#RoboCup2024 – daily digest: 19 July
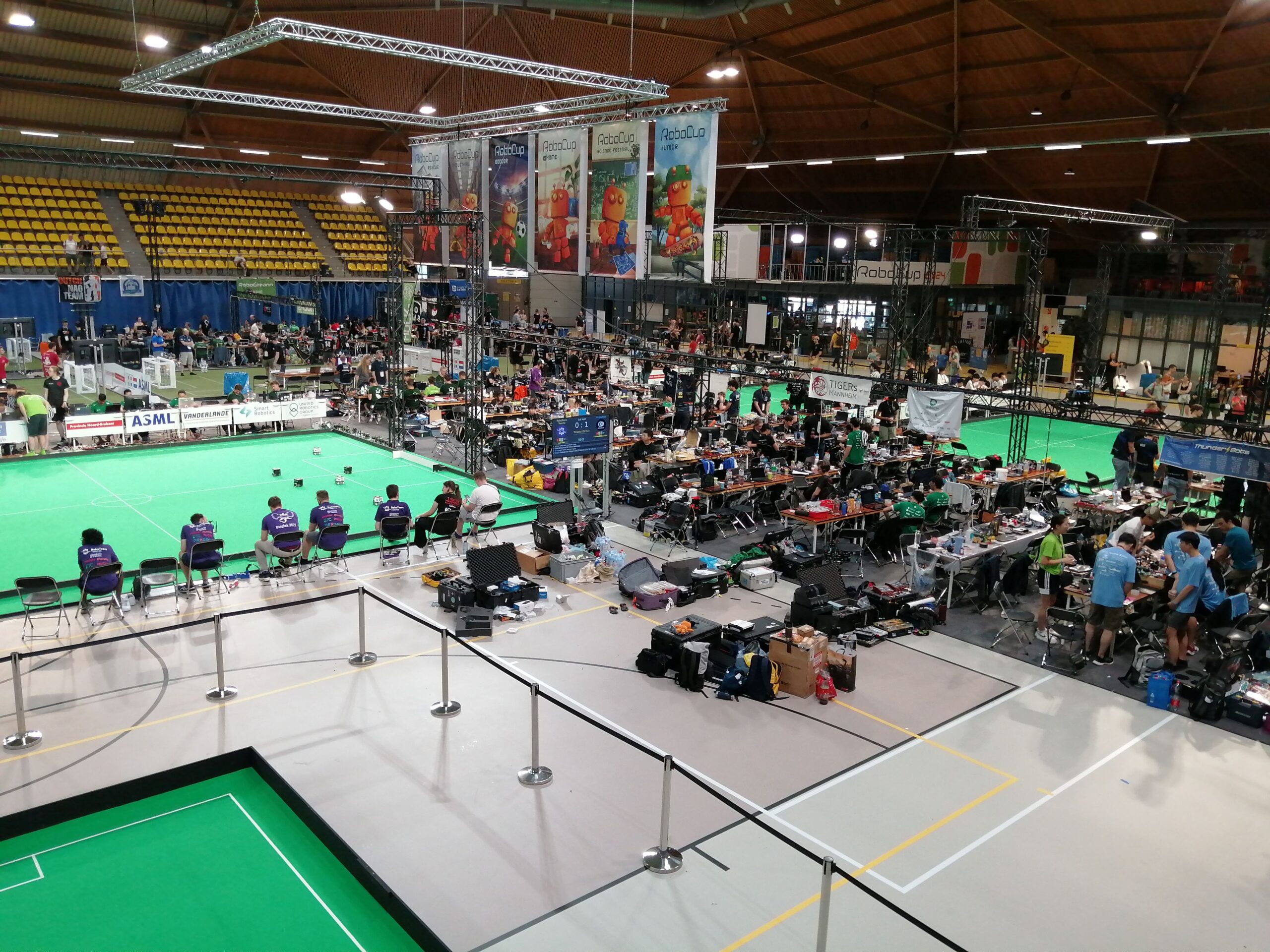 The main soccer arena.
The main soccer arena.
RoboCup is an international scientific initiative with the goal to advance the state of the art of intelligent robots. As part of this initiative, a series of competitions and events are held throughout the year. The main showcase event is an international affair with teams travelling from far and wide to put their machines through their paces.
This year, RoboCup is being held in three arenas in the Genneper Parken, Eindhoven, The Netherlands. The organisers are expecting over 2,000 participants, from 45 different countries, with around 300 teams signed up to take part in the various competitions.
Although RoboCup started out as a football (or soccer) playing competition, other leagues have since been introduced, focussing on robots in industrial, rescue, and home settings. There is even a dedicated league for young roboticists – RoboCupJunior – where participants can take part in either football, rescue, or artistic events.
