Top 6 Applications Of AI In Food Processing Industry
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Food Industry
Among all other sectors, the food and beverages processing industry still has not adopted revolutionizing digital technologies like AI, Machine Learning (ML), and Internet-of-Technology (IoT). The sector is progressing slowly and generating fewer contributions to the domestic and national economy.
But, since the past few years, food and beverage processing companies are highly switching to integrate AI capabilities in their systems or applications to enhance work efficiency. According to research reports, it is expected that the food processing industry will create over $150 billion business by the end of 2022 through leveraging AI capabilities.
AI technology will play a crucial role in the future of businesses across all sectors (The Significance Of AI Technology By Industry) and the food processing and handling industry is one of them. The use of Artificial Intelligence in Food Processing has been witnessing rapid growth in recent years.
Food and beverages processing companies are increasingly embracing AI technologies for improving operational efficiencies and delivering consumer products on time to catch up with the market demand opportunities. They are enjoying the benefits of AI in the Food Industry. In this article, we guide you few significant AI use cases in the food and beverages industry.
Recommend To Read: Artificial Intelligence In Agriculture & Food Process
AI Use Cases In Food and Beverages Industry
In this 21st century, modernizing food processing with AI technology is essential to balance the supply and demand, strengthen the distribution network, and build brand reliability on delivering products on time. Because a food processing company has to use AI-like technologies to fasten the production and monitor the entire inventory and warehouse operation virtually to never give a chance for a single disruption across their operations.
This is why AI in food and beverage industry has become a hot topic. Its automation and intelligence capabilities are flagging a green signal for the increasing use of artificial intelligence in the food processing industry.
Let us discuss a few popular applications of AI in food and beverage industry that assist companies in dealing with challenges related to supply, distribution and logistics, employee productivity, and warehouse management like operations.
[contact-form-7]Key Applications Of Artificial Intelligence (AI) In Food Industry
-
AI In Food Industry For Sorting Raw Products
It is the best application of Artificial Intelligence in the Food Industry. Proper sorting of food products is one of the greatest challenges for the consumer products manufacturing facilities because the feedstock we receive from various farmers is not identical or uniform.
Once you have a look at the different fruits & vegetables like carrot, apple, grapes, tomato, orange, and many more will have their shapes and sizes. Food processing plants are required to segregate millions of raw products depending on color, shape, and size. Manual grading, sorting, and peeling-like functions will consume hours of the time of labor. But, the use of Artificial Intelligence in food processing operations will automate all these functions and improve work efficiency. The automation systems use various tools and technologies and offer these benefits:
- Enhancement of speed in sorting.
- Yield improvement
- Minimization of labor costs.
- Reduces wastage and improves production
Hence, food growers, packers, and processors are all using AI and IoT sensor-based advanced equipment and machinery to sort or peel several fresh food products to exploit output and reduce wastage.
For instance, TOMRA is a top sensor-based food processing machine manufacturing company in the world. It offers a range of advanced processing machinery that use AI and are embedded with IoT sensors to improve productivity and save time in sorting, peeling, and other initial operations.
Besides, a Japanese food company is also using TensorFlow machine learning technology to detect the oddities instantly in their diced potatoes. The company found that these AI systems are working more accurately beyond expectations. It became a significant advantage in their production. The company is further planning to expand AI utilization to reap all the benefits of AI in the Food Industry.
Have any AI & ML Project idea visit: Artificial intelligence in Manufacturing
-
AI in Food Industry For Ensuring Personal Hygiene
It is one of the best examples of Artificial Intelligence in the Food Industry. Since we are living in a COVID environment, all employees (who are involved in food processing) need to wear the mask, head caps, and hand gloves to ensure food safety.
As we care about our kitchen, food processing companies will also have to maintain hygiene to ensure the quality of the end products. On the other side, personal and plant hygiene is necessary to make sure that the plant is compliant with the rules and regulations of higher authorities.
The software development companies are making use of AI and ML to develop Facial recognition apps and solutions that monitor employees 24*7 to check whether they are following all hygiene protocols or not.
Hence, AI-powered facial and object recognition software solutions ensure 99.9% of accuracy in monitoring workers in real-time and taking screens of people who violate the safety precautions across the production line.
Recommend to Read: Best Facial Recognition Apps currently available on iOS and Android
-
AI in Food Industry For Decision Making
The role of artificial intelligence in food industry has a high demand for instant decision making and optimizing business results.
AI is not only helping food processing companies in making sorting processes easier and creating the best flavor combinations. The role of AI in food industry is also engaged in assisting food companies in deriving valuable insights into sales and business growth tactics.
For instance, knowing customer taste preferences and producing products that ensure new tastes and match the preferences of consumers are two big deals for food products manufacturing companies.
Here, AI comes into the picture. AI software, coupled with ML and deep learning algorithms, involves extracting useful business insights from vast data input. Based on the data related to the previous product’s demand and ingredients added in it to enrich its flavor, AI applications will create extremely new combinations that enhance the product’s tastes.
