actually works. No rip-and-replace. No multi-year implementations.
FAQs
Why do cash flow forecasting apps struggle to work across systems?
Most forecasting tools rely on partial data from a single source. When ERP, banking, CRM, and payment systems are disconnected, forecasts miss timing delays, customer behavior changes, and real liquidity risks.
How do AI agents improve cross-system cash flow forecasting?
AI agents continuously ingest data from multiple systems, run and select the best forecasting models, and automatically update projections when conditions change. This allows finance teams to react in minutes instead of days.
Do you need perfect data before automating cash flow forecasts?
No. Even imperfect data can deliver better results than manual spreadsheets. The key is starting with trusted, API-ready systems and improving data quality iteratively as integrations mature.
How do finance teams trust AI-generated forecasts?
Trust comes from explainability. The system must show why numbers changed, highlight key drivers, surface confidence ranges, and log every data source, model decision, and human override for auditability.
What platforms support enterprise-grade, integrated forecasting?
Platforms like DataRobot support cross-system integration, AI agent orchestration, explainable forecasting, and built-in governance, helping finance teams scale forecasting without ripping out existing systems.
The post How to make a cash flow forecasting app work for other systems appeared first on DataRobot.
Humanoid home robots are on the market—but do we really want them?
Humanoid robots that ‘catch themselves’ instead of falling: What a new walking algorithm changes
Quantum computer breakthrough tracks qubit fluctuations in real time
Solving Real-World Problems with Robotics That Actually Work
Robot Talk Episode 145 – Robotics and automation in manufacturing, with Agata Suwala

Claire chatted to Agata Suwala from the Manufacturing Technology Centre about leveraging robotics to make manufacturing systems more sustainable.
Agata Suwala is a Technology Manager at the Manufacturing Technology Centre, where she leads cutting-edge work in automation and robotics. With over a decade of experience in R&D, Agata specialises in developing and implementing advanced manufacturing systems—particularly for the aerospace sector—transforming complex, skill-intensive processes through automation. Her recent focus is on enabling the transition to a circular economy by leveraging automation and robotics to create sustainable, scalable technologies.
Reversible, detachable robotic hand redefines dexterity
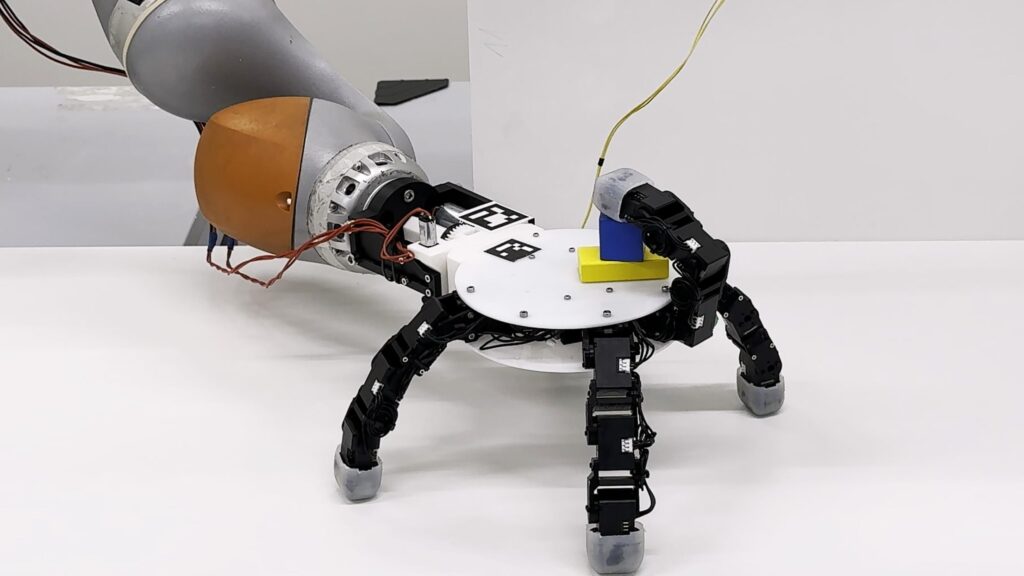 2025 LASA/CREATE/EPFL CC BY SA.
2025 LASA/CREATE/EPFL CC BY SA.
By Celia Luterbacher
With its opposable thumb, multiple joints and gripping skin, human hands are often considered to be the pinnacle of dexterity, and many robotic hands are designed in their image. But having been shaped by the slow process of evolution, human hands are far from optimized, with the biggest drawbacks including our single, asymmetrical thumbs and attachment to arms with limited mobility.
“We can easily see the limitations of the human hand when attempting to reach objects underneath furniture or behind shelves, or performing simultaneous tasks like holding a bottle while picking up a chip can,” says Aude Billard, head of the Learning Algorithms and Systems Laboratory (LASA) in EPFL’s School of Engineering. “Likewise, accessing objects positioned behind the hand while keeping the grip stable can be extremely challenging, requiring awkward wrist contortions or body repositioning.”
A team composed of Billard, LASA researcher Xiao Gao, and Kai Junge and Josie Hughes from the Computational Robot Design and Fabrication Lab designed a robotic hand that overcomes these challenges. Their device, which can support up to six identical silicone-tipped fingers, fixes the problem of human asymmetry by allowing any combination of fingers to form opposing pairs in a thumb-like pinch. Thanks to its reversible design, the ‘back’ and ‘palm’ of the robotic hand are interchangeable. The hand can even detach from its robotic arm and ‘crawl’, spider-like, to grasp and carry objects beyond the arm’s reach.
“Our device reliably and seamlessly performs ‘loco manipulation’ — stationary manipulation combined with autonomous mobility – which we believe has great potential for industrial, service, and exploratory robotics,” Billard summarizes. The research has been published in Nature Communications.
Human applications – and beyond
While the robotic hand looks like something from a futuristic sci-fi movie, the researchers say they drew inspiration from nature.
“Many organisms have evolved versatile limbs that seamlessly switch between different functionalities like grasping and locomotion. For example, the octopus uses its flexible arms both to crawl across the seafloor and open shells, while in the insect world, the praying mantis use specialized limbs for locomotion and prey capture,” Billard says.
Indeed, the EPFL robot can crawl while maintaining a grip on multiple objects, holding them under its ‘palm’, on its ‘back’, or both. With five fingers, the device can replicate most of the traditional human grasps. When equipped with more than five fingers, it can single-handedly tackle tasks usually requiring two human hands – such as unscrewing the cap on a large bottle or driving a screw into a block of wood with a screwdriver.
“There is no real limitation in the number of objects it can hold; if we need to hold more objects, we simply add more fingers,” Billard says.
The researchers foresee applications of their innovative design in real-world settings that demand compactness, adaptability, and multi-modal interaction. For example, the technology could be used to retrieve objects in confined environments or expand the reach of traditional industrial arms. And while the proposed robotic hand is not itself anthropomorphic, they also believe it could be adapted for prosthetic applications.
“The symmetrical, reversible functionality is particularly valuable in scenarios where users could benefit from capabilities beyond normal human function,” Billard says. “For example, previous studies with users of additional robotic fingers demonstrate the brain’s remarkable adaptability to integrate additional appendages, suggesting that our non-traditional configuration could even serve in specialized environments requiring augmented manipulation abilities.”
Reference
A detachable crawling robotic hand, Xiao Gao (高霄), Kunpeng Yao (姚坤鹏), Kai Junge, Josie Hughes & Aude Billard, Nat Commun 17, 428 (2026).