I am lucky enough to be able to attend this year, and, for the next three days, I’ll be bringing you a daily digest of some of the exciting happenings from Eindhoven.
Today, 19 July, sees the competition in full swing. The main soccer arena, boasting multiple pitches, hosts a number of the different leagues which form RoboCupSoccer.
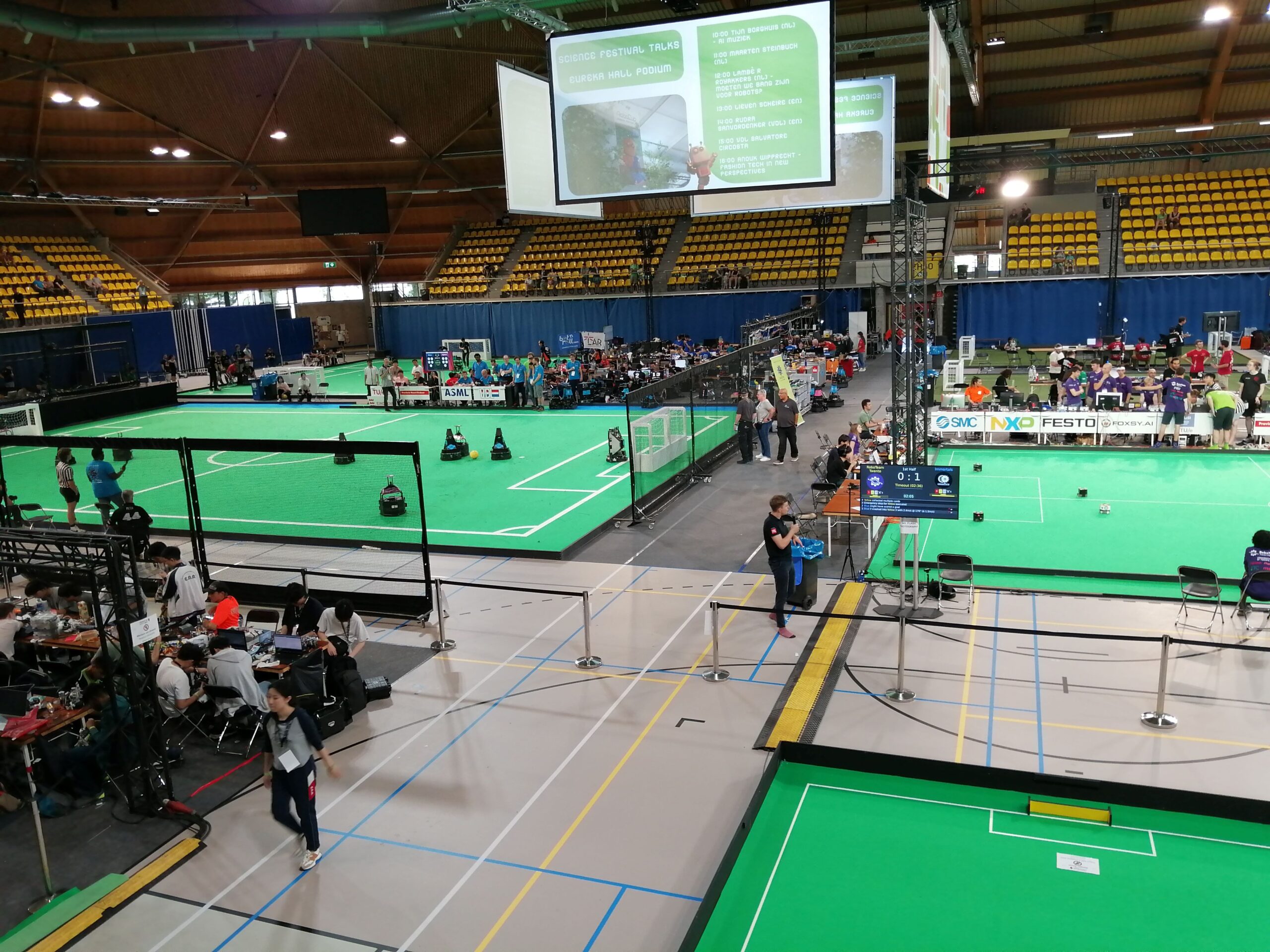 Some of the pitches in the main soccer arena.
Some of the pitches in the main soccer arena.
My first port of call was the Standard Platform League, where the round 5 champions cup match between SPQR Team vs rUNSWift was taking place. SPQR ran out winners and advance to round 6. In this league, all teams compete with identical robots (currently the humanoid NAO by Aldebaran). The robots operate fully autonomously, meaning that there is no external control from neither humans nor computers.