Hence, AI in food and beverage industry would help companies take immediate decisions and improve production operations.
-
AI For Faster Equipment Cleaning Process
It is one of the best AI use cases in food and beverages sector. In food processing industries, maintaining proper cleanliness is the most difficult task to handle or deal with.
Most of the food processing companies say they are very much clean like white paper because most of the process involves the automation process. No human labor is involved in the processing.
The method or procedure currently we are following has no sensors by which it cannot see what is happening inside the equipment. Due to this reason, companies are designing the procedure in such a way that it should run as long as required.
Companies are modernizing food processing with AI in many ways. AI-based self-optimizing clean-in-place tools are one of them. For the testing process, it uses optical fluorescence & ultrasonic sensing imaging technologies to know how much microbial debris & food is left in the equipment or inside the device.
Recommend To Read: Top 10 Use Cases Of Artificial Intelligence In The Manufacturing Industry
-
Developing new products
It is a popular application of Artificial Intelligence in food industry. AI in food and beverage industry is gaining popularity for its intelligence in offering the best flavor combinations to increase sales and generate profits for companies.
Since food service industry deals will produce products in various spices, ingredients, and flavors, it is challenging for companies to manufacture products that what customers are exactly looking out for. But, advanced technologies like AI can tackle this with ease. With the help of AI in the production process, food service companies can derive the probability of customer preferences and create taste-rich products for consumers.
Yes. Most of the food processing and packaging industries use AI and produce the best products in the market.
For instance, in the USA, the world’s biggest beverages manufacturer and supplier Coca-Cola has installed self-service soft drink fountains and allowed customers to personalize their drink choice. As per their taste preferences, customers can create thousands of drinks by selecting different flavors to their base flavors.
These fountains are programmed with AI software that can process vast data sets related to consumer taste preferences. Thanks to such advanced AI technology-enabled machines. The core advantage of this AI system is it recommends new flavor combinations and lets customers enjoy a new taste.
6. Streamlining The Supply Chain
It is the best examples of Artificial Intelligence in the food industry. While automating the entire food processing functions, AI technology is widely used for making the supply chain operations compliant with the rules and regulations of the specific authorities.
This AI application for the food processing industry can modernize the supply chain operations and maintain transparency from load pickup and warehouse shifting to distribution.
Here are a few benefits of AI in supply chain management:
- AI ensures high safety across the supply chain
- AI offers a transparent supply chain management system
- Better Inventory management
- Efficient maintenance of warehouse
- Low operational costs
- 100% delivery is as scheduled
- 24/7 product monitoring
- Reduces operational downtime
- Overall, AI augments end-to-end functions
Now, we will have a brief discussion on what challenges are hampering the use and growth of AI in food and beverage industry.
Challenges Of AI In The Food Industry
Though the impact of artificial intelligence in food industry is positive way, the technology is still facing a few challenges to roll out across the global food processing and handling sector. Here are a few challenges of AI in the food industry.
- Lack of proper awareness of implementing the features of AI
- Lack of knowledge on how AI technology improves processes and assists companies in achieving business objectives.
- In the initial phase, companies are facing failures in training the AI machines, systems, and applications with the right set of data.
- Lack of proper training to employees to work along with intelligent and advanced AI applications
- Since the cost of AI implementation and integration is quite expensive, the food processing service companies are going back to adopting AI technologies for automating their processes.
These are a few core challenges of AI in the food industry. To bring a revolution in the growth of AI, the companies need to get advice from the AI development companies. Being the best AI services and solutions provider (USA, India, & UAE), USM Business systems builds an efficient and powerful automation solution for optimizing your food business.
Final Words
The benefits of AI in the Food Industry are incredible. AI will modernize the food processing industry and take it to new heights. The food industry is at its initial phase to completely adopt AI technology.
The top mobile app development service providers would help you create results-driven AI consultancy and app development services and solutions.
Are you looking to integrate AI solutions to automate your food processing and packages business?
Let’s connect with our AI experts & discuss your app idea.
[contact-form-7]
A new robotic gripper made of measuring tape is sizing up fruit and veggie picking
Hopping gives this tiny robot a leg up
Insect-sized jumping robot can traverse challenging terrains and carry heavy payloads
A new robotic gripper made of measuring tape is sizing up fruit and veggie picking
3D-printed open-source robot offers accessible solution for materials synthesis
Engineers bring sign language to ‘life’ using AI to translate in real-time
The enterprise path to agentic AI
TL;DR:
CIOs face mounting pressure to adopt agentic AI — but skipping steps leads to cost overruns, compliance gaps, and complexity you can’t unwind. This post outlines a smarter, staged path to help you scale AI with control, clarity, and confidence.
AI leaders are under immense pressure to implement solutions that are both cost-effective and secure. The challenge lies not only in adopting AI but also in keeping pace with advancements that can feel overwhelming.
This often leads to the temptation to dive headfirst into the latest innovations to stay competitive.
However, jumping straight into complex multi-agent systems without a solid foundation is akin to constructing the upper floors of a building before laying its base, resulting in a structure that’s unstable and potentially hazardous.
In this post, we walk through how to guide your organization through each stage of agentic AI maturity — securely, efficiently, and without costly missteps.
Understanding key AI concepts
Before delving into the stages of AI maturity, it’s essential to establish a clear understanding of key concepts:
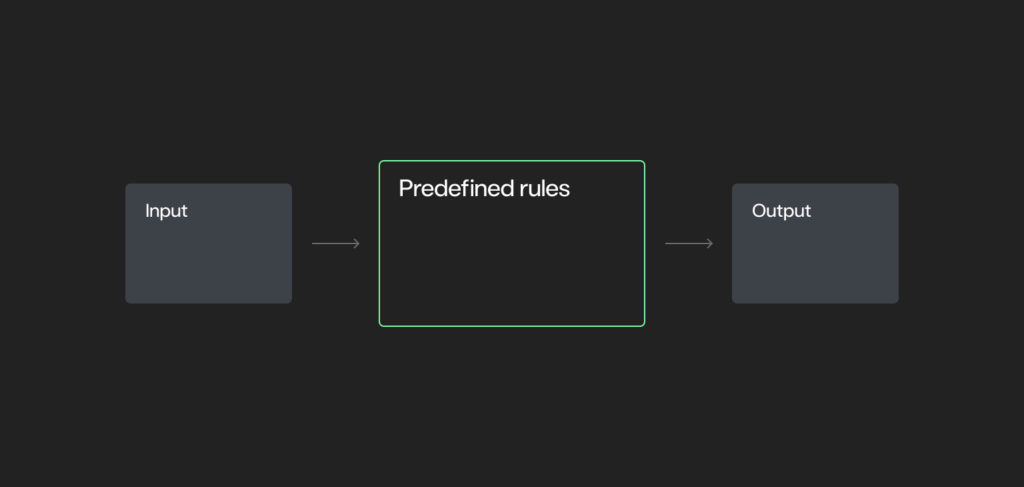
Deterministic systems
Deterministic systems are the foundational building blocks of automation.
- Follow a fixed set of predefined rules where the outcome is fully predictable. Given the same input, the system will always produce the same output.
- Does not incorporate randomness or ambiguity.
- While all deterministic systems are rule-based, not all rule-based systems are deterministic.
- Ideal for tasks requiring consistency, traceability, and control.
- Examples: Basic automation scripts, legacy enterprise software, and scheduled data transfer processes.
Rule-based systems
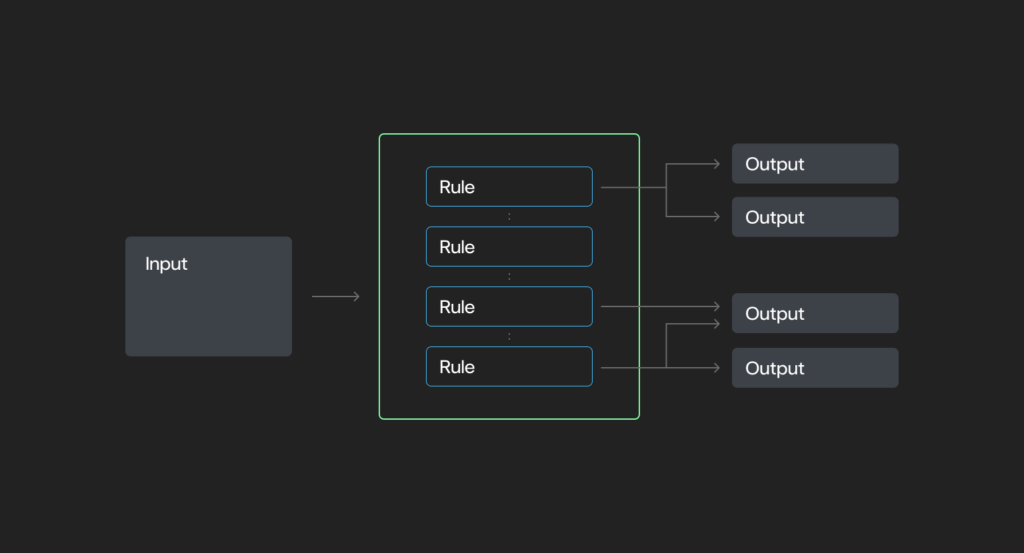
A broader category that includes deterministic systems but can also introduce variability (e.g., stochastic behavior).
- Operate based on a set of predefined conditions and actions — “if X, then Y.”
- May incorporate: deterministic systems or stochastic elements, depending on design.
- Powerful for enforcing structure.
- Lack autonomy or reasoning capabilities.
- Examples: Email filters, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) ) and complex infrastructure protocols like internet routing.