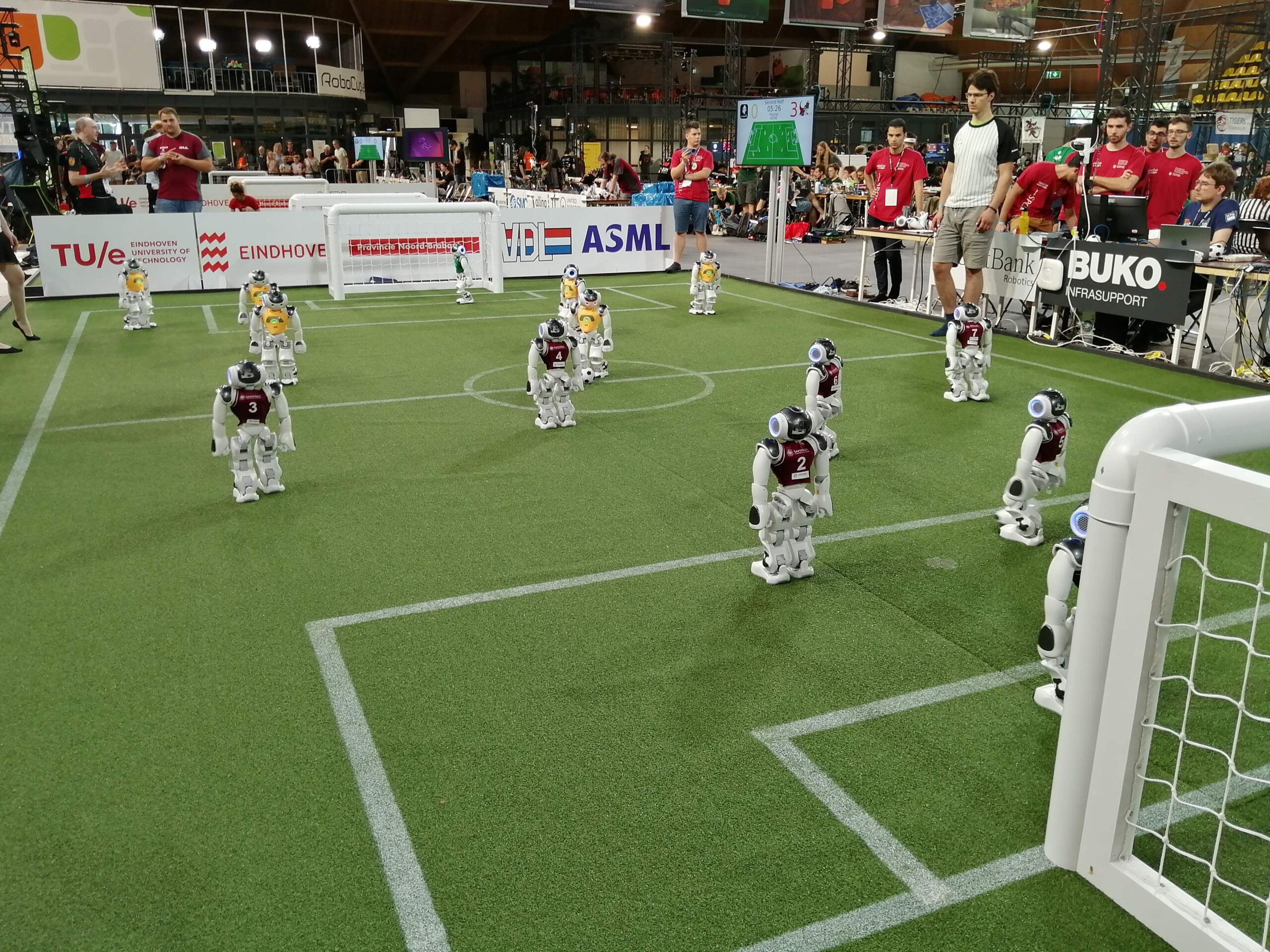 Standard platform league. Round 5 champions cup match between SPQR Team vs rUNSWift.
Standard platform league. Round 5 champions cup match between SPQR Team vs rUNSWift.
Goal! pic.twitter.com/dMfNDUKNZc
— AIhub (@aihuborg) July 19, 2024
The Humanoid AdultSize league is arguably the most challenging of the leagues, with many constraints placed on the robots to make them as human-like as possible. For example, they must have roughly human-like body proportions, they need to walk on two legs, and they are only allowed to use human-like sensors (up to two cameras to sense the environment). In this AdultSize competition, two robots from each team compete, and the team members walk behind the robots to catch them in case of a fall. Such a mishap could prove costly in terms of potential hardware damage.
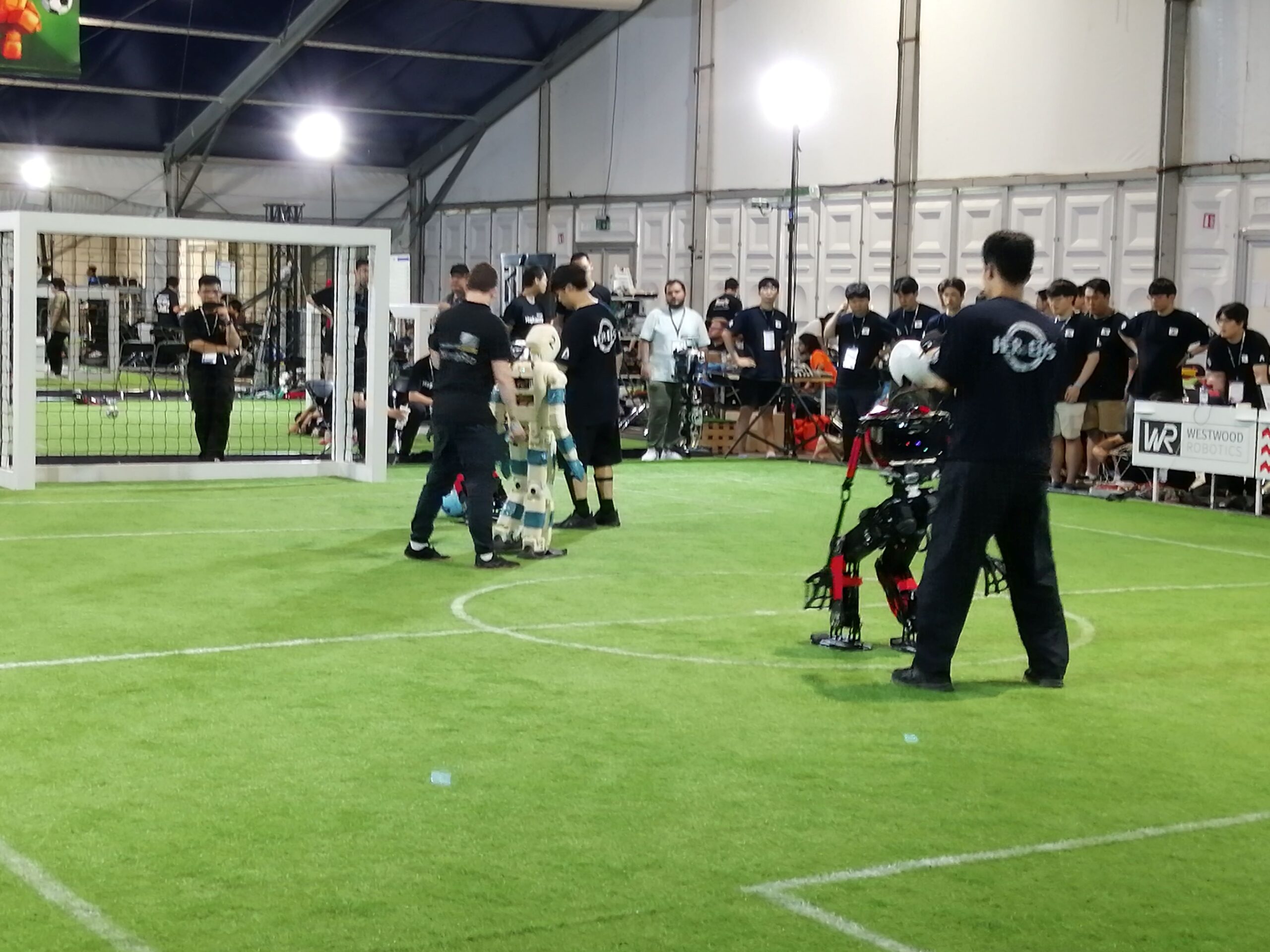 Action from the Humanoid AdultSize League.
Action from the Humanoid AdultSize League.
The RoboCup Rescue Robot League sees teams developing robotic systems with the goal of enabling emergency responders to perform extremely hazardous tasks from safer stand-off distances. During the competition, teams compete in a round-robin, putting their robots through their paces on a number of different challenges. The leading teams following this initial phase progress to the finals on Sunday. The tasks include navigating in complex environments, opening doors, and sensing. Teams may run the machines completely autonomously, or with some assistive control. More points are awarded for completely autonomous operation.