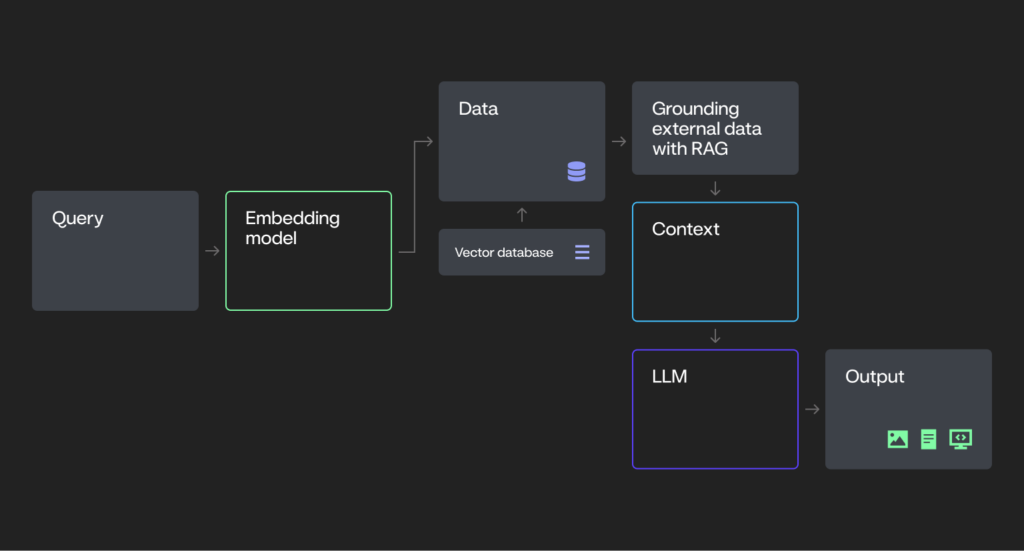
Process AI
A step beyond rule-based systems.
- Powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision-Language Models (VLMs)
- Trained on extensive datasets to generate diverse content (e.g., text, images, code) in response to input prompts.
- Responses are grounded in pre-trained knowledge and can be enriched with external data via techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
- Does not make autonomous decisions — operates only when prompted.
- Examples: Generative AI chatbots, summarization tools, and content-generation applications powered by LLMs.
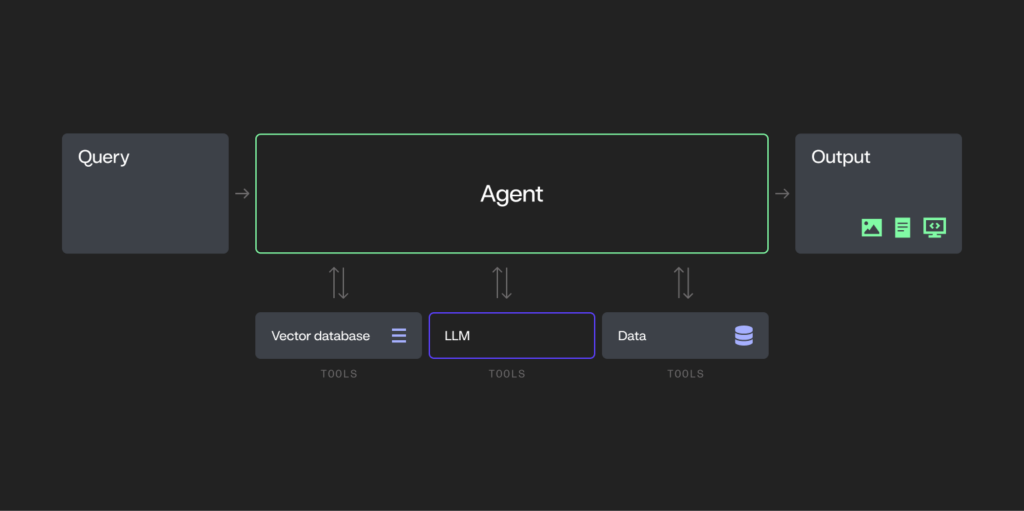
Single-agent systems
Introduce autonomy, planning, and tool usage, elevating foundational AI into more complex territory.
- AI-driven programs designed to perform specific tasks independently.
- Can integrate with external tools and systems (e.g., databases or APIs) to complete tasks.
- Do not collaborate with other agents — operate alone within a task framework.
- Not to be confused with RPA: RPA is ideal for highly standardized, rules-based tasks where logic doesn’t require reasoning or adaptation.
- Examples: AI-driven assistants for forecasting, monitoring, or automated task execution that operate independently.
Multi-agent systems
The most advanced stage, featuring distributed decision-making, autonomous coordination, and dynamic workflows.
- Comprised of multiple AI agents that interact and collaborate to achieve complex objectives.
- Agents dynamically decide which tools to use, when, and in what sequence.
- Capabilities include planning, reflection, memory utilization, and cross-agent collaboration.
- Examples: Distributed AI systems coordinating across departments like supply chain, customer service, or fraud detection.
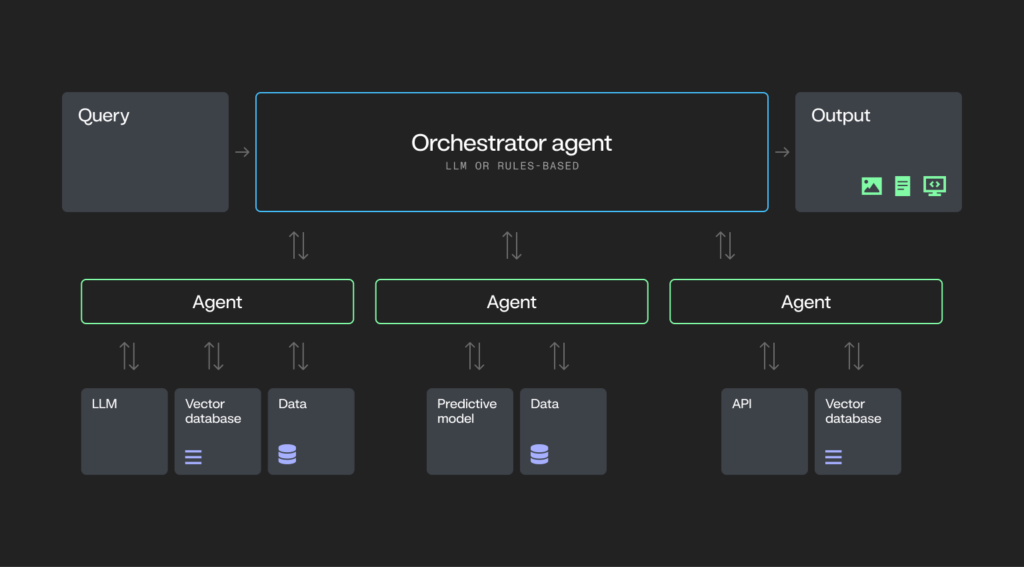
What makes an AI system truly agentic?
To be considered truly agentic, an AI system typically demonstrates core capabilities that enable it to operate with autonomy and adaptability:
- Planning. The system can break down a task into steps and create a plan of execution.
- Tool calling. The AI selects and uses tools (e.g., models, functions) and initiates API calls to interact with external systems to complete tasks.
- Adaptability. The system can adjust its actions in response to changing inputs or environments, ensuring effective performance across varying contexts.
- Memory. The system retains relevant information across steps or sessions.
These characteristics align with widely accepted definitions of agentic AI, including frameworks discussed by AI leaders such as Andrew Ng.
With these definitions in mind, let’s explore the stages required to progress toward implementing multi-agent systems.
Understanding agentic AI maturity stages
For the purposes of simplicity, we’ve delineated the path to more complex agentic flows into three stages. Each stage presents unique challenges and opportunities concerning cost, security, and governance.
Stage 1: Process AI
What this stage looks like
In the Process AI stage, organizations typically pilot generative AI through isolated use cases like chatbots, document summarization, or internal Q&A. These efforts are often led by innovation teams or individual business units, with limited involvement from IT.
Deployments are built around a single LLM and operate outside core systems like ERP or CRM, making integration and oversight difficult.
Infrastructure is often pieced together, governance is informal, and security measures may be inconsistent.
Supply chain example for process AI
In the Process AI stage, a supply chain team might use a generative AI-powered chatbot to summarize shipment data or answer basic vendor queries based on internal documents. This tool can pull in data through a RAG workflow to provide insights, but it does not take any action autonomously.
For example, the chatbot could summarize inventory levels, predict demand based on historical trends, and generate a report for the team to review. However, the team must then decide what action to take (e.g., place restock orders or adjust supply levels).
The system simply provides insights — it doesn’t make decisions or take actions.
Common obstacles
While early AI initiatives can show promise, they often create operational blind spots that stall progress, drive up costs, and increase risk if left unaddressed.
- Data integration and quality. Most organizations struggle to unify data across disconnected systems, limiting the reliability and relevance of generative AI output.
- Scalability challenges. Pilot projects often stall when teams lack the infrastructure, access, or strategy to move from proof of concept to production.
- Inadequate testing and stakeholder alignment. Generative outputs are frequently released without rigorous QA or business user acceptance, leading to trust and adoption issues.
- Change management friction. As generative AI reshapes roles and workflows, poor communication and planning can create organizational resistance.
- Lack of visibility and traceability. Without model tracking or auditability, it’s difficult to understand how decisions are made or pinpoint where errors occur.
- Bias and fairness risks. Generative models can reinforce or amplify bias in training data, creating reputational, ethical, or compliance risks.
- Ethical and accountability gaps. AI-generated content can blur ethical lines or be misused, raising questions around responsibility and control.
- Regulatory complexity. Evolving global and industry-specific regulations make it difficult to ensure ongoing compliance at scale.
Tool and infrastructure requirements
Before advancing to more autonomous systems, organizations must ensure their infrastructure is equipped to support secure, scalable, and cost-effective AI deployment.