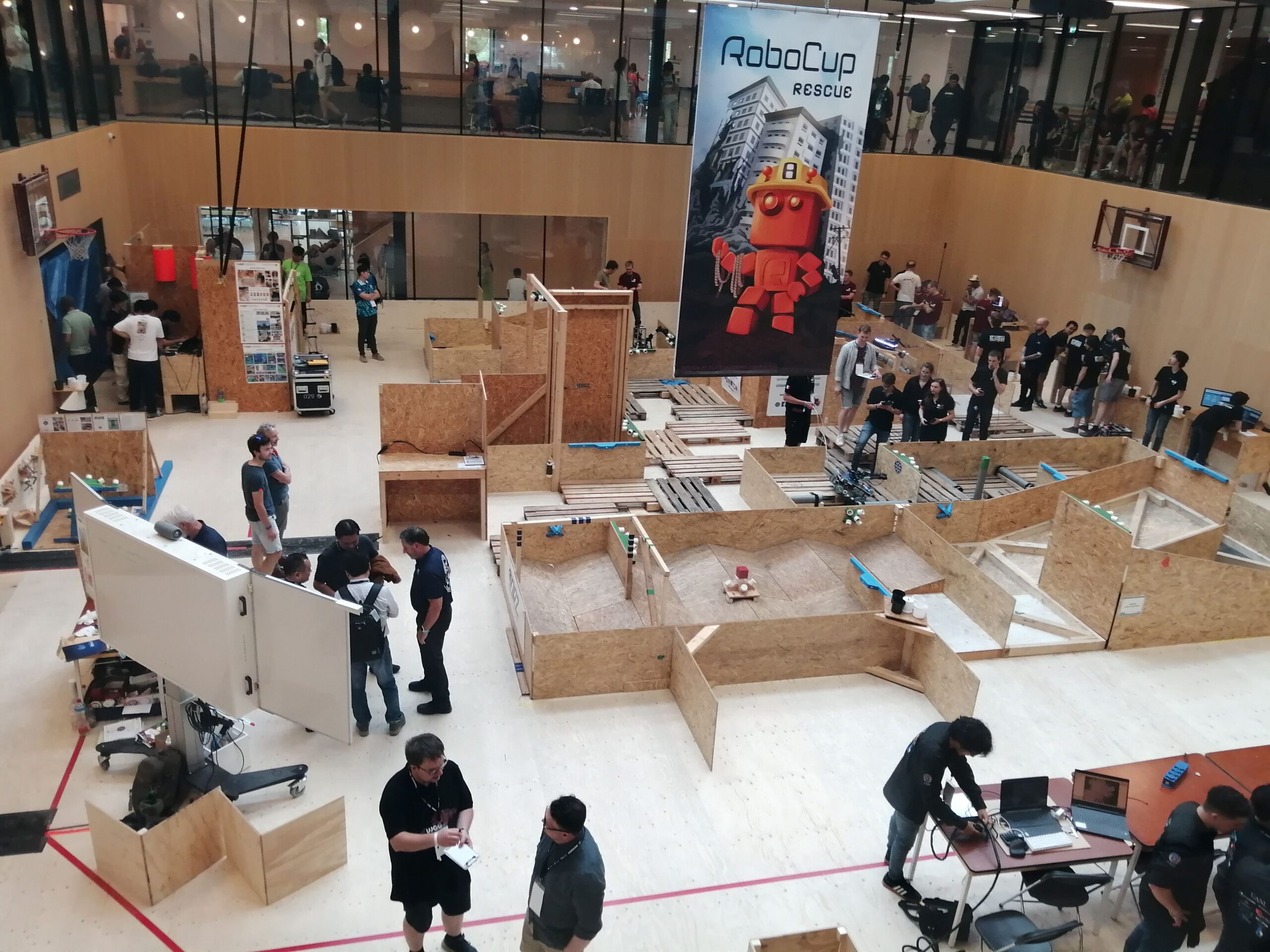 RoboCup Rescue arena from above.
RoboCup Rescue arena from above.
Some action from the @robocup_org #RoboCup2024 Rescue league, where teams compete in a variety of challenges.
Team Hector Darmstadt in the "Obstacles: pallets with pipes" challenge pic.twitter.com/4Ll75uENjM
— AIhub (@aihuborg) July 19, 2024
KMUTNB navigate rough terrain, including gravel and sand pic.twitter.com/rsI7NliEwd
— AIhub (@aihuborg) July 19, 2024
You can keep up with more RoboCup2024 news here.
Researchers use light to control ferrofluid droplet movements in water
IBM Uses AI for the Next Generation of Support
This month, IBM had an interesting briefing on how AI could be used to improve the customer support experience, drive deeper engagement with customers, and effectively improve customer loyalty while dramatically reducing support costs. This sounds unusually good given how […]
The post IBM Uses AI for the Next Generation of Support appeared first on TechSpective.
How a S.E.A of Data Unlocks AI’s Potential in Recruitment
The emergence of artificial intelligence is elevating operational efficiency for organizations worldwide. Conference keynotes and media headlines are dominated by the latest AI advancements, generating intrigue and excitement. While the full potential of AI remains unknown, organizations across all industries […]
The post How a S.E.A of Data Unlocks AI’s Potential in Recruitment appeared first on TechSpective.
New framework allows robots to learn via online human demonstration videos
Google DeepMind at ICML 2024
Can Robotics Truly Drive Down Energy Costs?
Analyzing internal world models of humans, animals and AI
Target’s AI Gamble: Empowering Staff or Replacing Them?
Target’s recent announcement of a chain-wide rollout for their Store Companion chatbot, a GenAI (Generative Artificial Intelligence) tool, has sparked a wave of interest. While the press release (Target Corporation, June 20, 2024) touts benefits like increased efficiency and improved support for team members, some industry watchers are raising questions about the potential impact on...
The post Target’s AI Gamble: Empowering Staff or Replacing Them? appeared first on 1redDrop.
DataRobot Ranked #1 for Governance Use Case by Gartner®: Inside Our Trusted AI Governance Framework
In today’s rapidly evolving AI landscape, strong governance is more critical than ever as organizations strive to harness the power of AI. Drawing on DataRobot’s ten years of experience in enterprise AI, we have dedicated ourselves to building an AI platform with the highest ranking for Governance Use Case among all 18 recognized vendors by Gartner® in the market and a governance framework that we believe exceeds industry standards.
At DataRobot, we’ve always prioritized establishing a solid AI governance framework that ensures our customers can build, deploy and monitor generative and predictive AI assets with confidence. This framework helps teams maintain the quality and integrity of assets in production which is key in ensuring sustainable value.
We believe this commitment has led us to be ranked the highest in Governance Use Case by Gartner®, with an impressive 4.10 out of 5 governance score. In our opinion, this recognition is a testament to our unwavering dedication to upholding the highest standards of integrity, quality, and transparency across all AI operations.
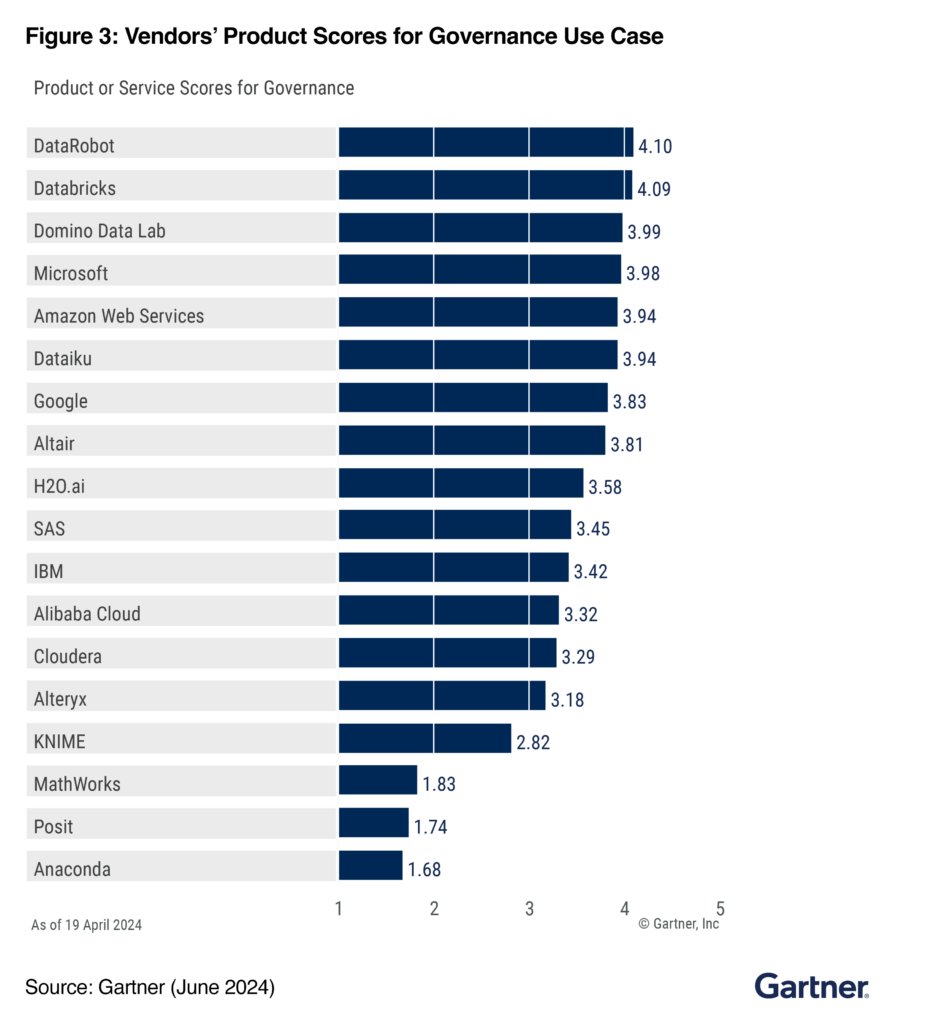
The Growing Need for Strong AI and Data Governance
With the advent of generative AI, the demand for reliable governance has never been stronger or more urgent. As AI continues to become more deeply embedded across all sectors, the potential risks associated with its deployment grow accordingly.