- Fast, flexible vector database updates to manage embeddings as new data becomes available.
- Scalable data storage to support large datasets used for training, enrichment, and experimentation.
- Sufficient compute resources (CPUs/GPUs) to power training, tuning, and running models at scale.
- Security frameworks with enterprise-grade access controls, encryption, and monitoring to protect sensitive data.
- Multi-model flexibility to test and evaluate different LLMs and determine the best fit for specific use cases.
- Benchmarking tools to visualize and compare model performance across assessments and testing.
- Realistic, domain-specific data to test responses, simulate edge cases, and validate outputs.
- A QA prototyping environment that supports quick setup, user acceptance testing, and iterative feedback.
- Embedded security, AI, and business logic for consistency, guardrails, and alignment with organizational standards.
- Real-time intervention and moderation tools for IT and security teams to monitor and control AI outputs in real time.
- Robust data integration capabilities to connect sources across the organization and ensure high-quality inputs.
- Elastic infrastructure to scale with demand without compromising performance or availability.
- Compliance and audit tooling that enables documentation, change tracking, and regulatory adherence.
Preparing for the next stage
To build on early generative AI efforts and prepare for more autonomous systems, organizations must lay a solid operational and organizational foundation.
- Invest in AI-ready data. It doesn’t need to be perfect, but it must be accessible, structured, and secure to support future workflows.
- Use vector database visualizations. This helps teams identify knowledge gaps and validate the relevance of generative responses.
- Apply business-driven QA/UAT. Prioritize acceptance testing with the end users who will rely on generative output, not just technical teams.
- Stand up a secure AI registry. Track model versions, prompts, outputs, and usage across the organization to enable traceability and auditing.
- Implement baseline governance. Establish foundational frameworks like role-based access control (RBAC), approval flows, and data lineage tracking.
- Create repeatable workflows. Standardize the AI development process to move beyond one-off experimentation and enable scalable output.
- Build traceability into generative AI usage. Ensure transparency around data sources, prompt construction, output quality, and user activity.
- Mitigate bias early. Use diverse, representative datasets and regularly audit model outputs to identify and address fairness risks.
- Gather structured feedback. Establish feedback loops with end users to catch quality issues, guide improvements, and refine use cases.
- Encourage cross-functional oversight. Involve legal, compliance, data science, and business stakeholders to guide strategy and ensure alignment.
Key takeaways
Process AI is where most organizations begin — but it’s also where many get stuck. Without strong data foundations, clear governance, and scalable workflows, early experiments can introduce more risk than value.
To move forward, CIOs need to shift from exploratory use cases to enterprise-ready systems — with the infrastructure, oversight, and cross-functional alignment required to support safe, secure, and cost-effective AI adoption at scale.
Stage 2: Single-agent systems
What this stage looks like
At this stage, organizations begin tapping into true agentic AI — deploying single-agent systems that can act independently to complete tasks. These agents are capable of planning, reasoning, and calling tools like APIs or databases to get work done without human involvement.
Unlike earlier generative systems that wait for prompts, single-agent systems can decide when and how to act within a defined scope.
This marks a clear step into autonomous operations—and a critical inflection point in an organization’s AI maturity.
Supply chain example for single-agent systems
Let’s revisit the supply chain example. With a single-agent system in place, the team can now autonomously manage inventory. The system monitors real-time stock levels across regional warehouses, forecasts demand using historical trends, and places restock orders automatically via an integrated procurement API—without human input.
Unlike the process AI stage, where a chatbot only summarizes data or answers queries based on prompts, the single-agent system acts autonomously. It makes decisions, adjusts inventory, and places orders within a predefined workflow.
However, because the agent is making independent decisions, any errors in configuration or missed edge cases (e.g., unexpected demand spikes) could result in issues like stockouts, overordering, or unnecessary costs.
This is a critical shift. It’s not just about providing information anymore; it’s about the system making decisions and executing actions, making governance, monitoring, and guardrails more crucial than ever.
Common obstacles
As single-agent systems unlock more advanced automation, many organizations run into practical roadblocks that make scaling difficult.
- Legacy integration challenges. Many single-agent systems struggle to connect with outdated architectures and data formats, making integration technically complex and resource-intensive.
- Latency and performance issues. As agents perform more complex tasks, delays in processing or tool calls can degrade user experience and system reliability.
- Evolving compliance requirements. Emerging regulations and ethical standards introduce uncertainty. Without robust governance frameworks, staying compliant becomes a moving target.
- Compute and talent demands. Running agentic systems requires significant infrastructure and specialized skills, putting pressure on budgets and headcount planning.
- Tool fragmentation and vendor lock-in. The nascent agentic AI landscape makes it hard to choose the right tooling. Committing to a single vendor too early can limit flexibility and drive up long-term costs.
- Traceability and tool call visibility. Many organizations lack the necessary level of observability and granular intervention required for these systems. Without detailed traceability and the ability to intervene at a granular level, systems can easily run amok, leading to unpredictable outcomes and increased risk.