In 2023 alone, the AI industry saw a 40% increase in reported incidents related to data breaches and model bias, highlighting the urgent need for robust governance frameworks. According to a recent survey by PwC, 85% of AI leaders cite governance as their top concern, emphasizing the importance of trust, confidence, and the security of valuable intellectual property.
At DataRobot, our AI governance capabilities are specifically designed to address these critical needs. Our platform provides comprehensive tools and protocols to bridge the confidence gap for our customers.
DataRobot enables the rapid and secure deployment of machine learning and generative AI applications into production within an average timeframe of 2 to 4 weeks. This accelerated deployment is facilitated by features such as automated compliance documentation, real-time risk management, full model transparency, and most importantly strong guards and intervention methods.
This dual focus on governance and speed means that our customers can maintain a competitive advantage in AI without worrying about reputation damage or costly compliance issues.
Key Governance Features that Set DataRobot Apart
AI has always been a team sport, and generative AI has made AI assets more accessible to a broader set of users, increasing the need for collaboration. Meeting high governance standards across all phases of the AI lifecycle — building, testing, production and management — is a must.
DataRobot Governance Umbrella
The DataRobot Governance Umbrella encapsulates our comprehensive approach to governance standards for both ML and GenAI development and management.
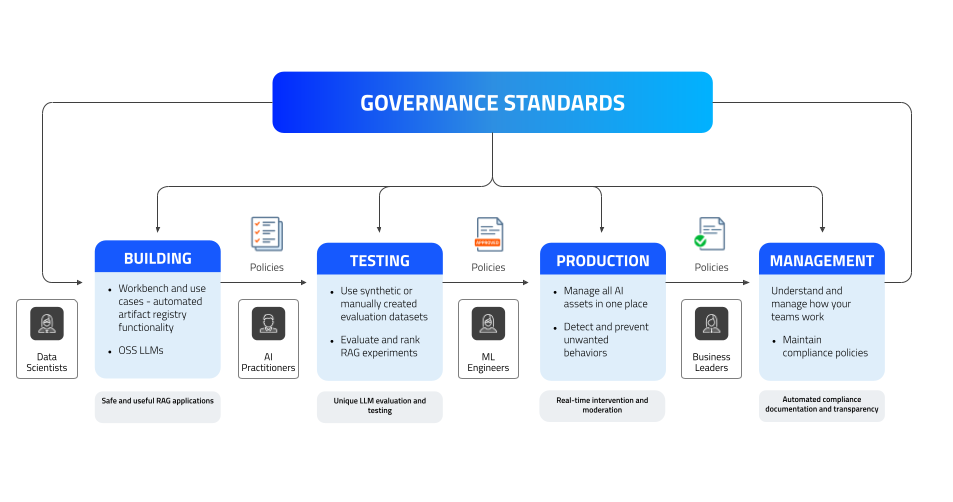
Our AI governance framework is designed to ensure that AI solutions are effective, efficient, and compliant, ultimately ensuring value with AI. It also extends compliance capabilities by ensuring that risk is mitigated across all AI assets throughout the end-to-end AI process:
- Build phase: Data scientists and AI practitioners lay the groundwork for creating robust AI solutions.
- Testing phase: Models undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet our standards and perform reliably under various conditions.
- Production phase: Models are deployed and managed in a live environment.
- Monitoring and management phase: Oversight and governance tools help teams maintain the compliance, integrity and accuracy of AI solutions for operational excellence.
Our framework safeguards AI models and aligns them with operational and compliance goals. To do so, the DataRobot platform offers six unique features that empower each phase in the framework and make DataRobot stand out:
- Visibility and Traceability: Full traceability of data, model lineage and versioning ensures that every change is tracked and documented which makes applications safe and useful.
- Audits and Compliance Documentation: Automated generation of compliance reports and audit trails to meet regulatory requirements and fulfill transparency.
- Unique LLM Evaluation and Testing: Detect potential risks utilizing both synthetic and real datasets to evaluate your predictive and generative AI models and benchmark performance.
- CI/CD Testing: The ability to run prototype testing and evaluate ML or generative solutions with quality metrics to rank RAG experiments.
- Real-time Intervention, Moderation and Alerting: Continuous monitoring with instant notifications and intervention capabilities enabled by guard models and metrics to address issues as they arise.
- AI Catalog: Easily register, track and version all AI assets, whether they were built on or off the DataRobot AI Platform, all through a secure centralized hub.
Secure Collaboration Across Teams
From the build to the management phase, we prioritize data privacy, security, and efficiency as our customers like to move fast.
The Workbench in DataRobot provides an integrated environment for developing AI use cases with features for automated artifact registration for code, prompts, experiments and more. This helps accelerate the creation and iteration of useful AI models without sacrificing safety, or limiting collaboration.
The Registry in DataRobot enables AI practitioners to catalog, version, and govern all AI assets ensuring more control over models. Encryption at rest and the option to bring your own key (BYOK) features ensure that our clients’ information is protected at all times, reinforcing trust and reliability.
Flexibility and Adaptability
The DataRobot AI Platform is one of the most open platforms for AI. We give our users the ultimate control and choice when it comes to their generative AI initiatives. The platform supports custom-built models, third-party APIs, and open source LLMs to prevent vendor lock-in and technical debt, and protect sensitive data.
This flexibility and full governance behind company firewalls ensure that our customers can adapt their AI initiatives to meet evolving business needs with trusted security. Our platform also offers built-in GPU support to accelerate model training and processing, enabling data scientists to handle complex computations promptly.
At DataRobot, we offer equal governance for both predictive and generative AI, ensuring comprehensive oversight and control across all AI models. Our governance framework provides robust tools and protocols, including full model transparency, real-time risk management, and automated compliance documentation. Whether deploying predictive models or generative AI applications, our platform ensures that all AI assets adhere to the highest standards of security, integrity, and accountability. This balanced approach allows our customers to confidently and efficiently manage all of their AI initiatives, knowing that both predictive and generative models are governed with the same level of rigor and precision.
Recognized by Gartner, Trusted by Leaders
Our governance framework has garnered praise from industry analysts, underscoring the real-world value and reliability that our platform provides. In addition to this, DataRobot has also been ranked highest in Governance Use Case by Gartner.
As much as this recognition from Gartner means to us, the most impactful feedback is from our customer community. Their testimonials highlight how our robust governance functionalities have positively impacted their AI initiatives, ensuring safe, successful and confident deployments:
Tom Thomas, VP of Data Strategy, Analytics & Business Intelligence at FordDirect
“DataRobot is an indispensable partner helping us maintain our reputation both internally and externally by deploying, monitoring, and governing generative AI responsibly and effectively.”
Arvind Thinagarajan, VP, Data Science & Analytics at Gannett | USA Today Network
“With DataRobot, we’ve already automated multiple steps in the machine learning lifecycle for hundreds of our models. These are models mostly in the realm of predictive AI as of now. This allows us to create efficiencies and saves time for my team of data scientists with steps like data pre-processing, model building, governance of those models, and measuring the performance of those models. We believe that our partnership can extend to the generative AI realm as well.”
At DataRobot, we are committed to enabling our customers to achieve their goals with confidence and excellence. Our Governance, recognized by Gartner and lauded by our customers, in our opinion, underscores our dedication to providing a reliable, transparent, and accountable AI platform. We are proud to be the trusted choice for organizations seeking to leverage AI responsibly and effectively.
Book a product tour and explore how our AI governance and compliance capabilities help you achieve value rapidly and scale AI use cases effectively.
Gartner Critical CapabilitiesTM for Data Science and Machine Learning Platforms, Machine Learning (ML) Engineering, Afraz Jaffri, Aura Popa, Peter Krensky, Jim Hare, Tong Zhang, Maryam Hassanlou, Raghvender Bhati, Published June 24, 2024.
GARTNER is a registered trademark and service mark of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally, and MAGIC QUADRANT and PEER INSIGHTS are registered trademarks of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates and are used herein with permission. All rights reserved.
Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
This graphic was published by Gartner, Inc. as part of a larger research document and should be evaluated in the context of the entire document. The Gartner document is available upon request from DataRobot.
The post DataRobot Ranked #1 for Governance Use Case by Gartner®: Inside Our Trusted AI Governance Framework appeared first on DataRobot AI Platform.