Tool and infrastructure requirements
At this stage, your infrastructure needs to do more than just support experimentation—it needs to keep agents connected, running smoothly, and operating securely at scale.
- Integration platform with tools that facilitate seamless connectivity between the AI agent and your core business systems, ensuring smooth data flow across environments.
- Monitoring systems designed to track and analyze the agent’s performance and outcomes, flag issues, and surface insights for ongoing improvement.
- Compliance management tools that help enforce AI policies and adapt quickly to evolving regulatory requirements.
- Scalable, reliable storage to handle the growing volume of data generated and exchanged by AI agents.
- Consistent compute access to keep agents performing efficiently under fluctuating workloads.
- Layered security controls that protect data, manage access, and maintain trust as agents operate across systems.
- Dynamic intervention and moderation that can understand processes aren’t adhering to policies, intervene in real-time and send alerts for human intervention.
Preparing for the next stage
Before layering on additional agents, organizations need to take stock of what’s working, where the gaps are, and how to strengthen coordination, visibility, and control at scale.
- Evaluate current agents. Identify performance limitations, system dependencies, and opportunities to improve or expand automation.
- Build coordination frameworks. Establish systems that will support seamless interaction and task-sharing between future agents.
- Strengthen observability. Implement monitoring tools that provide real-time insights into agent behavior, outputs, and failures at the tool level and the agent level.
- Engage cross-functional teams. Align AI goals and risk management strategies across IT, legal, compliance, and business units.
- Embed automated policy enforcement. Build in mechanisms that uphold security standards and support regulatory compliance as agent systems expand.
Key takeaways
Single-agent systems offer significant capability by enabling autonomous actions that enhance operational efficiency. However, they often come with higher costs compared to non-agentic RAG workflows, like those in the process AI stage, as well as increased latency and variability in response times.
Since these agents make decisions and take actions on their own, they require tight integration, careful governance, and full traceability.
If foundational controls like observability, governance, security, and auditability aren’t firmly established in the process AI stage, these gaps will only widen, exposing the organization to greater risks around cost, compliance, and brand reputation.
Stage 3: Multi-agent systems
What this stage looks like
In this stage, multiple AI agents work together — each with its own task, tools, and logic — to achieve shared goals with minimal human involvement. These agents operate autonomously, but they also coordinate, share information, and adjust their actions based on what others are doing.
Unlike single-agent systems, decisions aren’t made in isolation. Each agent acts based on its own observations and context, contributing to a system that behaves more like a team, planning, delegating, and adapting in real time.
This kind of distributed intelligence unlocks powerful use cases and massive scale. But as one can imagine, it also introduces significant operational complexity: overlapping decisions, system interdependencies, and the potential for cascading failures if agents fall out of sync.
Getting this right demands strong architecture, real-time observability, and tight controls.
Supply chain example for multi-agent systems
In earlier stages, a chatbot was used to summarize shipments and a single-agent system was deployed to automate inventory restocking.
In this example, a network of AI agents are deployed, each specializing in a different part of the operation, from forecasting and video analysis to scheduling and logistics.
When an unexpected shipment volume is forecasted, agents kick into action:
- A forecasting agent projects capacity needs.
- A computer vision agent analyzes live warehouse footage to find underutilized space.
- A delay prediction agent taps time series data to anticipate late arrivals.
These agents communicate and coordinate in real time, adjusting workflows, updating the warehouse manager, and even triggering downstream changes like rescheduling vendor pickups.
This level of autonomy unlocks speed and scale that manual processes can’t match. But it also means one faulty agent — or a breakdown in communication — can ripple across the system.
At this stage, visibility, traceability, intervention, and guardrails become non-negotiable.
Common obstacles
The shift to multi-agent systems isn’t just a step up in capability — it’s a leap in complexity. Each new agent added to the system introduces new variables, new interdependencies, and new ways for things to break if your foundations aren’t solid.
- Escalating infrastructure and operational costs. Running multi-agent systems is expensive—especially as each agent drives additional API calls, orchestration layers, and real-time compute demands. Costs compound quickly across multiple fronts:
- Specialized tooling and licenses. Building and managing agentic workflows often requires niche tools or frameworks, increasing costs and limiting flexibility.
- Resource-intensive compute. Multi-agent systems demand high-performance hardware, like GPUs, that are costly to scale and difficult to manage efficiently.
- Scaling the team. Multi-agent systems require niche expertise across AI, MLOps, and infrastructure — often adding headcount and increasing payroll costs in an already competitive talent market.
- Specialized tooling and licenses. Building and managing agentic workflows often requires niche tools or frameworks, increasing costs and limiting flexibility.
- Operational overhead. Even autonomous systems need hands-on support. Standing up and maintaining multi-agent workflows often requires significant manual effort from IT and infrastructure teams, especially during deployment, integration, and ongoing monitoring.
- Deployment sprawl. Managing agents across cloud, edge, desktop, and mobile environments introduces significantly more complexity than predictive AI, which typically relies on a single endpoint. In comparison, multi-agent systems often require 5x the coordination, infrastructure, and support to deploy and maintain.
- Misaligned agents. Without strong coordination, agents can take conflicting actions, duplicate work, or pursue goals out of sync with business priorities.
- Security surface expansion. Each additional agent introduces a new potential vulnerability, making it harder to protect systems and data end-to-end.
- Vendor and tooling lock-in. Emerging ecosystems can lead to heavy dependence on a single provider, making future changes costly and disruptive.
- Cloud constraints. When multi-agent workloads are tied to a single provider, organizations risk running into compute throttling, burst limits, or regional capacity issues—especially as demand becomes less predictable and harder to control.
- Autonomy without oversight. Agents may exploit loopholes or behave unpredictably if not tightly governed, creating risks that are hard to contain in real time.
- Dynamic resource allocation. Multi-agent workflows often require infrastructure that can reallocate compute (e.g., GPUs, CPUs) in real time—adding new layers of complexity and cost to resource management.
- Model orchestration complexity. Coordinating agents that rely on diverse models or reasoning strategies introduces integration overhead and increases the risk of failure across workflows.
- Fragmented observability. Tracing decisions, debugging failures, or identifying bottlenecks becomes exponentially harder as agent count and autonomy grow.
- No clear “done.” Without strong task verification and output validation, agents can drift off-course, fail silently, or burn unnecessary compute.
Tool and infrastructure requirements
Once agents start making decisions and coordinating with each other, your systems need to do more than just keep up — they need to stay in control. These are the core capabilities to have in place before scaling multi-agent workflows in production.
- Elastic compute resources. Scalable access to GPUs, CPUs, and high-performance infrastructure that can be dynamically reallocated to support intensive agentic workloads in real time.
- Multi-LLM access and routing. Flexibility to test, compare, and route tasks across different LLMs to control costs and optimize performance by use case.
- Autonomous system safeguards. Built-in security frameworks that prevent misuse, protect data integrity, and enforce compliance across distributed agent actions.
- Agent orchestration layer. Workflow orchestration tools that coordinate task delegation, tool usage, and communication between agents at scale.
- Interoperable platform architecture. Open systems that support integration with diverse tools and technologies, helping you avoid lock-in and enabling long-term flexibility.
- End-to-end dynamic observability and intervention. Monitoring, moderation, and traceability tools that not only surface agent behavior, detect anomalies, and support real-time intervention, but also adapt as agents evolve. These tools can identify when agents attempt to exploit loopholes or create new ones, triggering alerts or halting processes to re-engage human oversight
Preparing for the next stage
There’s no playbook for what comes after multi-agent systems, but organizations that prepare now will be the ones shaping what comes next. Building a flexible, resilient foundation is the best way to stay ahead of fast-moving capabilities, shifting regulations, and evolving risks.
- Enable dynamic resource allocation. Infrastructure should support real-time reallocation of GPUs, CPUs, and compute capacity as agent workflows evolve.
- Implement granular observability. Use advanced monitoring and alerting tools to detect anomalies and trace agent behavior at the most detailed level.
- Prioritize interoperability and flexibility. Choose tools and platforms that integrate easily with other systems and support hot-swapping components and streamlined CI/CD workflows so you’re not locked into one vendor or tech stack.
- Build multi-cloud fluency. Ensure your teams can work across cloud platforms to distribute workloads efficiently, reduce bottlenecks, avoid provider-specific limitations, and support long-term flexibility.
- Centralize AI asset management. Use a unified registry to govern access, deployment, and versioning of all AI tools and agents.
- Evolve security with your agents. Implement adaptive, context-aware security protocols that respond to emerging threats in real time.
- Prioritize traceability. Ensure all agent decisions are logged, explainable, and auditable to support investigation and continuous improvement.
- Stay current with tools and strategies. Build systems and workflows that can continuously test and integrate new models, prompts, and data sources.
Key takeaways
Multi-agent systems promise scale, but without the right foundation, they’ll amplify your problems, not solve them.
As agents multiply and decisions become more distributed, even small gaps in governance, integration, or security can cascade into costly failures.
AI leaders who succeed at this stage won’t be the ones chasing the flashiest demos—they’ll be the ones who planned for complexity before it arrived.
Advancing to agentic AI without losing control
AI maturity doesn’t happen all at once. Each stage — from early experiments to multi-agent systems— brings new value, but also new complexity. The key isn’t to rush forward. It’s to move with intention, building on strong foundations at every step.
For AI leaders, this means scaling AI in ways that are cost-effective, well-governed, and resilient to change.
You don’t have to do everything right now, but the decisions you make now shape how far you’ll go.
Want to evolve through your AI maturity safely and efficiently? Request a demo to see how our Agentic AI Apps Platform ensures secure, cost-effective growth at each stage.
The post The enterprise path to agentic AI appeared first on DataRobot.